Lempäälä
Lempäälä (Swedish: Lempäälä, also Lembois, Lempälä) is a municipality in the Pirkanmaa region of Finland with 23,209 inhabitants (31 January 2019).[2] Lempäälä is located south of the city of Tampere. The municipality covers an area of 307.06 square kilometres (118.56 sq mi) of which 37.51 km2 (14.48 sq mi) is water.[1] The population density is 86.1 inhabitants per square kilometre (223/sq mi).
Lempäälä | |
|---|---|
Municipality | |
| Lempäälän kunta Lempäälä kommun | |
 Canal of Lempäälä | |
 Coat of arms | |
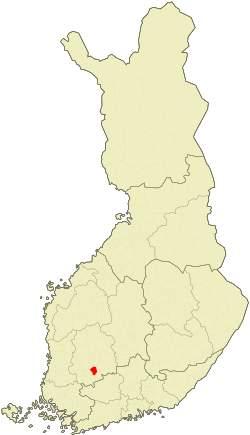 Location of Lempäälä in Finland | |
| Coordinates: 61°19′N 023°45′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Pirkanmaa |
| Sub-region | Tampere sub-region |
| Charter | 1866 |
| Government | |
| • Municipality manager | Heidi Rämö |
| Area (2018-01-01)[1] | |
| • Total | 307.06 km2 (118.56 sq mi) |
| • Land | 269.56 km2 (104.08 sq mi) |
| • Water | 37.51 km2 (14.48 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 241st largest in Finland |
| Population (2019-01-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 23,209 |
| • Rank | 45th largest in Finland |
| • Density | 86.1/km2 (223/sq mi) |
| Population by native language | |
| • Finnish | 98.1% (official) |
| • Swedish | 0.4% |
| • Others | 1.5% |
| Population by age | |
| • 0 to 14 | 22.7% |
| • 15 to 64 | 65.1% |
| • 65 or older | 12.2% |
| Time zone | UTC+02:00 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+03:00 (EEST) |
| Municipal tax rate[5] | 20% |
| Website | www.lempaala.fi |
The municipality center of Lempäälä is situated on an isthmus between the lakes Vanajavesi and Pyhäjärvi which are connected by the Kuokkalankoski rapids and the canal of Lempäälä that was built during the 1870s and is still in use.
The first written account of the parish of Lempäälä is from 1430. The oldest building of the town is a medieval church named after Saint Birgitta and was built in 1504.[6] The only remaining article from medieval times in the church is a wooden crucifix carved out of birch.
Finnish novelist Yrjö Kokko lived in Lempäälä, and is buried in the graveyard.
Ideapark, the second largest shopping mall in Nordic countries, is located in Lempäälä along the Helsinki–Tampere motorway.
Kuokkala
Kuokkala is a neighbourhood to the north of Lempäälä town which houses a ’museoraitti’ (museum trail). Several buildings now house collections of historical items, including a shop museum (also a shop and information office), hairdressers & barbers, cobblers, WW2 memorabilia, household equipment, blacksmiths, carpenters, a 19th-century Finish dwelling, and a special exhibit relating to the ex-Finnish region of Sakkola.[7]
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Lempäälä is twinned with:


References
- "Area of Finnish Municipalities 1.1.2018" (PDF). National Land Survey of Finland. Retrieved 30 January 2018.
- "Suomen virallinen tilasto (SVT): Väestön ennakkotilasto [verkkojulkaisu]. Tammikuu 2019" (in Finnish). Statistics Finland. Retrieved 15 March 2019.
- "Population according to language and the number of foreigners and land area km2 by area as of 31 December 2008". Statistics Finland's PX-Web databases. Statistics Finland. Retrieved 29 March 2009.
- "Population according to age and gender by area as of 31 December 2008". Statistics Finland's PX-Web databases. Statistics Finland. Retrieved 28 April 2009.
- "List of municipal and parish tax rates in 2011". Tax Administration of Finland. 29 November 2010. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- Pyhä Birgitta määräsi kirkon paikan – Lempäälän kunta Archived 2007-09-30 at the Wayback Machine
- Leaflet about Kuokkalan museoraitti published by museum.
External links
![]()
- Municipality of Lempäälä – Official site
