Gould Belt
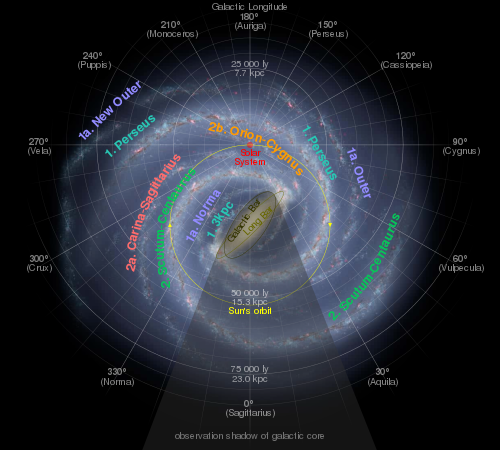
The Gould Belt is a partial ring of stars in the Milky Way, about 3000 light years across, tilted toward the galactic plane by about 16 to 20 degrees. It contains many O- and B-type stars, and may represent the local spiral arm to which the Sun belongs—currently the Sun is about 325 light years from the arm's center. The belt is thought to be from 30 to 50 million years old, and of unknown origin. It is named after Benjamin Gould, who identified it in 1879.[1][2][3]

The belt contains bright stars in many constellations including (in order going more or less eastward) Cepheus, Lacerta, Perseus, Orion, Canis Major, Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux (the Southern Cross), Centaurus, Lupus, and Scorpius (including the Scorpius-Centaurus Association). The Milky Way visible in the sky also passes through most of these constellations, but a bit southeast of Lupus.
Overview
Star-forming regions and OB associations that make up this region include the Orion Nebula and the Orion molecular clouds, the Scorpius-Centaurus OB Association, Cepheus OB2, Perseus OB2, and the Taurus-Auriga Molecular Clouds. The Serpens Molecular Cloud containing star-forming regions W40 and Serpens south is often included in Gould Belt surveys, but is not formally part of the Gould Belt due to its greater distance.
A theory proposed around 2009 suggests that the Gould Belt formed about 30 million years ago when a blob of dark matter collided with the molecular cloud in our region. There is also evidence for similar Gould belts in other galaxies.[4][5]
See also
- Gould Belt Survey
- Local Bubble
- Local Interstellar Cloud
- Orion Arm – Minor spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy; contains the Solar System
- Perseus Arm
- Radcliffe wave
References
- Sir Patrick Moore, ed. (2002) [1987]. Astronomy Encyclopædia (Revised ed.). Great Britain: Philip's. p. 164.
- "The Gould Belt". The GAIA Study Report. Archived from the original on 2003-08-04. Retrieved 2006-07-18.
- "Gould Belt". The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology Astronomy and Spaceflight. Retrieved 2006-07-18.
- "Orion's dark secret: Violence shaped the night sky", New Scientist, 21 Nov. 2009, pp. 42–5.
- Bekki, Kenji (2009). "Dark impact and galactic star formation: origin of the Gould belt". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters. 398 (1): L36–L40. arXiv:0906.5117. Bibcode:2009MNRAS.398L..36B. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00702.x. Archived from the original on 2012-12-08.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gould Belt. |

.jpg)