Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to β-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.
| Beta-lactamase | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
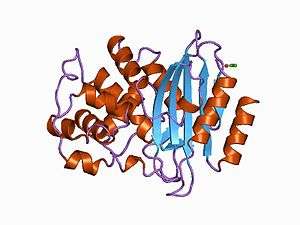 Structure of Streptomyces albus beta-lactamase | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | β-lactamase domain | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00144 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0013 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001466 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PS00146 | ||||||||||
| SCOPe | 56601 / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| β-lactamase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
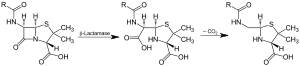 Action of β-lactamase and decarboxylation of the intermediate | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.5.2.6 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9073-60-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
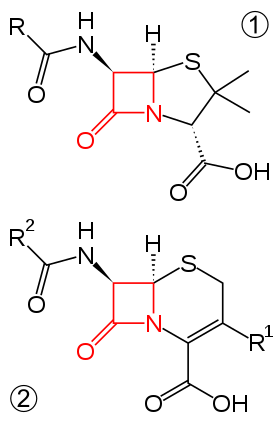
Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.[1]
Structure
The structure of a Streptomyces β-lactamase is given by 1BSG.
Penicillinase
Penicillinase is a specific type of β-lactamase, showing specificity for penicillins, again by hydrolysing the β-lactam ring. Molecular weights of the various penicillinases tend to cluster near 50 kiloDaltons.
Penicillinase was the first β-lactamase to be identified. It was first isolated by Abraham and Chain in 1940 from Gram-negative E. coli even before penicillin entered clinical use,[2] but penicillinase production quickly spread to bacteria that previously did not produce it or produced it only rarely. Penicillinase-resistant beta-lactams such as methicillin were developed, but there is now widespread resistance to even these.
Resistance in Gram-negative bacteria
Among Gram-negative bacteria, the emergence of resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins has been a major concern. It appeared initially in a limited number of bacterial species (E. cloacae, C. freundii, S. marcescens, and P. aeruginosa) that could mutate to hyperproduce their chromosomal class C β-lactamase. A few years later, resistance appeared in bacterial species not naturally producing AmpC enzymes (K. pneumoniae, Salmonella spp., P. mirabilis) due to the production of TEM- or SHV-type ESBLs (extended spectrum beta lactamases). Characteristically, such resistance has included oxyimino- (for example ceftizoxime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, and ceftazidime, as well as the oxyimino-monobactam aztreonam), but not 7-alpha-methoxy-cephalosporins (cephamycins; in other words, cefoxitin and cefotetan); has been blocked by inhibitors such as clavulanate, sulbactam or tazobactam and did not involve carbapenems and temocillin. Chromosomal-mediated AmpC β-lactamases represent a new threat, since they confer resistance to 7-alpha-methoxy-cephalosporins (cephamycins) such as cefoxitin or cefotetan but are not affected by commercially available β-lactamase inhibitors, and can, in strains with loss of outer membrane porins, provide resistance to carbapenems.[3]
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)
Members of the family commonly express plasmid-encoded β-lactamases (e.g., TEM-3, TEM-4, and SHV-1), which confer resistance to penicillins but not to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins. In the mid-1980s, a new group of enzymes, the extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), was detected (first detected in 1979).[4] The prevalence of ESBL-producing bacteria have been gradually increasing in acute care hospitals.[5] ESBLs are beta-lactamases that hydrolyze extended-spectrum cephalosporins with an oxyimino side chain. These cephalosporins include cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, and ceftazidime, as well as the oxyimino-monobactam aztreonam. Thus ESBLs confer multi-resistance to these antibiotics and related oxyimino-beta lactams. In typical circumstances, they derive from genes for TEM-1, TEM-2, or SHV-1 by mutations that alter the amino acid configuration around the active site of these β-lactamases. A broader set of β-lactam antibiotics are susceptible to hydrolysis by these enzymes. An increasing number of ESBLs not of TEM or SHV lineage have recently been described.[6] The ESBLs are frequently plasmid encoded. Plasmids responsible for ESBL production frequently carry genes encoding resistance to other drug classes (for example, aminoglycosides). Therefore, antibiotic options in the treatment of ESBL-producing organisms are extremely limited. Carbapenems are the treatment of choice for serious infections due to ESBL-producing organisms, yet carbapenem-resistant (primarily ertapenem resistant) isolates have recently been reported. ESBL-producing organisms may appear susceptible to some extended-spectrum cephalosporins. However, treatment with such antibiotics has been associated with high failure rates.
