Norzagaray
Norzagaray, officially the Municipality of Norzagaray (Tagalog: Bayan ng Norzagaray), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 111,348 people.[5]
Norzagaray | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Norzagaray | |
Municipal Hall | |
 Seal | |
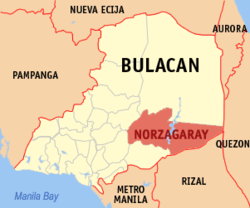 Map of Bulacan with Norzagaray highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Norzagaray Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 14°55′N 121°03′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Central Luzon (Region III) |
| Province | Bulacan |
| District | 3rd District |
| Founded | August 13, 1860 [1] |
| Named for | Fernándo Norzagaray y Escudero |
| Barangays | 13 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Alfredo G. Germar [3] |
| • Vice Mayor | Rogelio P. Santos Jr. |
| • Congressman | Lorna C. Silverio |
| • Electorate | 67,280 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 309.77 km2 (119.60 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,188 m (3,898 ft) |
| Population (2015 census)[5] | |
| • Total | 111,348 |
| • Density | 360/km2 (930/sq mi) |
| • Households | 24,396 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 8.55% (2015)[6] |
| • Revenue | |
| • Assets | |
| • Expenditure | |
| Utilities | |
| • Electricity | MERALCO |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 3013 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)44 |
| Climate type | tropical monsoon climate |
| Native languages | Tagalog Southern Alta |
| Website | norzagaray |
It is the location of Angat Dam which sits on the lower realms of the Sierra Madre mountain range, the Dam is notable for being a major water and power supply for the National Capital Region.
History
The nucleus of what today is the town of Norzagaray traces from the old barrio Casay and barrio Matictic which was ecclesiastically and politically administered by the Augustinians from the town of Angat as its visitas as shown in the document "Mapa del Teritorio de Bulacan" by Fray Emmanuel Blanco O.S.A in 1832 which appeared in another document "Administracion Espiritual de los Padres Agustinos calzados de la Provincia del Dulce Nombre de Jesus de las Islas Filipinas" of Fray Francisco Villacorta in 1833.
The people of Barrio Casay worked for reforms politically, socially and economically, in order to be separated from Angat. They succeeded in their separation bid through Governor-General Fernándo Norzagaray y Escudero (1857-1860) who issued a Real Cedula declaring barrio Casay together with barrio Matictic to be constituted as a new independent town from Angat. Political boundaries of Angat and Pueblo de Casay y Matictic were demarcated and the newly created town was renamed as "Norzagaray" in honor of the said Governor-General Fernando de Norzagaray.
Cityhood
As early as 2005, the town’s Sangguniang Bayan approved Resolution No. 60, Series of 2005 requesting the Senate of the Philippines through its president, Franklin Drilon and the House of Representatives thru its speaker, Jose de Venecia Jr. to co-sponsor a bill for Norzagaray’s conversion into a city and creation of a lone legislative district.
Geography
The town of Norzagaray is bordered by City of San Jose del Monte, Bulacan and Rodriguez, Rizal, to the south; by General Nakar, Quezon to the east; Santa Maria to the west; Angat, Bulacan is north-west; and Doña Remedios Trinidad, Bulacan is to the north.
Barangays
Norzagaray is politically subdivided into 13 barangays. Friendship Village Resources (FVR) was created into a barangay under Sangguniang Panlalawigan Kapasiyahan Bilang 179-T 2002 and Sangguniang Panlalawigan Kautusan Bilang 003 on April 18, 2002; ratified on October 12, 2002; taken from barangay Tigbe.
