Moulvibazar District
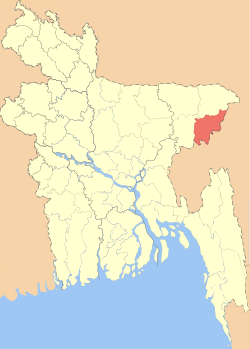
Moulvibazar (Bengali: মৌলভীবাজার) also spelled Maulvibazar,[1] Moulavibazar,[2] and Maulavibazar,[3] is the southeastern district of Sylhet Division (Greater Sylhet) in northeastern Bangladesh, named after the town of Moulvibazar. It is bordered by the Indian states of Tripura and Assam to the south and east, respectively; and by the Bangladeshi districts of Habiganj to the west and Sylhet to the north.
Moulvibazar মৌলভীবাজার | |
|---|---|
 Tea gardens in Srimangal | |
 Location of Moulvibazar District in Bangladesh | |
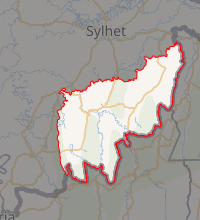
Expandable map of Moulvibazar District | |
| Country | |
| Division | Sylhet Division |
| Government | |
| • Zila Parishad Chairman | Azizur Rahman (Awami League) |
| • Deputy Commissioner | Nazia Shirin |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,799.38 km2 (1,080.85 sq mi) |
| Population (2011 census) | |
| • Total | 1,919,062 |
| • Density | 690/km2 (1,800/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Moulvibazari |
| Time zone | UTC+06:00 (BST) |
| Postal code | 3200 |
| Website | moulvibazar |
Etymology
The name of the district, Moulvibazar is named after its headquarter town, Moulvibazar. The word is derived from two words, moulvi and bazar, meaning 'Market of the Moulvi'. 'Moulvi' is an Islamic honorific title and 'bazar' is the Bengali word for market or township. Moulvibazar is named after Moulvi Syed Qudratullah, a local judge and a descendant of Shah Mustafa, an Islamic preacher active during the advent of Islam in the region. It is believed that the name was coined in the 1771 when Syed Qudratullah established a small bazaar on his zamindari land and local people named it as Moulvibazar.[4] This market was established at riverside of the present Poschim Bazar (West Market), which gradually expanded over the time.[5][6]
History
Copper plates has been found from 930 AD in Paschimbagh, Tengubazar Mandir, Rajnagar and one of Raja Marundanath from the 11th century in Kalapur, Srimangal. The district was also part of the ancient Kamarupa kingdom. It is suggested that the area was inhabited by Buddhists and Hindus as evidence from inscriptions suggests there was an ancient university in Panchgaon, Rajnagar.[7] The terrain was headquarters of the ancient Ita Kingdom founded by Raja Bhanu Narayan and its capital was in the villages of Bhumiura and Eolatoli.[8] Other regions included Chandrapur or Chandrarajya which is modern-day Moulvibazar Sadar.
After the Conquest of Sylhet in 1303, many disciples of Shah Jalal scattered across the Sylhet region and the rest of Bengal. Shah Mustafa of Baghdad, a descendant of Abdul Qadir Gilani, migrated to Chandrapur ruled by Raja Chandra Singh where he lived on top of a small hill with his son Syed Ismail and would preach to the local people. Mustafa would eventually succeed Singh as the ruler of Chandrapur after marrying the Raja's daughter. Other Sufi disciples and saints who preached in Moulvibazar included Shah Kala, Haji Rasul, Shah Dorong, Helimuddin Nurnali, Hamid Faruqi, Syed Nasrullah, Syed Yasin, Syed Ismail, Nur Ali Shah, Shah Wali Muhammad, Sheikh Shihabuddin, Sabur Shah, Shah Helal and Shah Kamaluddin.[6]
The final raja of the Ita Kingdom, Raja Subid Narayan lost a battle in 1610 in which the region became under the rule of Khwaja Usman, a fierce opponent of the Mughal Empire. He then established his new capital in Uhar, Kamalganj and managed to gain control of South Sylhet.[9] However, this rule was short-lived after Mughal General Islam Khan I's attack in 1612.[10] An important battle between the Mughal Empire and the Baro-Bhuyans was held in Pathan Ushar, Kamalganj. This led to the death of Afghan leader Khwaja Usman.[11]
The Panchgaon Factory in Rajnagar Upazila produced cannons for the Mughal Empire. The famous Jahan Kosha Cannon, built by Janardan Karmakar remains in display in Dhaka.[7]
After the Battle of Plassey in 1757, the British gave the region surrounding Moulvibazar high importance, especially in tea production. A rebellion against the permanent settlement of the British took place in Latu in 1857. On 1 April 1882, the area was declared a sub-division, or mahakuma, and named "South Srihatta" (and later "South Sylhet"), consisting of 26 parganas.[11] A mass deforestation took place from 1898 to 1899, clearing the Longla-Singla Reserve in order to make space for settlements.