Types
TEM beta-lactamases (class A)
TEM-1 is the most commonly encountered beta-lactamase in Gram-negative bacteria. Up to 90% of ampicillin resistance in E. coli is due to the production of TEM-1.[7] Also responsible for the ampicillin and penicillin resistance that is seen in H. influenzae and N. gonorrhoeae in increasing numbers. Although TEM-type beta-lactamases are most often found in E. coli and K. pneumoniae, they are also found in other species of Gram-negative bacteria with increasing frequency. The amino acid substitutions responsible for the extended-spectrum beta lactamase (ESBL) phenotype cluster around the active site of the enzyme and change its configuration, allowing access to oxyimino-beta-lactam substrates. Opening the active site to beta-lactam substrates also typically enhances the susceptibility of the enzyme to β-lactamase inhibitors, such as clavulanic acid. Single amino acid substitutions at positions 104, 164, 238, and 240 produce the ESBL phenotype, but ESBLs with the broadest spectrum usually have more than a single amino acid substitution. Based upon different combinations of changes, currently 140 TEM-type enzymes have been described. TEM-10, TEM-12, and TEM-26 are among the most common in the United States.[8][9][10] The term TEM comes from the name of the Athenian patient (Temoniera) from which the isolate was recovered in 1963.[11]
SHV beta-lactamases (class A)
SHV-1 shares 68 percent of its amino acids with TEM-1 and has a similar overall structure. The SHV-1 beta-lactamase is most commonly found in K. pneumoniae and is responsible for up to 20% of the plasmid-mediated ampicillin resistance in this species. ESBLs in this family also have amino acid changes around the active site, most commonly at positions 238 or 238 and 240. More than 60 SHV varieties are known. SHV-5 and SHV-12 are among the most common.[8]
CTX-M beta-lactamases (class A)
These enzymes were named for their greater activity against cefotaxime than other oxyimino-beta-lactam substrates (e.g., ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, or cefepime). Rather than arising by mutation, they represent examples of plasmid acquisition of beta-lactamase genes normally found on the chromosome of Kluyvera species, a group of rarely pathogenic commensal organisms. These enzymes are not very closely related to TEM or SHV beta-lactamases in that they show only approximately 40% identity with these two commonly isolated beta-lactamases. More than 80 CTX-M enzymes are currently known. Despite their name, a few are more active on ceftazidime than cefotaxime. They have mainly been found in strains of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and E. coli, but have also been described in other species of Enterobacteriaceae and are the predominant ESBL type in parts of South America. (They are also seen in eastern Europe) CTX-M-14, CTX-M-3, and CTX-M-2 are the most widespread. CTX-M-15 is currently (2006) the most widespread type in E. coli the UK and is widely prevalent in the community.[12] An example of beta-lactamase CTX-M-15, along with ISEcp1, has been found to have recently transposed onto the chromosome of Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC BAA-2146.[13]
OXA beta-lactamases (class D)
OXA beta-lactamases were long recognized as a less common but also plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase variety that could hydrolyze oxacillin and related anti-staphylococcal penicillins. These beta-lactamases differ from the TEM and SHV enzymes in that they belong to molecular class D and functional group 2d . The OXA-type beta-lactamases confer resistance to ampicillin and cephalothin and are characterized by their high hydrolytic activity against oxacillin and cloxacillin and the fact that they are poorly inhibited by clavulanic acid. Amino acid substitutions in OXA enzymes can also give the ESBL phenotype. While most ESBLs have been found in E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and other Enterobacteriaceae, the OXA-type ESBLs have been found mainly in P. aeruginosa. OXA-type ESBLs have been found mainly in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Turkey and France. The OXA beta-lactamase family was originally created as a phenotypic rather than a genotypic group for a few beta-lactamases that had a specific hydrolysis profile. Therefore, there is as little as 20% sequence homology among some of the members of this family. However, recent additions to this family show some degree of homology to one or more of the existing members of the OXA beta-lactamase family. Some confer resistance predominantly to ceftazidime, but OXA-17 confers greater resistance to cefotaxime and cefepime than it does resistance to ceftazidime.
