Milbemycin
The milbemycins are a group of macrolides chemically related to the avermectins and were first isolated in 1972 from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. They are used in veterinary medicine as antiparasitic agents against worms, ticks and fleas.[1]
Mechanism of action
Like avermectins, milbemycins are products of fermentation by Streptomyces species. They have a similar mechanism of action, but a longer half-life than the avermectins. They open glutamate-sensitive chloride channels in neurons and myocytes of invertebrates, leading to hyperpolarisation of these cells and blocking of signal transfer.
Examples
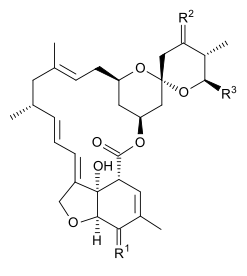
| Name | =R1 | =R2 | –R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milbemectin | –H, (β)–OH | –H, –H | –CH3 : –CH2CH3 = 3:7 |
| Milbemycin oxime | =NOH | –H, –H | –CH3 : –CH2CH3 = 3:7 |
| Moxidectin | –H, (β)–OH | =NOCH3 | (Z)–C(CH3)=CH–CH(CH3)2[1] |
| Nemadectin | –H, (β)–OH | –H, (α)–OH | (Z)–C(CH3)=CH–CH(CH3)2[1] |
gollark: Also "let's spy on everyone because terrorists".
gollark: ```'I [suspect] that we are throwing more and more of our resources, including the cream of our youth, into financial activities remote from the production of goods and services, into activities that generate high private rewards disproportionate to their social productivity. I suspect that the immense power of the computer is being harnessed to this 'paper economy', not to do the same transactions more economically but to balloon the quantity and variety of financial exchanges.'--James Tobin, July 1984```
gollark: What about vertexlords?
gollark: Stupid TVTropes adblocker complaining. They can have their 0.01p when they switch to nice unobtrusive textual ads which don't incorporate piles of tracking.
gollark: Depends how complex a process you're okay with to get the energy.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.