Outline of the Solar System
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Solar System:
Solar System – gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets (including Earth), with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly, the moons, two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.
Regions and celestial objects of the Solar System
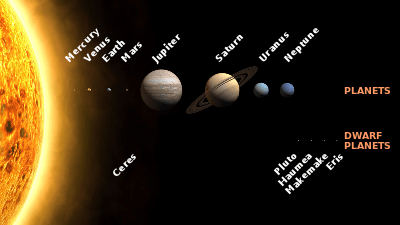
Planets and declared dwarf planets of the Solar System. Sizes are to scale. Distances from the Sun are not to scale.
- Sun
- Interplanetary medium
- Inner Solar System
- Outer Solar System
- Outer planets
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Titan
- Rhea
- Moons of Saturn
 Planets, most of the moons, and some asteroids of the Solar System. Sizes are in logarithmic scale.
Planets, most of the moons, and some asteroids of the Solar System. Sizes are in logarithmic scale.
- Uranus
- Neptune
- Centaurs
- Outer planets
- Comets
- Trans-Neptunian region
- Farthest regions
- Heliopause
- Sedna
- Oort cloud
- Boundaries
Location of the Solar System
- Universe
- Observable universe
- Laniakea Supercluster
- Virgo Supercluster
- Local Sheet
- Local Group
- Milky Way subgroup
- Milky Way
- Orion–Cygnus Arm
- Gould Belt
- Local Bubble
- Local Interstellar Cloud – immediate galactic neighborhood of the Solar System.
- Alpha Centauri – star system nearest to the Solar System, at about 4.4 light years away
- Solar System – star and planetary system where the Earth is located.
- Earth – the only planet known to have life, including intelligent life, including humans.
- Local Interstellar Cloud – immediate galactic neighborhood of the Solar System.
- Local Bubble
- Gould Belt
- Orion–Cygnus Arm
- Milky Way
- Milky Way subgroup
- Local Group
- Local Sheet
- Virgo Supercluster
- Laniakea Supercluster
- Observable universe
Structure and composition of the Solar System
- Interplanetary space
- Physical characteristics of the Sun
- Structure of the Sun
- Physical characteristics of Mercury
- Structure of Mercury
- Geology of Mercury
- Physical characteristics of Venus
- Structure of Venus
- Atmosphere of Venus
- Geology of Venus
- Volcanology of Venus
- Physical characteristics of the Earth
- Figure of the Earth
- Structure of the Earth
- Earth's magnetic field
- Atmosphere of Earth
- Geology of Earth
- Lithosphere of Earth
- Hydrosphere of Earth
- Physical characteristics of Mars
- Structure of Mars
- Atmosphere of Mars
- Geology of Mars
- Geography of Mars
- Water on Mars
- Physical characteristics of Jupiter
- Structure of Jupiter
- Rings of Jupiter
- Atmosphere of Jupiter
- Physical characteristics of Saturn
- Structure of Saturn
- Rings of Saturn
- Atmosphere of Saturn
- Physical characteristics of Uranus
- Structure of Uranus
- Rings of Uranus
- Atmosphere of Uranus
- Physical characteristics of Neptune
- Structure of Neptune
- Rings of Neptune
- Atmosphere of Neptune
History of the Solar System
History of the Solar System
Discovery and exploration of the Solar System
Discovery and exploration of the Solar System –
- Timeline of Solar System exploration
- Development of hypotheses
- Exploration by celestial body
- Solar system models
Formation and evolution of the Solar System
Formation and evolution of the Solar System –
- Nebular hypothesis
- Terrestrial planets
- Iron planets
- Mercury
- Silicate planets
- Geodynamics of Venus
- History of Earth
- Formation of Earth
- Geological history of Mars
- Iron planets
- Giant planets
- Gas giants
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Ice giants
- Uranus
- Neptune
- Gas giants
gollark: Relatedly, did you know that es5nRAhwlkcssYxeidyqS10lmKeaaJKACS6KVPJs/2txC4wwLJ06MdqSwiKu4qeTjpFwo1qQN47csoAaYpDS2+WWQ/Skrb1/YWGoFGJ7gJzw2eyTmrZ3FtHHqkmzxEureb1VmQK2wb8pm/na697aAkZQ/7WTF5E3slpcfaaOjcjjFvsqGBn+TszpCZQy0JvuDmGoJMqvm2/wHrfq6WDXXtsTsARgNBONiw/rQKHJGhqhgM/m6oz7+phc+z15G4Oxy7Is0TUnTvZe0nMNNnF8vHzbjq91aHrpbfMqxssOu83Zir85PDTeR0VrlMHowP3stp8jFLK6HRYNtqO+4+t9ZA==?
gollark: Thanks!
gollark: It's communism, which is too poorly defined to implement.
gollark: Also, that's too vague.
gollark: You didn't respond in time, so that has been interpreted as communism.
See also
- Outline of astronomy
- Outline of space exploration
- HIP 11915 (a solar analog whose planetary system contains a Jupiter analog)
- Lists of geological features of the Solar System
- List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
- List of Solar System extremes
- Planetary mnemonic
- Solar System in fiction
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.