Others
Other plasmid-mediated ESBLs, such as PER, VEB, GES, and IBC beta-lactamases, have been described but are uncommon and have been found mainly in P. aeruginosa and at a limited number of geographic sites. PER-1 in isolates in Turkey, France, and Italy; VEB-1 and VEB-2 in strains from Southeast Asia; and GES-1, GES-2, and IBC-2 in isolates from South Africa, France, and Greece. PER-1 is also common in multiresistant acinetobacter species in Korea and Turkey. Some of these enzymes are found in Enterobacteriaceae as well, whereas other uncommon ESBLs (such as BES-1, IBC-1, SFO-1, and TLA-1) have been found only in Enterobacteriaceae.
Treatment
While ESBL-producing organisms were previously associated with hospitals and institutional care, these organisms are now increasingly found in the community. CTX-M-15-positive E. coli are a cause of community-acquired urinary infections in the UK,[12] and tend to be resistant to all oral β-lactam antibiotics, as well as quinolones and sulfonamides. Treatment options may include nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin, mecillinam and chloramphenicol. In desperation, once-daily ertapenem or gentamicin injections may also be used.
Inhibitor-resistant β-lactamases
Although the inhibitor-resistant β-lactamases are not ESBLs, they are often discussed with ESBLs because they are also derivatives of the classical TEM- or SHV-type enzymes. These enzymes were at first given the designation IRT for inhibitor-resistant TEM β-lactamase; however, all have subsequently been renamed with numerical TEM designations. There are at least 19 distinct inhibitor-resistant TEM β-lactamases. Inhibitor-resistant TEM β-lactamases have been found mainly in clinical isolates of E. coli, but also some strains of K. pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, P. mirabilis, and Citrobacter freundii. Although the inhibitor-resistant TEM variants are resistant to inhibition by clavulanic acid and sulbactam, thereby showing clinical resistance to the beta-lactam—lactamase inhibitor combinations of amoxicillin-clavulanate (co-amoxiclav), ticarcillin-clavulanate (co-ticarclav), and ampicillin/sulbactam, they normally remain susceptible to inhibition by tazobactam and subsequently the combination of piperacillin/tazobactam, although resistance has been described. This is no longer a primarily European epidemiology, it is found in northern parts of America often and should be tested for with complex UTI's.[9]
AmpC-type β-lactamases (class C)
AmpC type β-lactamases are commonly isolated from extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. AmpC β-lactamases (also termed class C or group 1) are typically encoded on the chromosome of many Gram-negative bacteria including Citrobacter, Serratia and Enterobacter species where its expression is usually inducible; it may also occur on Escherichia coli but is not usually inducible, although it can be hyperexpressed. AmpC type β-lactamases may also be carried on plasmids.[3] AmpC β-lactamases, in contrast to ESBLs, hydrolyse broad and extended-spectrum cephalosporins (cephamycins as well as to oxyimino-β-lactams) but are not inhibited by β-lactamase inhibitors such as clavulanic acid. AmpC-type β-lactamase organisms are often clinically grouped through the acronym, "SPACE": Serratia, Pseudomonas or Proteus, Acinetobacter, Citrobacter, and Enterobacter.
Carbapenemases
Carbapenems are famously stable to AmpC β-lactamases and extended-spectrum-β-lactamases. Carbapenemases are a diverse group of β-lactamases that are active not only against the oxyimino-cephalosporins and cephamycins but also against the carbapenems. Aztreonam is stable to the metallo-β-lactamases, but many IMP and VIM producers are resistant, owing to other mechanisms. Carbapenemases were formerly believed to derive only from classes A, B, and D, but a class C carbapenemase has been described.
IMP-type carbapenemases (metallo-β-lactamases) (class B)
Plasmid-mediated IMP-type carbapenemases (IMP stands for active-on-imipenem), 19 varieties of which are currently known, became established in Japan in the 1990s both in enteric Gram-negative organisms and in Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter species. IMP enzymes spread slowly to other countries in the Far East, were reported from Europe in 1997, and have been found in Canada and Brazil.
