Leucoanthocyanidin
Leucoanthocyanidin (flavan-3,4-diols) are colorless chemical compounds related to anthocyanidins and anthocyanins. Leucoanthocyanins can be found in Anadenanthera peregrina and in several species of Nepenthes including N. burbidgeae, N. muluensis, N. rajah, N. tentaculata, and N. × alisaputrana.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
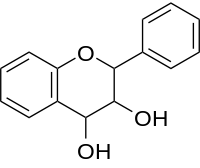
| IUPAC name
2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,4-diol | |
| Other names
Flavan-3,4-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 242.26 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Such compounds include:
- Leucocyanidin
- Leucodelphinidin
- Leucofisetinidin
- Leucomalvidin
- Leucopelargonidin
- Leucopeonidin
- leucorobinetinidin
- Melacacidin
- Teracacidin from Acacia obtusifolia and Acacia maidenii heartwoods[1]
Leucoanthocyanidins have been demonstrated to be intermediates in anthocyanidin biosynthesis in flowers of Matthiola incana.[2]
Bate-smith recommended in 1954 the use of the Forestal solvent for the isolation of leuco-anthocyanins.[3]
Metabolism
Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase uses flavan-3,4-diols to produce 3-hydroxyanthocyanidins.[4] The gene encoding the enzyme (PpLDOX) has been identified in peach[5] and expression has been studied in Vitis vinifera.[6]
References
- Clark-Lewis, JW; Dainis, I (1967). "Flavan derivatives. XIX. Teracacidin and isoteracacidin from Acacia obtusifolia and Acacia maidenii heartwoods; Phenolic hydroxylation patterns of heartwood flavonoids characteristic of sections and subsections of the genus Acacia". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 20 (10): 2191–2198. doi:10.1071/CH9672191.
- Leucoanthocyanidins as intermediates in anthocyanidin biosynthesis in flowers of Matthiola incana R. Br. Werner Heller, Lothar Britsch, Gert Forkmann and Hans Grisebach, 1984
- Bate-SMITH, EC (September 1954). "Leuco-anthocyanins. 1. Detection and identification of anthocyanidins formed leuco-anthocyanins in plant tissues". Biochem. J. 58 (1): 122–5. doi:10.1042/bj0580122. PMC 1269852. PMID 13198862.
- "leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase on mondofacto.com". Archived from the original on 2012-03-04. Retrieved 2009-09-03.
- Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase gene (PpLDOX): a potential functional marker for cold storage browning in peach, E. A. Ogundiwin, C. P. Peace, C. M. Nicolet, V. K. Rashbrook, T. M. Gradziel, F. A. Bliss, D. Parfitt and C. H. Crisosto, 2008
- Regulation of the leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase gene expression in Vitis vinifera, Gollop R; Farhi S.; Perl A. 2001