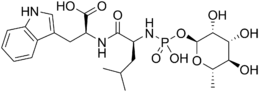
Phosphoramidon
Phosphoramidon is a chemical compound derived from cultures of Streptomyces tanashiensis. It is an inhibitor of the enzyme thermolysin,[2] a membrane metallo-endopeptidase inhibitor,[3] and an endothelin converting enzyme inhibitor.[3] Chemically, phosphoramidon differs from its closely related peptidase inhibitor talopeptin by a single stereocenter.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[hydroxy-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyphosphoryl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Other names
N-[N-[[(6-deoxy-α-L-mannoopyranosyl)oxy]hydroxyphosphinyl]-L-leucyl]-L-tryptophan | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.164 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H34N3O10P | |
| Molar mass | 543.510 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to slightly yellow solid |
| Soluble as sodium salt[1] | |
| Solubility in DMSO and methanol | Soluble as sodium salt[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Because of its enzyme inhibitory properties, phosphoramidon is widely used as a biochemical tool.
References
- Phosphoramidon, Enzo Life Sciences
- Kitagishi K, Hiromi K (1984). "Binding between thermolysin and its specific inhibitor, phosphoramidon". Journal of Biochemistry. 95 (2): 529–34. PMID 6715312.
- Phosphoramidon at PubChem
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.