In 1912, there was an anti-British protest held in the village of Jagatshi in the Sadar Upazila. It was organised by Swami Dayananda having its seat at Dolgovinda Ashram. In 1921, the anti-British Khilafat Movement also spread to Moulvibazar and campaigners that were present included Chittaranjan Das, Hussain Ahmed Madani and Sarojini Naidu.[1] On the same year, the non-cooperation movement also spread here after being established by Purnendu Kishore Sengupta in Vidia Ashram, Rangirkul, Kulaura. The peasant rebellion led by Panchanan Singh, Qasim Ali, Baikuntha Sharma and Themba Singh was also held in the 1900s in Vanubal, Kamalganj. In 1960, the South Sylhet sub-division was renamed as Moulvibazar by the mahakuma administrator Dr M A Sattar.[4]
Armed resistance begun at the village of Srirainagar in Kanakpur on 27 March 1971. The Pakistani army was said to have made a surprise attack on the procession there in which two people were killed. On 20 December, a number of people were killed and wounded by mine explosions at the premises of the Moulvibazar Government High School.[1]
On 22 February 1984, the President of Bangladesh, H M Ershad, upgraded its sub-division status to a district as a part of his decentralisation programme. Shakir Uddin Ahmed was made the district's inaugural deputy commissioner whilst Mukhleshur Rahman was made the first district police super.[4]
Geography
Moulvibazar is in Sylhet, a district to the North-East of Bangladesh. It is 2,707 km² in area, and has a population of 1.38 million. It is situated between 24.10 degree 24.35 degree north latitude and between 90.35 degree and 91.20-degree east longitude. It is surrounded by Sylhet District in the north, Habiganj District in the west and Indian states of Assam and Tripura in the east and south respectively.
The main rivers of the district are the Manu, the Dholoi and the Juri which flow from India. Every year during the rainy season, when there is excessive rainfall in India, the surplus water flows through these rivers and causes floods in low-lying parts of Moulvibazar (for example, the villages of Balikhandi and Shampashi on the northern side of the river Manu). Unless the rivers are properly dredged the floods can be devastating.
In the last few years Moulvibazar has had a muti-million dollar flood defence system built, which is the only one like it in the whole country.[12]
Administration

Moulvibazar is made up of 7 subdivisions or upazilas. They are:
- Moulvibazar Sadar
- Kamalganj
- Kulaura
- Rajnagar
- Sreemangal
- Barlekha (originally part of Joldhup in Karimganj)
- Juri (formed in 2005 from unions of Kulaura and Barlekha)
There are 67 Unions, 2,064 Villages and 5 Pourashavas namely Kamalganj, Kulaura, Sreemongal, Barlekha and Moulvibazar. Almost 50,000 of the clan population belong to Manipuri, Khasia and Tripura clans. They tend to live in the areas of Kamalganj, Sreemongal and Kulaura Upazila of this district. There are 92 tea gardens in the district.
During the British colonial period, South Sylhet subdivision was divided into three tax collectory zilas, further divided into 28 parganas.[13] The incomplete list of parganas of South Sylhet are as follows:
- Noyakhali Zila: Chowallish, Balishira, Satgaon, Chautali, Giasnagar, Chaitanyanagar, Athanagiri
- Rajnagar Zila: Ita, Shamshernagar, Alinagar, Indeshwar, Panishail/Panishali, , Bhanugach, Adampur
- Hingazia Zila: Kanihati, Baramchal, Bhatera, Patharia, Yaqubnagar
Later on, South Sylhet subdivision was divided into five thanas:[14]
- Moulvibazar Thana: Parganas - Shamshernagar, Chowallish, Shaistanagar, Howlisatrasati
- Kamalganj Thana: Parganas - Adampur, Bhanugach, Chhoychiri, Shamshernagar
- Kulaura Thana: Parganas - Kanihati, Patharia, Longla, Baramchal
- Rajnagar Thana: Parganas - Indeswar, Shamshernagar
- Srimangal Thana: Parganas - Balishira, Chautali
Economy


The main exports of Moulvibazar are bamboo, tea, pineapple, cane, jackfruit, oranges, agar, rubber, mangoes and lemons. Ninety-one of Bangladesh's 153 tea gardens are located in Moulvibazar. The area is also home to the three largest tea gardens (size and production wise) in the world. Pineapples from the Sreemangal area are famous for their flavour and natural sweetness. Srimangal is known as the 'tea capital of Bangladesh' due to the high frequency of tea plantations found there.
