Nigerose
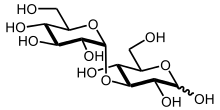
Nigerose, also known as sakebiose, is an unfermentable sugar obtained by partial hydrolysis of nigeran, a polysaccharide found in black mold, but is also readily extracted from the dextrans found in rice molds and many other fermenting microorganisms,[2] such as L. mesenteroides.[3] It is a disaccharide made of two glucose residues, connected with a 1->3 link. It is a product of the caramelization of glucose.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-[(3R,4S,5R,6R)-2,3,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-4-yl]oxyoxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names
3-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Nigerose |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.29648 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Nigerose - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- Matsuda, Kazuo; H. Wanatabe; K. Fujimoto; K. Aso (1961). "Isolation of Nigerose and Kojibiose from Dextrans". Nature. 191 (4785): 278. doi:10.1038/191278a0. PMID 13768213.
- Matsuda, Kazuo; Hiroshi Watanabe; Kiyoshi Aso (1962-03-10). "Acetolysis of polysaccharides I. Isolation of nigerose from the acetolysate of a dextran produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B-421". Tohoku Journal of Agricultural Research. Faculty of Agriculture, Tohoku University. 12 (4): 351–357. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- Sugisawa, Hirqshi; Edo, Hiroshi (1966). "The Thermal Degradation of Sugars I. Thermal Polymerization of Glucose". Journal of Food Science. 31 (4): 561. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1966.tb01905.x.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.