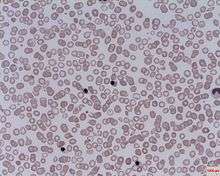
Nucleated red blood cell
A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a mammalian red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells. NRBCs are normally found in the bone marrow of individuals of all ages and in the blood of fetuses and newborn infants.[1][2] After infancy, RBCs normally contain a nucleus only during the very early stages of the cell's life, and the nucleus is ejected as a normal part of cellular differentiation before the cell is released into the bloodstream. Thus, if NRBCs are seen on an adult's peripheral blood smear, it suggests that there is a very high demand for the bone marrow to produce RBCs, and immature RBCs are being released into circulation. Possible pathologic causes include anemia, myelofibrosis, thalassemia, miliary tuberculosis, cancers involving bone marrow (myelomas, leukemias, lymphomas), and in chronic hypoxemia.[3]
Nomenclature
Several names are used for nucleated RBCs—erythroblast, normoblast, and megaloblast—with one minor variation in word sense. [4] [5] [6] [7] The name normoblast always refers to normal, healthy cells that are the immediate precursors of normal, healthy, mature (anucleate) RBCs. The name megaloblast always refers to abnormally developed precursors. Often the name erythroblast is used synonymously with normoblast, but at other times it is considered a hypernym. In the latter sense, there are two types of erythroblasts: normoblasts as cells that develop as expected, and megaloblasts as unusually large erythroblasts that are associated with illness.
Healthy development
There are four stages in the normal development of a normoblast.
_diagram_en.svg.png)
| Illustration | Description | Image |
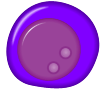 | Pronormoblast | |
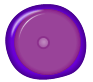 | Basophilic normoblast | 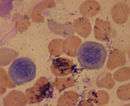 |
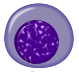 | Polychromatic normoblast (also polychromatophilic) | 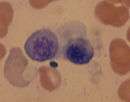 |
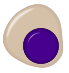 | Orthochromatic normoblast (also orthochromatophilic) |  |
Pathogenesis
A megaloblast is an unusually large erythroblast that can be associated with vitamin B12 deficiency (caused by pernicious anemia or dietary insufficiency), folic acid deficiency, or both (such anemias are collectively called megaloblastic anemias). This kind of anemia leads to macrocytes (abnormally large red cells) and the condition called macrocytosis. The cause of this cellular gigantism is an impairment in DNA replication that delays nuclear maturation and cell division. Because RNA and cytoplasmic elements are synthesized at a constant rate despite the cells' impaired DNA synthesis, the cells show nuclear-cytoplasmic asynchrony.
Additional images
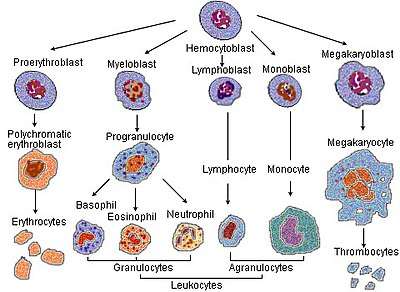 Blood cell lineage
Blood cell lineage_diagram_en.svg.png) Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis
References
- Greer, JP; Arber, DA; Glader, BE; List, AF; Means, RM; Rodgers, GM (19 November 2018). Wintrobe's Clinical Hematology (14th ed.). Wolters Kluwer Health. p. 192. ISBN 978-1-4963-6713-6.
- Kottke-Marchant, K; Davis, B (6 June 2012). Laboratory Hematology Practice. John Wiley & Sons. p. 294. ISBN 978-1-4443-9857-1.
- Blood Smear: Details on RBCs, WBCs
- "Erythroblast" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- "Normoblast" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- "Megaloblast" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Normoblasts at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
External links
- Pronormoblasts Presented by the University of Virginia
- Basophilic Normoblasts Presented by the University of Virginia
- Polychromatophilic Normoblasts Presented by the University of Virginia
- Orthochromatic Normoblasts Presented by the University of Virginia
- Histology image: 01804loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Bone Marrow and Hemopoiesis bone marrow smear, erythroblast series with proerythroblast "
- Histology at uiowa.edu