Tetrasaccharide
A tetrasaccharide is a carbohydrate which gives upon hydrolysis four molecules of the same or different monosaccharides.[1] For example, stachyose upon hydrolysis gives one molecule each of glucose and fructose and two molecules of galactose. The general formula of a tetrasaccharide is typically C24H42O21.
| Name | chemical compound | function/occur |
|---|---|---|
| Lychnose (1-α-Galactosyl-raffinose) | O-α-D-Galp-(1→6)-O-α-D-Glup-(1→2)-O-β-D-Fruf-(1→1)-O-α-D-Galp | |
| Maltotetraose | O-α-D-Glcp-(1→4)-O-α-D-Glcp-(1→4)-O-α-D-Glcp-(1→4)-D-Glcp | in Starchsyrup |
| Nigerotetraose | O-α-D-Glcp-(1→3)-O-α-D-Glcp-(1→3)-O-α-D-Glcp-(1→3)-D-Glcp | |
| Nystose (β-D-Fructosyl-1-kestose) | O-α-D-Glcp-(1→2)-β-D-Fruf-(1→2)-β-D-Fruf-(1→2)-β-D-Fruf | |
| Sesamose | O-α-D-Galp-(1→6)-O-α-D-Galp-(1→6)-O-β-D-Fruf-(2→1)-O-α-D-Glcp | |
| Stachyose | O-α-D-Galp-(1→6)-O-α-D-Galp-(1→6)-O-α-D-Glcp-(1→2)-β-D-Fruf | widespread in plants (artichoke, soybean) |
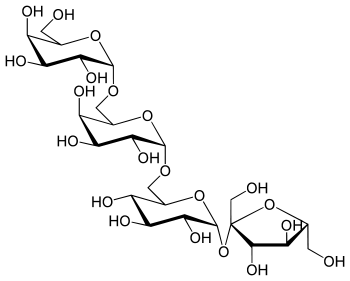
Chemical structure of stachyose
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.