| PSGC | Barangay | Population | ±% p.a. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015[5] | 2010[8] | |||||
| 031413003 | Bangkal | 1.3% | 1,419 | 1,325 | 1.31% | |
| 031413004 | Baraka | 0.5% | 523 | 581 | −1.98% | |
| 031413006 | Bigte | 10.9% | 12,118 | 11,032 | 1.80% | |
| 031413007 | Bitungol | 9.1% | 10,177 | 8,020 | 4.64% | |
| 031413015 | Matictic | 10.8% | 12,025 | 10,395 | 2.81% | |
| 031413016 | Minuyan | 9.0% | 10,038 | 8,810 | 2.52% | |
| 031413020 | Partida | 4.9% | 5,422 | 5,267 | 0.55% | |
| 031413021 | Pinagtulayan | 1.8% | 1,996 | 1,495 | 5.66% | |
| 031413022 | Poblacion | 14.6% | 16,262 | 15,642 | 0.74% | |
| 031413024 | San Mateo | 7.8% | 8,630 | 9,089 | −0.98% | |
| 031413031 | Tigbe | 14.4% | 16,058 | 14,846 | 1.51% | |
| 031413032 | San Lorenzo | 1.8% | 1,990 | 1,980 | 0.10% | |
| 031413033 | Friendship Village Resources (FVR) | 13.2% | 14,690 | 14,613 | 0.10% | |
| Total | 111,348 | 103,095 | 1.48% | |||
Climate
| Climate data for Norzagaray, Bulacan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
29 (84) |
31 (88) |
33 (91) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
28 (82) |
30 (86) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 20 (68) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 6 (0.2) |
4 (0.2) |
6 (0.2) |
17 (0.7) |
82 (3.2) |
122 (4.8) |
151 (5.9) |
123 (4.8) |
124 (4.9) |
99 (3.9) |
37 (1.5) |
21 (0.8) |
792 (31.1) |
| Average rainy days | 3.3 | 2.5 | 11.7 | 6.6 | 17.7 | 22.2 | 25.2 | 23.7 | 23.2 | 17.9 | 9.2 | 5.2 | 168.4 |
| Source: Meteoblue [9] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 5,131 | — |
| 1918 | 6,747 | +1.84% |
| 1939 | 10,789 | +2.26% |
| 1948 | 13,394 | +2.43% |
| 1960 | 12,202 | −0.77% |
| 1970 | 19,144 | +4.60% |
| 1975 | 23,750 | +4.42% |
| 1980 | 26,032 | +1.85% |
| 1990 | 33,485 | +2.55% |
| 1995 | 51,015 | +8.21% |
| 2000 | 76,978 | +9.22% |
| 2007 | 105,470 | +4.44% |
| 2010 | 103,095 | −0.83% |
| 2015 | 111,348 | +1.48% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[5][8][10][11] | ||
In the 2015 census, the population of Norzagaray was 111,348 people,[5] with a density of 360 inhabitants per square kilometre or 930 inhabitants per square mile.
Municipal government
Just as the national government, the municipal government is divided into three branches: executive, legislative and judiciary. The judicial branch is administered solely by the Supreme Court of the Philippines. The LGUs have control of the executive and legislative branch.
The executive branch is composed of the governor for the provinces, mayor for the cities and municipalities, and the barangay captain for the barangays.Local Government Code of the Philippines, Book III, Department of Interior and Local Government official website. The legislative branch is composed of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan (provincial assembly) for the provinces, Sangguniang Panlungsod (city assembly) for the cities, Sangguniang Bayan (town assembly) for the municipalities, Sangguniang Barangay (barangay council), and the Sangguniang Kabataan for the youth sector.
The seat of Government is vested upon the Mayor and other elected officers who hold office at the Town hall. The Sanguniang Bayan is the center of legislGermar
Elected Officials
- Mayor: ALFREDO G. GERMAR
- Vice Mayor: Geronimo G. Cristobal Jr.
- Councilors:
- Rogelio P. Santos, Jr.
- John Joseph C. Ople
- Alvin B. Cruz
- Jerry R. Sumbillo
- Zosimo SM. Cruz, Jr.
