United Nations geoscheme
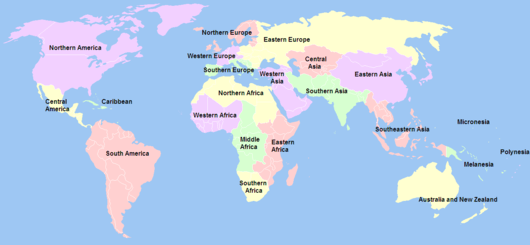
The United Nations geoscheme is a system which divides the countries of the world into regional and subregional groups. It was devised by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) based on the M49 coding classification.[1]
Usage
The creators note that "the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories".[1] The schema was created for statistical analysis and consists of macro-geographical regions arranged to the extent possible according to continents. Within each region, smaller geographical subregions and sometimes intermediate regions contain countries. Countries are also grouped nongeographically into selected economic and other sets.
Antarctica is a country-level area but not included in any geographical region.
The UNSD geoscheme does not set a standard for the entire United Nations System, and it often differs from geographic definitions used by the autonomous United Nations specialized agencies for their own organizational convenience. For instance, UNSD includes Georgia and Cyprus in Western Asia, yet the United Nations Industrial Development Organization and UNESCO include them in Europe.[2][3]
Alternative groupings
Other alternative groupings include the World Bank regional classification,[4] CIA World Factbook regions and Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers Geographic Regions.[5][6]
Americas
*Northern America, the Caribbean, and Central America together form the geographic continent of North America.[1]
Oceania
- Australia and New Zealand
- Melanesia
- Micronesia
- Polynesia
See also
References
- "UNSD — Methodology". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 2019-06-17.
- United Nations Industrial Organisation p. 14
- UNESCO, Europe and North America, Retrieved: 10 May 2016
- Katrin Elborgh-Woytek; Monique Newiak; Kalpana Kochhar; Stefania Fabrizio; Kangni Kpodar; Philippe Wingender; Benedict J. Clements; Gerd Schwartz (20 September 2013). Women, Work, and the Economy:Macroeconomic Gains from Gender Equity. International Monetary Fund. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-4843-9529-5.
Country groups are based on UN geoscheme and World Bank regional classification
- ICANN Geographic Regions
- ICANN Geographical Regions, Final Report by the ccNSO Regions Working Group, For Submission to the ICANN Board, 24 September 2007