VIM (Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase) (Class B)
A second growing family of carbapenemases, the VIM family, was reported from Italy in 1999 and now includes 10 members, which have a wide geographic distribution in Europe, South America, and the Far East and have been found in the United States. VIM-1 was discovered in P. aeruginosa in Italy in 1996; since then, VIM-2 - now the predominant variant - was found repeatedly in Europe and the Far East; VIM-3 and -4 are minor variants of VIM-2 and -1, respectively. VIM enzymes occur mostly in P. aeruginosa, also P. putida and, very rarely, Enterobacteriaceae.
Amino acid sequence diversity is up to 10% in the VIM family, 15% in the IMP family, and 70% between VIM and IMP. Enzymes of both the families, nevertheless, are similar. Both are integron-associated, sometimes within plasmids. Both hydrolyse all β-lactams except monobactams, and evade all β-lactam inhibitors. The VIM enzymes are among the most widely distributed MBLs, with >40 VIM variants having been reported. Biochemical and biophysical studies revealed that VIM variants have only small variations in their kinetic parameters but substantial differences in their thermal stabilities and inhibition profiles.[14]
OXA (oxacillinase) group of β-lactamases (class D)
The OXA group of β-lactamases occur mainly in Acinetobacter species and are divided into two clusters. OXA carbapenemases hydrolyse carbapenems very slowly in vitro, and the high MICs seen for some Acinetobacter hosts (>64 mg/L) may reflect secondary mechanisms. They are sometimes augmented in clinical isolates by additional resistance mechanisms, such as impermeability or efflux. OXA carbapenemases also tend to have a reduced hydrolytic efficiency towards penicillins and cephalosporins.[15]
KPC (K. pneumoniae carbapenemase) (class A)
A few class A enzymes, most noted the plasmid-mediated KPC enzymes, are effective carbapenemases as well. Ten variants, KPC-2 through KPC-11 are known, and they are distinguished by one or two amino acid substitutions (KPC-1 was re-sequenced in 2008 and found to be 100% homologous to published sequences of KPC-2). KPC-1 was found in North Carolina, KPC-2 in Baltimore and KPC-3 in New York. They have only 45% homology with SME and NMC/IMI enzymes and, unlike them, can be encoded by self-transmissible plasmids.
As of February 2009, the class A Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) globally has been the most common carbapenemase, and was first detected in 1996 in North Carolina, USA.[16] A 2010 publication indicated that KPC producing Enterobacteriaceae were becoming common in the United States.[17]
CMY (class C)
The first class C carbapenemase was described in 2006 and was isolated from a virulent strain of Enterobacter aerogenes.[18] It is carried on a plasmid, pYMG-1, and is therefore transmissible to other bacterial strains.[19]
SME (Serratia marcescens enzymes), IMI (IMIpenem-hydrolysing β-lactamase), NMC and CcrA
In general, these are of little clinical significance.
CcrA (CfiA). Its gene occurs in ca. 1–3% of B. fragilis isolates, but fewer produce the enzyme since expression demands appropriate migration of an insertion sequence. CcrA was known before imipenem was introduced, and producers have shown little subsequent increase.
