Project 985
Project 985 (Chinese: 985工程; pinyin: Jiǔbāwǔ gōngchéng) is a project that was first announced by CPC General secretary and Chinese President Jiang Zemin at the 100th anniversary of Peking University on May 4, 1998, to promote the development and reputation of the Chinese higher education system by founding world-class universities in the 21st century.[1] The name derives from the date of the announcement, May 1998, or 98/5 according to the Chinese date format.[2] The project involves both national and local governments allocating large amounts of funding to certain universities[3] in order to build new research centers, improve facilities, hold international conferences, attract world-renowned faculty and visiting scholars, and help Chinese faculty attend conferences abroad.[4] According to the Academic Ranking of World Universities 2018/19 and the Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2019/20, most of these 39 universities in Project 985 are considered as among the top 500 universities in the world.[5][6]
| History of the People's Republic of China (PRC) |
|---|
.svg.png) |
|
Hu and the fourth generation |
| History of |
| Generations of leadership |
|
|
In 2009, the original 9 founding member universities of Project 985 formed the C9 League,[4] which is referred to as the Chinese equivalent of the US Ivy League.[7] By the end of the second phase of the project, 39 universities were sponsored. It was announced in 2011 that the project had closed, and no new schools would be able to join.[8]
In September 2017, a related plan called the Double First Class University Plan was announced.[9][10] It was unclear whether this plan represents a new way of ranking universities in China,[9] or replaces Project 211 and Project 985.[10]
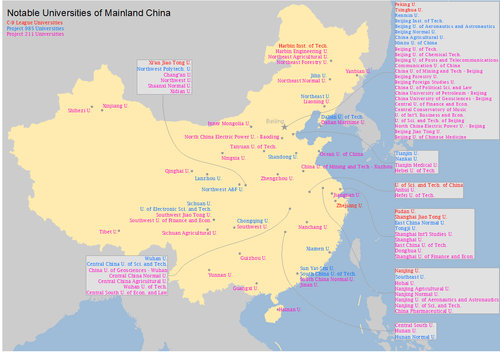
List of sponsored universities
There are 39 universities sponsored by Project 985.[11][12] The project also assigned funding to each university.[13]
- Peking University (RMB1.8 billion)
- Tsinghua University (RMB1.8 billion)
- Zhejiang University (RMB1.4 billion)
- Nanjing University (RMB1.2 billion)
- Fudan University (RMB1.2 billion)
- Shanghai Jiao Tong University (RMB1.2 billion)
- Xi'an Jiaotong University (RMB900 million)
- Harbin Institute of Technology (RMB1 billion)
- University of Science and Technology of China (RMB900 million)
- Beijing Normal University (RMB1.2 billion)
- Beijing Institute of Technology (RMB1 billion)
- Beihang University (RMB900 million)
- Central South University (RMB400 million)
- Minzu University of China (RMB500 million)
- Renmin University of China (RMB500 million)
- China Agricultural University (unknown)
- Chongqing University (RMB540 million)
- Dalian University of Technology (RMB400 million)
- East China Normal University (RMB600 million)
- Huazhong University of Science and Technology (RMB600 million)
- Hunan University (RMB400 million)
- Jilin University (RMB700 million)
- Lanzhou University (RMB450 million)
- Nankai University (RMB700 million)
- Northwestern Polytechnical University (RMB900 million)
- Northeastern University (RMB400 million)
- Northwest A&F University (RMB450 million)
- Ocean University of China (RMB300 million)
- Southeast University (RMB600 million)
- Shandong University (RMB1.2 billion)
- Sichuan University (RMB720 million)
- South China University of Technology (RMB400 million)
- Sun Yat-sen University (RMB1.2 billion)
- Tianjin University (RMB700 million)
- Tongji University (RMB600 million)
- University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (RMB360 million)
- Wuhan University (RMB800 million)
- Xiamen University (RMB800 million)
- National University of Defense Technology (unknown)
See also
References
- Project 985,The University of Edinburgh
- "Project 211 and 985". China Education Center Ltd. Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- "985工程". Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- "International Rankings and Chinese Higher Education Reform". World Education News and Reviews. Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- "ARWU World University Rankings 2019 | Academic Ranking of World Universities 2019 | Top 1000 universities | Shanghai Ranking - 2019". www.shanghairanking.com. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- "World University Rankings". Times Higher Education (THE). August 20, 2019. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- "9所首批"985工程"建设高校签订《一流大学人才培养合作与交流协议书》". Archived from the original on October 15, 2009. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
- "Ministry of Education: no new "211" "985" project of the school". Archived from the original on May 11, 2019. Retrieved December 30, 2011.
- "China to develop 42 world-class universities". People's Daily. September 21, 2017.
- "双一流大学 (shuāngyīliú dàxué): Double top university plan". Archived from the original on September 25, 2017.
- "985工程一期重点共建". Ministry of Education PR CHINA. Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- "985工程二期重点共建". Ministry of Education PR CHINA. Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- "985工程重点共建协议对各大学的定位". Retrieved August 28, 2010.