Religion

The district of Moulvibazar consists 2967 mosques, 613 temples, 56 churches and 22 Buddhist temples. Notable mosques include the Mosque of Shah Mustafa, Goyghor Mosque, Jiladpur Mosque, and the Lawachara Jame Mosque. The revivalist Deobandi movement is popular in with Jamia Luthfia Anwarul Uloom Hamidnagar being a notable centre in Srimangal and many are part of the Tablighi Jamaat. Another Islamic institution is the Sujaul Senior Fazil Madrasha in Barlekha.
An small minority of Shia Muslims gather during Ashura every year at the Nawab Bari in Prithimpasha, which was home to an aristocratic Shia family in Kulaura. Begum Talib-un-Nisa Khatun of Prithimpasha's Chhoto Saheb Bari established the famous Rabir Bazar Jame Masjid in the late 18th century.[15]
Transport
The main transport systems used in the city are Cycle rickshaws, auto rickshaws (mainly known as baby-taxis or CNGs), buses, mini-buses and cars. There are about 10,000 rickshaws running each day. Bus service prices have increased as of 2008, up to 30% higher, prices ranges from Tk4 to 25.95.[16] The Kulaura Railway Station, Sreemangal Railway Station is the main railway station providing trains on national routes operated by the state-run Bangladesh Railway. Also Bhanugach Railway Station, Tilagaon, Vatera, Rashidpur Station is used by local peoples. There is a public-use airport in Shamshernagar.
Tourism

The District contains the highest amount of tea plantations in the country. Srimangal is known as the Tea Capital of Bangladesh and is the only place where one can have the original 7-layered tea. Moulvibazar also has notable religious sites such as the dargah and mosque of Shah Mustafa, a companion of Shah Jalal; as well as the Jiladpur Mosque and Goyghor Mosque, two ancient mosques from the 15th century. Moulvibazar town has many shopping malls and several Indian, Chinese and American eateries. Madhabkunda waterfall in Barlekha is probably the most well-known tourist attraction of the district. The Hum Hum waterfall located in the Razkandi Reserve Forest in Kamalganj was also recently discovered in 2010. The district also contains one of the country's major national parks, Lawachara National Park, famous for its biodiversity. The park was also the filming site for the 1956 film Around the World in 80 Days. Madhobpur Lake is the only place in the country in which you can find the white-bellied heron.[17] Hakaluki Haor, Hail Haor and Bilashchhara Lake are also other nearby wetland ecosystems. The memorial monument of Hamidur Rahman can be found in Kamalganj. There is also a multi-use stadium called Saifur Rahman Stadium.
Education
The Bangladesh Tea Research Institute can be found in Srimangal. It has made significant contributions in evolving and standardising the quality of tea, and introducing its research findings to the tea industry of Bangladesh.[18]
Notable people
- Syed Mujtaba Ali, writer, scholar and linguist
- Barrister Muntaquim Chodhury MNA, MP was MNA in 62 and 70 in East Pakistan and MP of Bangladesh First Parliamentary Election was also a senior member of constitution writing team in 1971
- Mohammad Ataul Karim is provost and executive vice chancellor at University of Massachusetts Dartmouth.[19]
- Tommy Miah, restaurateur and celebrity chef[20]
- Saifur Rahman, longest serving Finance Minister of Bangladesh.[21]
- Doly Begum, Canadian politician[22]
- Naser Rahman, former MP for Maulvibazar-3 and chairman of the Saifur Rahman Foundation
- Surendra Kumar Sinha, Chief Justice of Bangladesh (2015-2017)[23]
- Wali Tasar Uddin MBE, entrepreneur, restaurateur, community leader and chairman of the Bangladesh-British Chamber of Commerce.[24][25]
- Bajloor Rashid MBE, businessman and former president of the Bangladesh Caterers Association UK.[26][27]
- Nadia Shah, politician, councillor and former Mayor of Camden. In May 2016, she became the first female British Bangladeshi mayor.[28]
- Rowshanara Moni, singer and actress. In 2004, her debut album Nijhum Raat was released.[29]
- Shanaj Ahmed, cricketer for Sylhet Division
- Syed Mohammad Ali, founder of The Daily Star - the largest circulating daily English-language newspaper in Bangladesh.[30]
- Syed Abdul Majid CIE, first native minister of Assam, pioneer of the agricultural industry
- Shah Mustafa, associated with spreading Islam to Moulvibazar
- Dwijen Sharma, botanist, environmentalist and science writer.[31]
- Mahbubur Rahman Sufil, footballer and captain of Arambagh KS
- Syed Mohsin Ali, former Social Welfare Minister of Bangladesh
- Syeda Saira Mohsin, former MP for Maulvibazar-3
- Abdus Shahid, former chief whip for Bangladesh Awami League
- Shahab Uddin, Bangladeshi Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- Nawab Ali Abbas Khan, Jatiya Party politician and three-time MP for Maulvibazar-2
- Nawab Ali Haider Khan, 9th Nawab of Longla, minister and leader of the Independent Muslim Party
- Abdul Matin, former MP for Maulvibazar-2
- Rangalal Sen, National Professor of Bangladesh
See also
References
- Shah Abdul Wadud (2012). "Maulvibazar District". In Sirajul Islam and Ahmed A. Jamal (ed.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh.