NDM-1 (New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase) (class B)
Originally described from New Delhi in 2009, this gene is now widespread in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from India and Pakistan. As of mid-2010, NDM-1 carrying bacteria have been introduced to other countries (including the United States and UK), most probably due to the large number of tourists travelling the globe, who may have picked up the strain from the environment, as strains containing the NDM-1 gene have been found in environmental samples in India.[20] NDM have several variants which share different properties.[21]
Treatment of ESBL/AmpC/carbapenemases
General overview
In general, an isolate is suspected to be an ESBL producer when it shows in vitro susceptibility to the second-generation cephalosporins (cefoxitin, cefotetan) but resistance to the third-generation cephalosporins and to aztreonam. Moreover, one should suspect these strains when treatment with these agents for Gram-negative infections fails despite reported in vitro susceptibility. Once an ESBL-producing strain is detected, the laboratory should report it as "resistant" to all penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam, even if it is tested (in vitro) as susceptible. Associated resistance to aminoglycosides and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, as well as high frequency of co-existence of fluoroquinolone resistance, creates problems. Beta-lactamase inhibitors such as clavulanate, sulbactam, and tazobactam in vitro inhibit most ESBLs, but the clinical effectiveness of beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations cannot be relied on consistently for therapy. Cephamycins (cefoxitin and cefotetan) are not hydrolyzed by majority of ESBLs, but are hydrolyzed by associated AmpC-type β-lactamase. Also, β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations may not be effective against organisms that produce AmpC-type β-lactamase. Sometimes these strains decrease the expression of outer membrane proteins, rendering them resistant to cephamycins. In vivo studies have yielded mixed results against ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae. (Cefepime, a fourth-generation cephalosporin, has demonstrated in vitro stability in the presence of many ESBL/AmpC strains.) Currently, carbapenems are, in general, regarded as the preferred agent for treatment of infections due to ESBL-producing organisms. Carbapenems are resistant to ESBL-mediated hydrolysis and exhibit excellent in vitro activity against strains of Enterobacteriaceae expressing ESBLs.
According to genes
ESBLs
Strains producing only ESBLs are susceptible to cephamycins and carbapenems in vitro and show little if any inoculum effect with these agents.
For organisms producing TEM and SHV type ESBLs, apparent in vitro sensitivity to cefepime and to piperacillin/tazobactam is common, but both drugs show an inoculum effect, with diminished susceptibility as the size of the inoculum is increased from 105 to 107 organisms.
Strains with some CTX-M–type and OXA-type ESBLs are resistant to cefepime on testing, despite the use of a standard inoculum.
Inhibitor-resistant β-lactamases
Although the inhibitor-resistant TEM variants are resistant to inhibition by clavulanic acid and sulbactam, thereby showing clinical resistance to the beta-lactam—beta lactamase inhibitor combinations of amoxicillin-clavulanate (Co-amoxiclav), ticarcillin-clavulanate, and ampicillin/sulbactam, they remain susceptible to inhibition by tazobactam and subsequently the combination of piperacillin/tazobactam.
AmpC
AmpC-producing strains are typically resistant to oxyimino-beta lactams and to cephamycins and are susceptible to carbapenems; however, diminished porin expression can make such a strain carbapenem-resistant as well.
Carbapenemases
Strains with IMP-, VIM-, and OXA-type carbapenemases usually remain susceptible. Resistance to non-beta-lactam antibiotics is common in strains making any of these enzymes, such that alternative options for non-beta-lactam therapy need to be determined by direct susceptibility testing. Resistance to fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides is especially high.
According to species
Escherichia coli or Klebsiella
For infections caused by ESBL-producing Escherichia coli or Klebsiella species, treatment with imipenem or meropenem has been associated with the best outcomes in terms of survival and bacteriologic clearance. Cefepime and piperacillin/tazobactam have been less successful. Ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime have failed even more often, despite the organism's susceptibility to the antibiotic in vitro. Several reports have documented failure of cephamycin therapy as a result of resistance due to porin loss. Some patients have responded to aminoglycoside or quinolone therapy, but, in a recent comparison of ciprofloxacin and imipenem for bacteremia involving an ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae, imipenem produced the better outcome
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
There have been few clinical studies to define the optimal therapy for infections caused by ESBL producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
Detection
Beta-lactamase enzymatic activity can be detected using nitrocefin, a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate which changes color from yellow to red upon beta-lactamase mediated hydrolysis.[22]
Evolution
Beta-lactamases are ancient bacterial enzymes. The class B beta-lactamases (the metallo-beta-lactamases) are divided into three subclasses: B1, B2 and B3. Subclasses B1 and B2 are theorized to have evolved about one billion years ago and subclass B3s is theorized to have evolved before the divergence of the Gram-positive and Gram-negative eubacteria about two billion years ago.[23] PNGM-1 (Papua New Guinea Metallo-β-lactamase-1) has both metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) and tRNase Z activities, suggesting that PNGM-1 is thought to have evolved from a tRNase Z, and that the B3 MBL activity of PNGM-1 is a promiscuous activity and subclass B3 MBLs are thought to have evolved through PNGM-1 activity.[24]
The other three groups are serine enzymes that show little homology to each other. Structural studies have shown that groups A and D are sister taxa and that group C diverged before A and D.[25] These serine-based enzymes, like the group B betalactamases, are of ancient origin and are theorized to have evolved about two billion years ago.[26]
The OXA group (in class D) in particular is theorized to have evolved on chromosomes and moved to plasmids on at least two separate occasions.[27]
Etymology
The "β" (beta) refers to the nitrogen's position on the second carbon in the ring. Lactam is a portmanteau of lactone (from the Latin lactis, milk, since lactic acid was isolated from soured milk) and amide. The suffix -ase, indicating an enzyme, is derived from diastase (from the Greek diastasis, "separation"), the first enzyme discovered in 1833 by Payen and Persoz.[28]
See also
- ESBL-producing E. coli
- Nitrocefin
- β-lactamase inhibitor
References
- Neu HC (June 1969). "Effect of beta-lactamase location in Escherichia coli on penicillin synergy". Applied Microbiology. 17 (6): 783–6. doi:10.1128/AEM.17.6.783-786.1969. PMC 377810. PMID 4894721.
