Meighen Island
Meighen Island is an uninhabited member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, part of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
 Meighen Island, Nunavut | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Arctic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 79°59′N 099°30′W |
| Archipelago | Sverdrup Islands[1] Queen Elizabeth Islands Canadian Arctic Archipelago |
| Area | 955 km2 (369 sq mi) |
| Length | 56 km (34.8 mi) |
| Width | 30 km (19 mi) |
| Administration | |
Canada | |
| Territory | Nunavut |
| Region | Qikiqtaaluk |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited |
Features and history
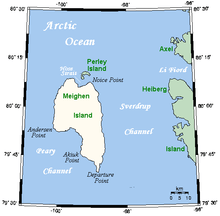
Located at 79°59'N 99°30'W, it measures 955 km2 (369 sq mi) in size and is topped with an ice cap. The island is permanently icebound, and its northwestern coast faces onto the open Arctic Ocean.
Unlike many Canadian Arctic islands, no traces of Inuit or Thule camps have been found, suggesting the island has never been inhabited, likely due to its extreme northern latitude. In 1909, two Inuit who had participated in Frederick Cook's polar expedition provided a map to Robert Peary that showed they had traveled and spent a night on a then unknown island with the position of Meighen Island. The map and testimony of the Inuit in question were published in an article by Peary in the Chicago Daily Tribune.[2] In 1916, Vilhjalmur Stefansson's Canadian Arctic Expedition sighted and landed on Meighen Island.[3] Stefansson at first believed that he had been the first to discover Meighen Island, but later read Peary's article on the Cook expedition and surmised that Cook had in fact discovered Meighen Island prior to himself.[4]
Naming
The island was later named after Arthur Meighen, Canadian prime minister 1920-21 and 1926.
Neighbouring islands
Meighen Island has few neighbours. It is about 40 km (25 mi) west of the next nearest major island, Axel Heiberg Island. About 4 km (2.5 mi) to Meighen's north, across the Hose Strait, lies small crescent-shaped Perley Island. The Fay Islands lie between Meighen Island and Axel Heiberg Island within the Sverdrup Channel.
References
- Mills, William James (2003). Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 421. ISBN 1-57607-422-6.
- Mills, William James (2003). Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. ISBN 9781576074220.
- Mills, William James (2003). Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. ISBN 9781576074220.
- Mills, William James (2003). Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. ISBN 9781576074220.