PCP site 2
PCP site 2 is a binding site that was identified as a high-affinity target for phencyclidine (PCP), an anesthetic and dissociative hallucinogen that acts primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist.[1] The site is distinct from the PCP binding site on the NMDA receptor (otherwise known as PCP site 1) and the common/main sites on the monoamine transporters (SERT, DAT, NET).[1] It is associated with monoamine reuptake inhibition, and it has been suggested that the site may be an allosteric/regulatory site of the monoamine transporters.[1]
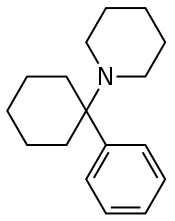
RTI-4793-14 (HBMP), a ligand with high affinity for the PCP site 2 and high selectivity for this site over the PCP site 1, has been developed.[2][3] Similarly to PCP, RTI-4793-1 inhibits monoamine reuptake with moderate potency, but unlike PCP, has very low potency as an NMDA receptor antagonist.[2] It shows a profile of a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI).[2] Although this was inferred to be related to binding to the PCP site 2, subsequent research found that RTI-4793-14 also has considerable affinity for the DAT; it does not appear to have been characterized at the SERT or NET, but may bind to them similarly, and these interactions could potentially explain its monoamine reuptake inhibition as an alternative to the PCP site 2.[3]
Activity profiles
| Compound | RTI-4793-14 | Phencyclidine | (+)-MK801 | Indatraline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCP site 2 | 37.9 | 92.4 | >10000 | 2529 |
| PCP site 1 (NMDAR) | >36000 | 117 | 4.58 | >20000 |
| [3H]5-HT uptake | 1024 | 1424 | >4700 | 4.49 |
| [3H]DA uptake | 547 | 347 | >10000 | 3.23 |
| [3H]CFT binding | 850 | 1547 | >15000 | 4.32 |
| [3H]Nisoxetine binding | 609 | 16628 | 6576 | 2.27 |
| NMDA-induced current | 768 | 2 | 0.020 | 95 |
| All values are IC50 (nM), except NMDA-induced current, which is IC50 (μM). | ||||
| Compound | PCP site 1 (Ki, nM) | PCP site 2 (Ki, nM) | Site 1 / Site 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (+)-MK-801 | 8.9 | 11367 | 0.00078 |
| Tenocyclidine | 19.8 | 197 | 0.10 |
| Phencyclidine | 43.8 | 154 | 0.28 |
| Dexoxadrol | 92 | 1234 | 0.075 |
| Tiletamine | 93 | 17050 | 0.0055 |
| Ketamine | 831 | 59388 | 0.014 |
| Vanoxerine | 30925 | 6841 | 4.5 |
| BTCP | 46436 | 2102 | 22.1 |
| Benztropine | 78179 | 2338 | 33.4 |
| Bupropion | 101239 | 37519 | 2.7 |
| Fluoxetine | 106402 | 1677 | 63.4 |
| (–)-Cocaine | 26739 | 423055 | 0.063 |
| Compound | PCP site 1 (Ki, nM) | PCP site 2 (Ki, nM) | Site 1 / Site 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pargyline | >1000000 | 3643 | >274 |
| D-Amphetamine | 80501 | 959 | 41.1 |
| Clomipramine | 63437 | 4684 | 13.5 |
| (–)-Cocaine | 282362 | 6014 | 46.9 |
| (+)-Cocaine | >1000000 | 6383 | >157 |
| Fluoxetine | 264590 | 929 | 285 |
| Mazindol | 218993 | 919 | 238 |
| Vanoxerine | 102118 | 3167 | 32 |
| Benztropine | 156890 | 183 | 857 |
| Xylamine | >1000000 | 679 | >1473 |
| Desipramine | 11954 | 2137 | 5.6 |
| Nomifensine | 139456 | 2604 | 54 |
| Bupropion | >1000000 | 704 | >1420 |
| BTCP | >1000000 | 1083 | >923 |
| Ketamine | 813 | 4702 | 0.17 |
| Tiletamine | 79.3 | 1394 | 0.057 |
| JMIII41C | 70 | 9298 | 0.0075 |
| JMII79B | 12.7 | 18557 | 0.00068 |
| PCA | 1262 | 1327 | 1.05 |
| PPA | 6463 | 3200 | 2.0 |
References
- Rothman RB (1994). "PCP site 2: a high affinity MK-801-insensitive phencyclidine binding site" (PDF). Neurotoxicol Teratol. 16 (4): 343–53. doi:10.1016/0892-0362(94)90022-1. PMID 7968938.
- Goodman CB, Thomas DN, Pert A, Emilien B, Cadet JL, Carroll FI, Blough BE, Mascarella SW, Rogawski MA, Subramaniam S (1994). "RTI-4793-14, a new ligand with high affinity and selectivity for the (+)-MK801-insensitive [3H]1-]1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine binding site (PCP site 2) of guinea pig brain". Synapse. 16 (1): 59–65. doi:10.1002/syn.890160107. PMID 8134901.
- Rothman RB, Silverthorn ML, Baumann MH, Goodman CB, Cadet JL, Matecka D, Rice KC, Carroll FI, Wang JB, Uhl GR (1995). "Studies of the biogenic amine transporters. VI. Characterization of a novel cocaine binding site, identified with [125I]RTI-55, in membranes prepared from whole rat brain minus caudate". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 274 (1): 385–95. PMID 7616423.