- Abraham EP, Chain E (1940). "An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin". Nature. 46 (3713): 837. Bibcode:1940Natur.146..837A. doi:10.1038/146837a0.
- Philippon A, Arlet G, Jacoby GA (January 2002). "Plasmid-determined AmpC-type beta-lactamases". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 46 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.1.1-11.2002. PMC 126993. PMID 11751104.
- Sanders CC, Sanders WE (June 1979). "Emergence of resistance to cefamandole: possible role of cefoxitin-inducible beta-lactamases". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 15 (6): 792–7. doi:10.1128/AAC.15.6.792. PMC 352760. PMID 314270.
- Spadafino JT, Cohen B, Liu J, Larson E (2014). "Temporal trends and risk factors for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in adults with catheter-associated urinary tract infections". Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control. 3 (1): 39. doi:10.1186/s13756-014-0039-y. PMC 4306238. PMID 25625011.
- Emery CL, Weymouth LA (August 1997). "Detection and clinical significance of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in a tertiary-care medical center". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 35 (8): 2061–7. doi:10.1128/JCM.35.8.2061-2067.1997. PMC 229903. PMID 9230382.
- Cooksey R, Swenson J, Clark N, Gay E, Thornsberry C (May 1990). "Patterns and mechanisms of beta-lactam resistance among isolates of Escherichia coli from hospitals in the United States". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 34 (5): 739–45. doi:10.1128/AAC.34.5.739. PMC 171683. PMID 2193616.
- Paterson DL, Hujer KM, Hujer AM, Yeiser B, Bonomo MD, Rice LB, Bonomo RA (November 2003). "Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream isolates from seven countries: dominance and widespread prevalence of SHV- and CTX-M-type beta-lactamases". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 47 (11): 3554–60. doi:10.1128/AAC.47.11.3554-3560.2003. PMC 253771. PMID 14576117.
- Bradford PA (October 2001). "Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in the 21st century: characterization, epidemiology, and detection of this important resistance threat". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 14 (4): 933–51, table of contents. doi:10.1128/CMR.14.4.933-951.2001. PMC 89009. PMID 11585791.
- Jacoby GA, Munoz-Price LS (January 2005). "The new beta-lactamases". The New England Journal of Medicine. 352 (4): 380–91. doi:10.1056/NEJMra041359. PMID 15673804.
- Ruiz, Joaquim (2018). "Etymologia: TEM". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 24 (4): 709. doi:10.3201/eid2404.et2404.
- Woodford N, Ward E, Kaufmann ME, et al. "Molecular characterisation of Escherichia coli isolates producing CTX-M-15 extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) in the United Kingdom" (PDF). Health Protection Agency. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2007. Retrieved 19 November 2006.
- Hudson CM, Bent ZW, Meagher RJ, Williams KP (7 June 2014). "Resistance determinants and mobile genetic elements of an NDM-1-encoding Klebsiella pneumoniae strain". PLOS ONE. 9 (6): e99209. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099209. PMC 4048246. PMID 24905728.