- Restituto B. Sumbillo
- Mamerto R. Bartolome
- Patricio I. Gener
- ABC President: Andrew Germar (Tigbe)
- SK Federation President: Mark Ivan Feliciano (Tigbe)
Economy
In 2017, Norzagaray generated a total revenue of P457.59 million, P73.23 million or 19% higher than its previous income in 2016, making it as the 4th richest municipality in Bulacan after Marilao, Santa Maria and Baliuag.[12]
- Major Industries:
Cement, Marble/Marble Processing, Food/Food Processing, Pyrotechnics
- Major Products:
Bakeries, Processed meat and Agricultural products
- Indigenous/Raw Materials Available:
Cement and Marbles
Tourism
Today, the town of Norzagaray is quickly rising in terms of commercial and economic status with tourist potentials. "Bakas" which is on a portion of the Angat River is recognized as one of the busiest places in the locality, particularly during summertime. People from distant towns often visit the place for relaxation.
Another potential spot for tourism is the Angat Watershed Forest Reserve where the Angat River Hydroelectric Plant or Angat Dam is located. The dam is the biggest hydroelectric plant the National Power Corporation (NPC) has ever constructed in terms of power capacity within the entire Philippines. Because of Angat Dam's size, its reservoir sinks to critical levels during the dry season necessitating the need for cloud seeding in some years. The 37-kilometre (23 mi) reservoir of this hydroelectric plant is covered with forests producing a cool climate.
Another is the Pinagrealan Cave located in Barangay Bigte. This cave is a subterranean network of caverns extending more than a kilometer deep. The Katipunero Revolutionaries during the war against Spain used it as a camp in 1896 and again during the Filipino-American War in 1898 as hideout of General Emilio Aguinaldo (the First President of the Philippines). It was also used as a sanctuary by the Japanese Imperial Army when the Philippines was liberated by joint Filipino and American Forces.
There are still other sites with tourism potential in the locality. However, some of these places are located in remote areas of the town, which are inaccessible to motor vehicles, therefore in need of immediate attention.
Historical and Cultural Heritage
The natives are religious and hear Mass or pray in the Catholic and INC churches. The town also remembers the 31 heroes of the Revolution.
- Monument of Sinfroso de la Cruz
Religious

- St. Andrew, the Apostle Church
- Iglesia Ni Cristo church
- Members Church of God International Locale Congregation of Norzagaray
- Members Church of God International Locale Congregation of North Hill Village
- Members Church of God International Locale Congregation of Hill Top
- Jesus is Lord Church Worldwide JIL
Santuario de Paz Memorial Park (Minuyan)
The town's prime eternal repose garden is located in Minuyan.
Infrastructure
Bulacan 11-billion peso bulk water supply project
On December 12, 2007, Bulacan and the Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System (MWSS) signed an agreement for the development of a P11-billion bulk water supply project. Ayala-owned Manila Water Co. Inc. will implement the project. MWSS and Manila Water will provide a financial package of an infrastructure grant, a P10-million development assistance and a P10-million royalty fee to the towns of Norzagaray and Doña Remedios Trinidad, which will host the water supply project.[13]
18-hectare landfill
On January 19, 2008, an 18-hectare waste disposal facility, a new sanitary landfill that would also be a tourist attraction opened in Norzagaray, Bulacan province. The president of Wacuman Corp. stated: "I want them to see our system in our place which should not be abhorred because we are using the new state-of-the-art technology." The facility has a category 4 rating (the highest category for a sanitary landfill) from the Department of Environment and Natural Resources[14]
References
- https://www.pressreader.com/philippines/philippine-daily-inquirer/20160910/282385513965346
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- Inquirer.net, Bulacan mayor reclaims post after SC reverses his dismissal by Ombudsman
- "Province: Bulacan". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- ""Commission on Audit 2017 Report-Bulacan"". Quezon City, Philippines: Commission on Audit. Retrieved 8 July 2018.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- "Norzagaray: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Bulacan". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- "Norzagaray Economy". Province of Bulacan Official Website. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- Abs-Cbn, Bulacan govt, MWSS ink deal on bulk water supply project
- abs-cbnnews.com, New landfill opens in Norzagaray, Bulacan
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Norzagaray, Bulacan. |