Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival.[1]
| Myeloblast | |
|---|---|
 Myeloblast | |
| Identifiers | |
| TH | H2.00.04.3.04002 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy | |
Structure
Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords.
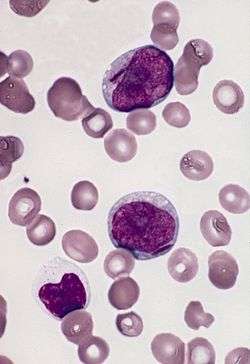
Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character and is devoid of granules, which is a major difference from the myeloblast's successor, the promyelocyte. The nucleolus is the site of assembly of ribosomal proteins, which are located in various particles dispersed over the cytoplasm. Mitochondria are present but have a rather small size.
The main features that distinguish a myeloblast from a lymphoblast upon microscopic examination are the presence of cytoplasmic granules, the lesser degree of condensation in the nuclear chromatin, and the increased prominence of the nucleoli.[2]
Development
These cells descend from the primitive reticulum cells, which are found in the stroma of the marrow. There is also an intermediate phase between the myeloblast and these primitive reticulum cells, namely the hemocytoblast. At this time several developing blood cell lines are available, like erythropoiesis and thrombopoiesis. Granulopoiesis is regulated by humoral agents, like colony-stimulating factor (CSF) and interleukin 3.
Function
_diagram_en.svg.png)
Granulopoiesis consists of 5 stages, in which the myeloblast is the first recognizable cell. Next in the differentiation sequence is the monoblast and the promyelocyte, which can develop into one of three different precursor cells: the neutrophilic, basophilic or eosinophilic myelocyte. This proliferation takes five divisions before the final stage is obtained. These divisions all take place in the first three stages of granulopoiesis.
Clinical significance
The most common problem with malfunctioning myeloblasts is acute myeloblastic leukemia.[3][4] The main clinical features of acute myeloblastic leukemia are caused by failure of hemopoiesis with anemia, hemorrhage and infection as a result. There is a progressive accumulation of leukemic cells, because some blast progenitor cells renew themselves and have a limited differentiated division. Sometimes acute myeloblastic leukemia can be initiated by earlier hematologic disorders, like myelodysplastic syndrome, pancytopenia, or hypoplasia of the bone marrow.
See also
- Granulopoiesis
- Hematopoiesis
- Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell
- Myeloid leukemia
References
- Metcalf D (January 2008). "Hematopoietic cytokines". Blood. 111 (2): 485–91. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-079681. PMC 2200848. PMID 18182579.
- Figure 12-14 in: Kumar V, Fausto N, Abbas AK, Mitchell RN (2007). Robbins Basic Pathology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 978-1-4160-2973-1.
- Murohashi I, Tohda S, Suzuki T, Nagata K, Yamashita Y, Nara N (July 1989). "Autocrine growth mechanisms of the progenitors of blast cells in acute myeloblastic leukemia". Blood. 74 (1): 35–41. PMID 2473799.
- Villamor N, Zarco MA, Rozman M, Ribera JM, Feliu E, Montserrat E (July 1998). "Acute myeloblastic leukemia with minimal myeloid differentiation: phenotypical and ultrastructural characteristics". Leukemia. 12 (7): 1071–5. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2401074. PMID 9665192.
Further reading
- Wilson JD, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Martin JB, Fauci AS, Root RK (1991). Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine (12th ed.). McGraw-Hill Inc.
- Curran RC, Crocker J (2000). Curran’s Atlas of Histopathology (4th ed.). Harvey Miller Publishers Ltd., Oxford University Press Inc.
- Bloom W, Fawcett DW (1986). A Textbook of Histology (12th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company.
- Williams MJ (May 1955). "Myeloblastic leukemia preceded by prolonged hematologic disorder". Blood. 10 (5): 502–9. PMID 14363331.
- Beutler E, Lichtman M, Coller B, Kipps T (1995). Williams Hematology (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill Inc.