- "List of Institutes in Moulavibazar District". Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh, Directorate General of Health Services. Retrieved 27 Aug 2013.
- "Estimates of Aman Rice, 2012-2013" (PDF). Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics Agriculture Wing. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-13. Retrieved 27 Aug 2013.
- "Itihash". Government of Bangladesh. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ইসলামী বিশ্বকোষ [ISLAMI BISHWAKOSH: The Encyclopedia of Islam in Bengali, 21st Volume] (in Bengali). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Islamic Foundation, Bangladesh. September 1996. pp. 448–452. Archived from the original on 11 February 2016.
- "Introduction". Moulvibazar.com. January 2016. Retrieved 4 September 2016.
- "Zila". Moulvibazar.com. January 2016. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- Sreehatter Itibritta – Purbangsho (A History of Sylhet).
- Sylhet: History and Heritage. Sylhet, Bangladesh: Bangladesh Itihas Samiti. 1999.
- "Patabhumi". Zilla Parishad. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
- "Bhougolik Porichiti". Moulvibazar Gov. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- "Aajker Taza Khobor". Londoni. 23 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- Sreehatter Itibritta – Purbangsho (A History of Sylhet), Part 2, Volume 1, Chapter 1, Achyut Charan Choudhury; Publisher: Mustafa Selim; Source publication, 2004
- Assam District Gazetteers - Supplement. 2. Shillong. 1915. p. 26.
- Chowdhury, Muhammad Shakil Rashid (29 May 2016). "রবিরবাজার জামে মসজিদ". Samakal.
- Sylhet city bus services hike fares on whim Archived 2009-06-15 at the Wayback Machine New Age Metro. 4 November 2008. Retrieved 25 May 2009.
- Choudhury, Anwaruddin (2000). The birds of Assam. Guwahati: Gibbon Books & World Wide Fund for Nature-India, North-East Regional Office. p. 48. ISBN 9788190086615.
- Minuddin Ahmed; AFM Badrul Alam (January 2003). "Bangladesh Tea Research Institute". In Sirajul Islam (ed.). Banglapedia. Dhaka: Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. ISBN 984-32-0576-6. Retrieved May 12, 2016.
- "UMass Dartmouth appoints new provost".
- "Institutionalising Diaspora Linkage: The Emigrant Bangladeshis in UK and USA" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. February 2004. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- "Saifur Rahman's life sketch". The Daily Star. 5 September 2009. Archived from the original on 7 October 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- "Doly Begum makes history, wins big in Ontario provincial polls". The Daily Star. 8 June 2018.
- "Justice Surendra Kumar Sinha". Supreme Court of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- "Dr Wali Tasar Uddin, MBE". British Bengali Success Stories. BritBangla. Retrieved 13 December 2008.
- "Dr Wali Tasar Uddin, MBE, JP" (PDF). British Bangladeshi Who's Who. British Bangla Media Group. July 2008. Retrieved 13 December 2008.
- "Bangladeshi restaurant boss Bajloor Rashid made MBE". BBC News. 31 December 2011. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- "Honour for food industry captain". This Is Kent. Kent. 6 January 2013. Archived from the original on 7 July 2013. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- "Britain's first woman mayor of Bangladeshi origin". Dhaka Tribune. 12 May 2017. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- "Rowshanara Moni: Nijhum Raat". cyList. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- Newspaper Trends: Bangladesh Archived 2009-03-19 at the Wayback Machine, World Advertising Research Center. Retrieved 14 September 2007
- দ্বিজেন শর্মা [Dwijen Sharma]. Gunijan Trust (in Bengali). Retrieved 17 April 2015.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Maulvibazar District. |
- Moulvibajar Jilar Itihas o Oitisyo, Rabbani Choudhury, Agami Prokashon, 2000
- Kazi Mahmudur Rahman, Faculty (Mentors' education Moulvibazar branch)