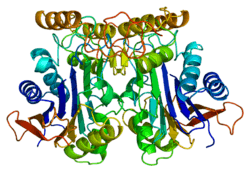Aspartylglucosaminidase
N(4)-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGA gene.[5]
Aspartylglucosaminidase is an amidohydrolase enzyme involved in the catabolism of N-linked oligosaccharides of glycoproteins. It cleaves asparagine from N-acetylglucosamines as one of the final steps in the lysosomal breakdown of glycoproteins. The lysosomal storage disease aspartylglycosaminuria is caused by a deficiency in the AGA enzyme.[5]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000038002 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031521 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: AGA aspartylglucosaminidase".
External links
- Human AGA genome location and AGA gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Ikonen E, Peltonen L (1993). "Mutations causing aspartylglucosaminuria (AGU): a lysosomal accumulation disease". Hum. Mutat. 1 (5): 361–5. doi:10.1002/humu.1380010503. PMID 1301945.
- Mononen I, Fisher KJ, Kaartinen V, Aronson NN (1993). "Aspartylglycosaminuria: protein chemistry and molecular biology of the most common lysosomal storage disorder of glycoprotein degradation". FASEB J. 7 (13): 1247–56. PMID 8405810.
- Enomaa N, Heiskanen T, Halila R, et al. (1992). "Human aspartylglucosaminidase. A biochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of the enzyme in normal and aspartylglucosaminuria fibroblasts". Biochem. J. 286 ( Pt 2) (Pt 2): 613–8. PMC 1132942. PMID 1530592.
- Ikonen E, Baumann M, Grön K, et al. (1991). "Aspartylglucosaminuria: cDNA encoding human aspartylglucosaminidase and the missense mutation causing the disease". EMBO J. 10 (1): 51–8. PMC 452610. PMID 1703489.
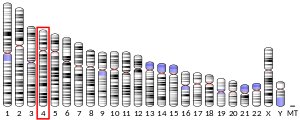
- Morris C, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J, et al. (1992). "Chromosomal localization of the human glycoasparaginase gene to 4q32-q33". Hum. Genet. 88 (3): 295–7. doi:10.1007/BF00197262. PMID 1733831.
- Ikonen E, Enomaa N, Ulmanen I, Peltonen L (1992). "In vitro mutagenesis helps to unravel the biological consequences of aspartylglucosaminuria mutation". Genomics. 11 (1): 206–11. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90120-4. PMID 1765378.
- Park H, Fisher KJ, Aronson NN (1991). "Genomic structure of human lysosomal glycosylasparaginase". FEBS Lett. 288 (1–2): 168–72. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)81027-6. PMID 1840528.
- Mononen T, Mononen I, Matilainen R, Airaksinen E (1991). "High prevalence of aspartylglycosaminuria among school-age children in eastern Finland". Hum. Genet. 87 (3): 266–8. doi:10.1007/BF00200902. PMID 1864600.
- Fisher KJ, Aronson NN (1991). "Characterization of the mutation responsible for aspartylglucosaminuria in three Finnish patients. Amino acid substitution Cys163----Ser abolishes the activity of lysosomal glycosylasparaginase and its conversion into subunits". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (18): 12105–13. PMID 1904874.
- Mononen I, Heisterkamp N, Kaartinen V, et al. (1991). "Aspartylglycosaminuria in the Finnish population: identification of two point mutations in the heavy chain of glycoasparaginase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (7): 2941–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.7.2941. PMC 51356. PMID 2011603.
- Halila R, Baumann M, Ikonen E, et al. (1991). "Human leucocyte aspartylglucosaminidase. Evidence for two different subunits in a more complex native structure". Biochem. J. 276 ( Pt 1) (Pt 1): 251–6. PMC 1151172. PMID 2039475.
- Fisher KJ, Tollersrud OK, Aronson NN (1991). "Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for human glycosylasparaginase. A single gene encodes the subunits of this lysosomal amidase". FEBS Lett. 276 (1–2): 232. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)80551-S. PMID 2265705.
- Fisher KJ, Tollersrud OK, Aronson NN (1990). "Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for human glycosylasparaginase. A single gene encodes the subunits of this lysosomal amidase". FEBS Lett. 269 (2): 440–4. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)81211-6. PMID 2401370.
- Tollersrud OK, Aronson NN (1989). "Purification and characterization of rat liver glycosylasparaginase". Biochem. J. 260 (1): 101–8. PMC 1138631. PMID 2775174.
- Hreidarsson S, Thomas GH, Valle DL, et al. (1983). "Aspartylglucosaminuria in the United States". Clin. Genet. 23 (6): 427–35. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb01977.x. PMID 6883788.
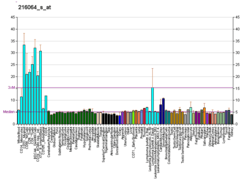
- Enomaa NE, Lukinmaa PL, Ikonen EM, et al. (1993). "Expression of aspartylglucosaminidase in human tissues from normal individuals and aspartylglucosaminuria patients". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 41 (7): 981–9. doi:10.1177/41.7.7685790. PMID 7685790.
- McCormack AL, Mononen I, Kaartinen V, Yates JR (1995). "Localization of the disulfide bond involved in post-translational processing of glycosylasparaginase and disrupted by a mutation in the Finnish-type aspartylglycosaminuria". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (7): 3212–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.7.3212. PMID 7852406.
- Tollersrud OK, Heiskanen T, Peltonen L (1994). "Human leucocyte glycosylasparaginase is an alpha/beta-heterodimer of 19 kDa alpha-subunit and 17 and 18 kDa beta-subunit". Biochem. J. 300 ( Pt 2) (Pt 2): 541–4. PMC 1138195. PMID 8002961.
External links
- Aspartylglucosylaminase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.