Phonon (software)
Phonon is the multimedia API provided by KDE and is the standard abstraction for handling multimedia streams within KDE software and also used by several Qt applications.
 | |
 An early screenshot of Phonon's setting manager | |
| Developer(s) | Matthias Kretz u.a. |
|---|---|
| Initial release | January 11, 2008[1] |
| Stable release | 4.11.1
/ September 26, 2019[2] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Linux, BSD, macOS, Solaris, Windows |
| Type | Multimedia framework |
| License | GNU Lesser General Public License 2.1 |
| Website | phonon |
Phonon was originally created to allow KDE and Qt software to be independent of any single multimedia framework such as GStreamer or xine and to provide a stable API for a major version's lifetime. It was done for various reasons: to create a simple KDE/Qt style multimedia API, to better support native multimedia frameworks on Windows and macOS, and to fix problems of frameworks becoming unmaintained or having API or ABI instability.
For example, a file can be played in four lines of C++ code,[3] compared to 30 lines in the old audio framework for KDE (aRts)[4]
Phonon::MediaObject* media = new Phonon::MediaObject(this);
createPath(media, new Phonon::AudioOutput(Phonon::MusicCategory, this));
media->setCurrentSource(QUrl("/tmp/example.wav"));
media->play();
Phonon is not designed to have every conceivable multimedia feature, but rather as a simple way to perform common functions of computer media players. Developers that require more control over a given media backend than Phonon can provide are recommended to use the native media API or the GStreamer API on systems for which it is available.[4]
History
The idea behind Phonon started at aKademy 2004 in Ludwigsburg near Stuttgart (Germany), where a new multimedia API had to be chosen to replace aRts. No consensus was reached but a few developers got together and decided to try to develop a new framework with multiple backends. The earliest version was called KDEMM (KDE MultiMedia) and was only supported by JuK and Amarok. Matthias Kretz continued to work single handed on the project as part of his university thesis, The project changed name once more but in February 2006 the name Phonon was finally chosen. The first official release was part of KDE 4.0 in January 2008, the same year Phonon was adopted by Qt and released as part of Qt 4.4. Even though support for Phonon in Qt will continue for the 4.x series, Qt has already replaced Phonon with QtMultimedia and QtMobility.[5][6][7]
Features
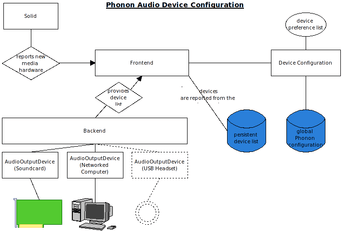
- Phonon interfaces with various backends with what developers call "engines"; each engine works with one specific backend. Each backend will let Phonon control basic functions like play, pause, and seek. Phonon will also support higher level functions such as how tracks fade into each other.[8]
- Phonon can switch multimedia frameworks on the fly. The user can switch between frameworks even while listening to music, with only a slight pause during the switch. This change will also be system wide, affecting all applications that use Phonon, so changing frameworks will be much easier.
- Using Solid, Phonon gives users greater control over accessories like headsets, speakers, and microphones. An example was given that one could have a VoIP conversation only be played through one's headset, but have all other sounds come out through speakers.[8]
Backends
See also
- PulseAudio – prevailing sound server for desktop use
- JACK Audio Connection Kit – prevailing sound server for professional audio production
References
- "KDE 4.0 Released". 2018-01-11. Retrieved 2019-10-23.
- "Release announcement for Phonon 4.11.1". 2019-09-26. Retrieved 2019-10-23.
- Kretz, Matthias. "MediaObject Class Reference". Archived from the original on 2008-04-26. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- Sanders, N. (2006-05-09). "Phonon and the future of KDE multimedia". Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- Guthrie, Colin. "Qt Multimedia/Mobility vs. Phonon: FIGHT!!!". Retrieved 2010-11-20.
- "QtMultimedia Module". Retrieved 2010-11-20.
- "Qt Mobility Project APIs Overview". Retrieved 2010-11-20.
- Unrau, Troy (2007-02-06). "The Road to KDE 4: Phonon Makes Multimedia Easier". Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- "Phonon - KDE UserBase Wiki". Retrieved 2012-03-01.
External links
- Phonon home page
- Phonon code (hosted in git.kde.org)

