Parallelogram law
In mathematics, the simplest form of the parallelogram law (also called the parallelogram identity) belongs to elementary geometry. It states that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the four sides of a parallelogram equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two diagonals. Using the notation in the diagram on the right, the sides are (AB), (BC), (CD), (DA). But since in Euclidean geometry a parallelogram necessarily has opposite sides equal, i.e. (AB) = (CD) and (BC) = (DA), the law can be stated as

If the parallelogram is a rectangle, the two diagonals are of equal lengths (AC) = (BD), so
and the statement reduces to the Pythagorean theorem. For the general quadrilateral with four sides not necessarily equal,
where x is the length of the line segment joining the midpoints of the diagonals. It can be seen from the diagram that x = 0 for a parallelogram, and so the general formula simplifies to the parallelogram law.
Proof

In the parallelogram on the left, let AD=BC=a, AB=DC=b, ∠BAD = α. By using the law of cosines in triangle ΔBAD, we get:
In a parallelogram, adjacent angles are supplementary, therefore ∠ADC = 180°-α. By using the law of cosines in triangle ΔADC, we get:
By applying the trigonometric identity to the former result, we get:
Now the sum of squares can be expressed as:
After simplifying this expression, we get:
The parallelogram law in inner product spaces
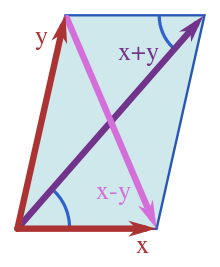
In a normed space, the statement of the parallelogram law is an equation relating norms:
In an inner product space, the norm is determined using the inner product:
As a consequence of this definition, in an inner product space the parallelogram law is an algebraic identity, readily established using the properties of the inner product:
Adding these two expressions:
as required.
If x is orthogonal to y, then and the above equation for the norm of a sum becomes:
which is Pythagoras' theorem.
Normed vector spaces satisfying the parallelogram law
Most real and complex normed vector spaces do not have inner products, but all normed vector spaces have norms (by definition). For example, a commonly used norm is the p-norm:
where the are the components of vector .
Given a norm, one can evaluate both sides of the parallelogram law above. A remarkable fact is that if the parallelogram law holds, then the norm must arise in the usual way from some inner product. In particular, it holds for the p-norm if and only if p = 2, the so-called Euclidean norm or standard norm.[1][2]
For any norm satisfying the parallelogram law (which necessarily is an inner product norm), the inner product generating the norm is unique as a consequence of the polarization identity. In the real case, the polarization identity is given by:
or equivalently by
- or
In the complex case it is given by:
For example, using the p-norm with p = 2 and real vectors and , the evaluation of the inner product proceeds as follows:
which is the standard dot product of two vectors.
See also
References
- Cantrell, Cyrus D. (2000). Modern mathematical methods for physicists and engineers. Cambridge University Press. p. 535. ISBN 0-521-59827-3.
if p ≠ 2, there is no inner product such that because the p-norm violates the parallelogram law.
- Saxe, Karen (2002). Beginning functional analysis. Springer. p. 10. ISBN 0-387-95224-1.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Parallelogram Law". MathWorld.
- The Parallelogram Law Proven Simply at Dreamshire blog
- The Parallelogram Law: A Proof Without Words at cut-the-knot
- A generalization of the "Parallelogram Law/Identity" to a Parallelo-hexagon and to 2n-gons in General - Relations between the sides and diagonals of 2n-gons (Douglas' Theorem) at Dynamic Geometry Sketches, an interactive dynamic geometry sketch.