Transportation in New England
Transportation in New England encompasses the region's rail and highway networks, seaports, and airports. New England has one of the United States' oldest intercity transportation systems, which remain important to the region's economy. It is also home to the continent's first subway system. The densely populated area has many cities and towns connected by rail and road, and the larger cities each have commercial airports with daily flights to destinations outside of the region.
Transportation
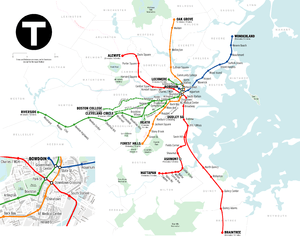
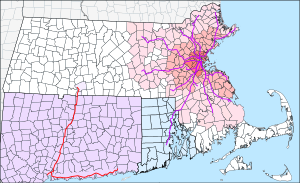
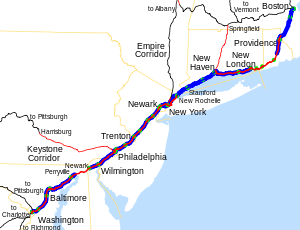
Rail
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) provides rail and subway service within the Boston metropolitan area, bus service in Greater Boston, and commuter rail service throughout eastern Massachusetts and parts of Rhode Island. The New York City Metropolitan Transportation Authority's Metro-North Railroad provides commuter rail service in southwestern Connecticut, while the Connecticut Department of Transportation operates the Shore Line East commuter rail service along the Connecticut coastline east of New Haven, and the Hartford Line northward to Springfield, Massachusetts. On a trial basis until Fall of 2021, Amtrak is working with CTrail to provide service north of its route from Springfield, through the Valley Flyer route to Greenfield.[3]
Amtrak provides interstate rail service throughout New England. Boston is the northern terminus of the Northeast Corridor line. The Vermonter connects Vermont to Massachusetts and Connecticut, while the Downeaster links Maine to Boston.
Air
The largest and busiest airport in New England is Logan International Airport in Boston, which has many daily flights to domestic and international destinations. Logan has two nearby regional airports considered to be reliever airports, T.F. Green Airport in Warwick, Rhode Island, and Manchester Boston Regional Airport in Manchester, New Hampshire. Bradley International Airport in Windsor Locks, Connecticut, is the region's second busiest airport.
Other commercial airports include Portland International Jetport, Bangor International Airport, Worcester Regional Airport, and Burlington International Airport.
Interstate Highways
Six mainline Interstate highways traverse New England. Interstate highways ending in an even number run east-west; those ending in odd numbers run north-south. At least one serves each state and its respective capital city:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
US Routes
- US Route 1
- US Route 2
- US Route 3
- US Route 4
- US Route 5
- US Route 6
- US Route 7
- US Route 20
- US Route 44
- US Route 201
- US Route 202
- US Route 302
References
- "Haverhill chamber chief supports train stop in Plaistow". Eagletribune.com. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved November 11, 2012.
- "Plaistow officials hopeful MBTA considers rail extension". Eagletribune.com. March 9, 2008. Archived from the original on July 29, 2012. Retrieved November 11, 2012.
- "Valley Flyer". Trains in the Valley. Archived from the original on August 30, 2019.