- Makena A, Düzgün AÖ, Brem J, McDonough MA, Rydzik AM, Abboud MI, et al. (December 2015). "Comparison of Verona Integron-Borne Metallo-β-Lactamase (VIM) Variants Reveals Differences in Stability and Inhibition Profiles". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 60 (3): 1377–84. doi:10.1128/AAC.01768-15. PMC 4775916. PMID 26666919.
- Santillana E, Beceiro A, Bou G, Romero A (March 2007). "Crystal structure of the carbapenemase OXA-24 reveals insights into the mechanism of carbapenem hydrolysis" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (13): 5354–9. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.5354S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607557104. PMC 1838445. PMID 17374723.
- Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T (April 2009). "The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 9 (4): 228–36. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70054-4. PMID 19324295.
- Cuzon G, Naas T, Nordmann P (February 2010). "[KPC carbapenemases: what is at stake in clinical microbiology?]". Pathologie-Biologie (in French). 58 (1): 39–45. doi:10.1016/j.patbio.2009.07.026. PMID 19854586.
- Kim JY, Jung HI, An YJ, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Jeong SH, et al. (May 2006). "Structural basis for the extended substrate spectrum of CMY-10, a plasmid-encoded class C beta-lactamase". Molecular Microbiology. 60 (4): 907–16. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05146.x. PMID 16677302.
- Lee JH, Jung HI, Jung JH, Park JS, Ahn JB, Jeong SH, et al. (2004). "Dissemination of transferable AmpC-type beta-lactamase (CMY-10) in a Korean hospital". Microbial Drug Resistance. 10 (3): 224–30. doi:10.1089/mdr.2004.10.224. PMID 15383166.
- Walsh TR, Weeks J, Livermore DM, Toleman MA (May 2011). "Dissemination of NDM-1 positive bacteria in the New Delhi environment and its implications for human health: an environmental point prevalence study". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 11 (5): 355–62. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70059-7. PMID 21478057.
- Makena A, Düzgün AÖ, Brem J, McDonough MA, Rydzik AM, Abboud MI, et al. (December 2015). "Comparison of Verona Integron-Borne Metallo-β-Lactamase (VIM) Variants Reveals Differences in Stability and Inhibition Profiles". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 60 (3): 1377–84. doi:10.1128/AAC.01768-15. PMC 4775916. PMID 26666919.
- O'Callaghan CH, Morris A, Kirby SM, Shingler AH (April 1972). "Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 1 (4): 283–8. doi:10.1128/AAC.1.4.283. PMC 444209. PMID 4208895.
- Hall BG, Salipante SJ, Barlow M (July 2004). "Independent origins of subgroup Bl + B2 and subgroup B3 metallo-beta-lactamases". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 59 (1): 133–41. doi:10.1007/s00239-003-2572-9. PMID 15383916.
- Lee JH, Takahashi M, Jeon JH, Kang LW, Seki M, Park KS, et al. (2019). "β-lactamases: a molecular and evolutionary study". Emerging Microbes & Infections. 8 (1): 1688–1700. doi:10.1080/22221751.2019.1692638. PMC 6882493. PMID 31749408.
- Hall BG, Barlow M (September 2003). "Structure-based phylogenies of the serine beta-lactamases". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 57 (3): 255–60. doi:10.1007/s00239-003-2473-y. PMID 14629035.
- Hall BG, Barlow M (April 2004). "Evolution of the serine beta-lactamases: past, present and future". Drug Resistance Updates. 7 (2): 111–23. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2004.02.003. PMID 15158767.
- Barlow M, Hall BG (September 2002). "Phylogenetic analysis shows that the OXA beta-lactamase genes have been on plasmids for millions of years". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 55 (3): 314–21. Bibcode:2002JMolE..55..314B. doi:10.1007/s00239-002-2328-y. PMID 12187384.
- "Etymologia: β-Lactamase". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 22 (9): 1689–1631. 2016. doi:10.3201/eid2209.ET2209.
External links
- Online ESBL genotyping tool (EGT)
- Online Amino Acid Sequences for ESBL enzymes
- beta-Lactamases at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)