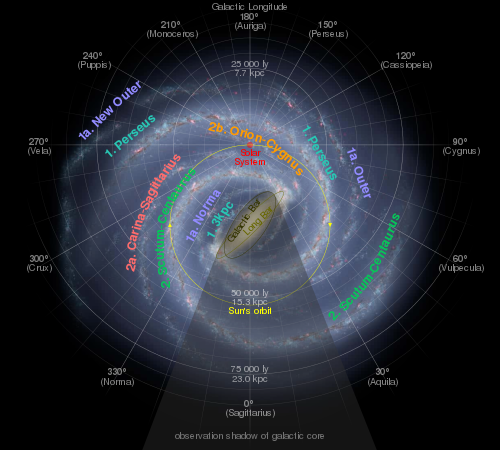
Orion Arm
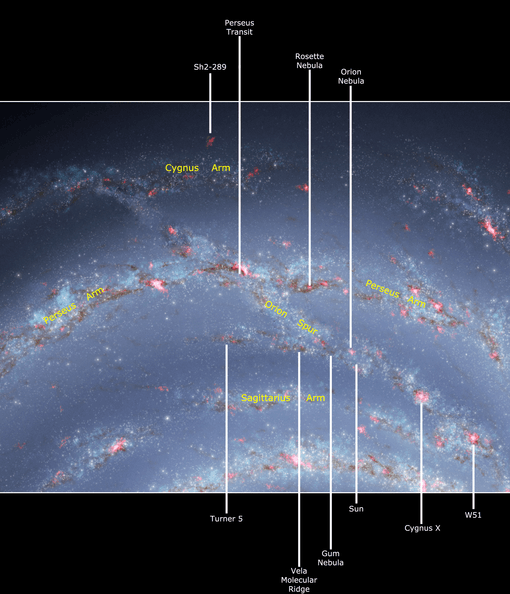
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is 3,500 light-years (1,100 parsecs) across and approximately 10,000 light-years (3,100 parsecs) in length,[2] containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion Bridge, and formerly, the Local Spur and Orion Spur.
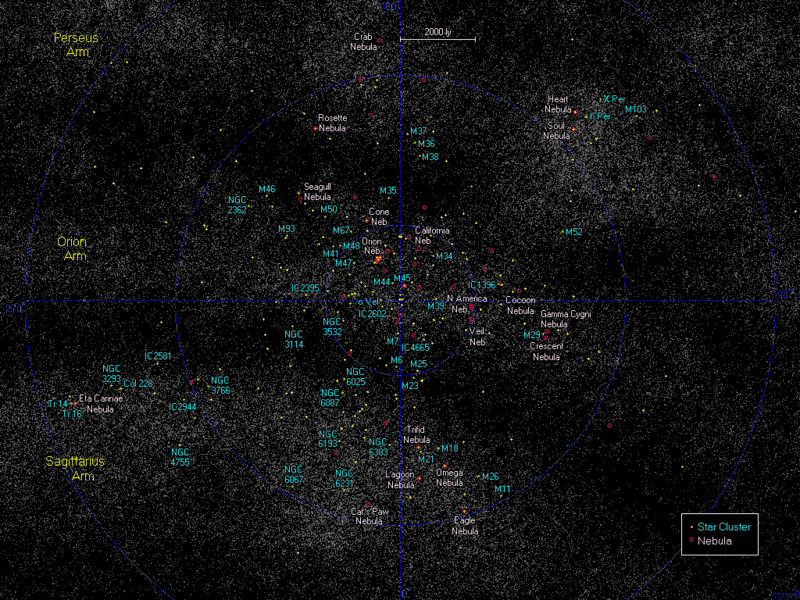
The arm is named for the Orion Constellation, which is one of the most prominent constellations of Northern Hemisphere winter (Southern Hemisphere summer). Some of the brightest stars and most famous celestial objects of the constellation (e.g. Betelgeuse, Rigel, the three stars of Orion's Belt, the Orion Nebula) are within it as shown on the interactive map below.
The arm is between the Carina–Sagittarius Arm (the local portions of which are toward the Galactic Center) and the Perseus Arm (the local portion of which is the main outer-most arm and one of two major arms of the galaxy).
Long thought to be a minor structure, namely a "spur" between the two arms mentioned, evidence was presented in mid 2013 that the Orion Arm might be a branch of the Perseus Arm, or possibly an independent arm segment.[3]
Within the arm, the Solar System is close to its inner rim, in a relative cavity in the arm's Interstellar Medium known as the Local Bubble, about halfway along the arm's length, approximately 8,000 parsecs (26,000 light-years) from the Galactic Center.
Messier objects
The Orion Arm contains a number of Messier objects:
- The Butterfly Cluster (M6)
- The Ptolemy Cluster (M7)
- Open Cluster M23
- Open Cluster M25
- The Dumbbell Nebula (M27)
- Open Cluster M29
- Open Cluster M34
- Open Cluster M35
- Open Cluster M39
- Winnecke 4 (M40)
- Open Cluster M41
- The Orion Nebula (M42)
- The De Mairan's Nebula
- The Beehive Cluster (M44)
- The Pleiades (M45)
- Open Cluster M46
- Open Cluster M47
- Open Cluster M48
- Open Cluster M50
- The Ring Nebula (M57)
- Open Cluster M67
- M73
- The Little Dumbbell Nebula (M76)
- Diffuse Nebula M78
- Open Cluster M93
- The Owl Nebula (M97)
Interactive maps

See also
- Gould Belt
- Jon Lomberg's Milky Way painting used as background for Kepler Mission diagram, showing our location on the Orion Spur
- Local Bubble
- Loop I Bubble
- List of Messier objects
- List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs
References
- See the "Spiral Arms" part of this NASA animation for details
- Harold Spencer Jones, T. H. Huxley, Proceedings of the Royal Institution of Great Britain, Royal Institution of Great Britain, v. 38–39
- Earth's Milky Way Neighborhood Gets More Respect, National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Dave Finley, 3 June 2013
- Vázquez, Ruben A.; May, Jorge; Carraro, Giovanni; Bronfman, Leonardo; Moitinho, André; Baume, Gustavo (January 2008). "Spiral Structure in the Outer Galactic Disk. I. The Third Galactic Quadrant". The Astrophysical Journal. 672 (2): 930–939. arXiv:0709.3973. Bibcode:2008ApJ...672..930V. doi:10.1086/524003.



.jpg)