Miercurea Ciuc
Miercurea Ciuc (Romanian pronunciation: [ˈmjerkure̯a t͡ʃjuk], ![]()
![]()
Miercurea Ciuc Csíkszereda | |
|---|---|
 The Mikó Castle | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Location in Harghita County | |
 Miercurea Ciuc Location in Romania | |
| Coordinates: 46°21′34″N 25°48′6″E | |
| Country | |
| County | Harghita |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Róbert Ráduly[1] (UDMR) |
| Population (2011)[2] | 38,966 |
| Time zone | EET/EEST (UTC+2/+3) |
| Vehicle reg. | HR |
| Website | www |

The city administers three villages:
- Ciba / Csiba
- Harghita-Băi / Hargita-fürdő
- Jigodin-Băi / Zsögöd-fürdő, including Jigodin / Csíkzsögöd
Demographics
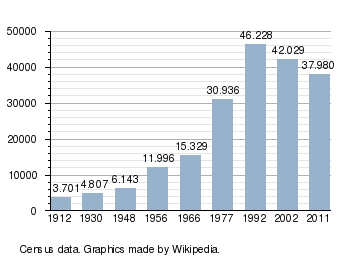
According to the census of 2011, there were 37,980 people living in the city. Of this population, 81.39% are ethnic Hungarians, while 17.4% are ethnic Romanians, 0.9% are ethnic Romani and 0.33% declare other nationalities.[3]
According to the census of 2002, there were 42,029 people living in the city. Of this population, 81.75% are ethnic Hungarians, while 17.3% are ethnic Romanians, 0.62% are ethnic Romani and 0.33% declare other nationalities.[4]
Demographic movements according to census data:
Roman Catholicism is the majority religion of Miercurea Ciuc, its adherents numbering 74.06% of the total population. Romanian Orthodox (14.99%), Hungarian Reformed (7.41%), and Unitarian (2.05%) adherents represent the most significant other religious groups.
History
The remains of three Dacian fortifications were found in the Jigodin neighbourhood of Miercurea Ciuc; they belong to the Dacian culture of the 1st century. In the Middle Ages it was the capital of Csíkszék (Csik seat). Between 1876 and 1918, Csíkszereda was the seat of Csík County of the historical Szeklerland in the Kingdom of Hungary. After the Treaty of Trianon in 1920, it became part of Kingdom of Romania, and was seat of the Ciuc County between 1927 and 1938.
Miercurea Ciuc became part of Hungary again between 1940 and 1944 as a result of the Second Vienna Award. In 1944, the Soviet Red Army captured the town. It was returned to Romania in 1945, a move confirmed by the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947. Between 1952–1960, the town was part of the Magyar Autonomous Region, later named the Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region between 1960–1968. In 1968, Miercurea Ciuc became the county seat of Harghita.
In the post-World War II period, the town was industrialized; among other projects, a tractor factory, a textile factory and, in the 1960s, a beer factory were built here. The factory is now owned by Heineken. The Ciuc Beer products have gained an increasing popularity in Romania.
Climate
Miercurea Ciuc has a cool continental climate (Köppen climate classification: Dfb - without a dry season, although summer is wetter than winter and with a cold summer). At an average temperature of 16.3 °C (61.3 °F), July is the hottest month of the year. January has the lowest average temperature of the year: −7.7 °C (18.1 °F). Between the driest and wettest months, the difference in precipitation is 64.5 millimetres (2.54 in).
Miercurea Ciuc is one of the coldest cities in Romania, with temperatures plummeting towards −20 °C (−4 °F) much more often than anywhere in the country, sometimes as early as November. Snow falls as early as October and as late as April.
| Climate data for Miercurea Ciuc, Romania | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12 (54) |
16 (61) |
23 (73) |
26 (79) |
30 (86) |
32 (90) |
35 (95) |
35 (95) |
33 (91) |
27 (81) |
22 (72) |
17 (63) |
35 (95) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −2.9 (26.8) |
0.7 (33.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
13.9 (57.0) |
19.1 (66.4) |
21.8 (71.2) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
20.1 (68.2) |
14.4 (57.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −7.7 (18.1) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
1.0 (33.8) |
7.2 (45.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.9 (58.8) |
16.3 (61.3) |
15.7 (60.3) |
12.3 (54.1) |
7.1 (44.8) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
5.9 (42.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −12.5 (9.5) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
0.5 (32.9) |
4.9 (40.8) |
8.0 (46.4) |
9.2 (48.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −33 (−27) |
−33 (−27) |
−28 (−18) |
−14 (7) |
−8 (18) |
−1 (30) |
0 (32) |
−3 (27) |
−8 (18) |
−14 (7) |
−27 (−17) |
−33 (−27) |
−33 (−27) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 28.8 (1.13) |
26.2 (1.03) |
26.9 (1.06) |
43.0 (1.69) |
70.6 (2.78) |
90.7 (3.57) |
83.2 (3.28) |
65.7 (2.59) |
39.8 (1.57) |
32.9 (1.30) |
28.4 (1.12) |
29.4 (1.16) |
565.9 (22.28) |
| Average precipitation days | 12 | 12 | 19 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 13 | 14 | 150 |
| Average snowy days | 8 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 43 |
| Source 1: [5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: [6] | |||||||||||||
Education
In 2001 the Sapientia Transylvanian Hungarian University opened in the building of the former Harghita Hotel. The privately run institution is the first Hungarian university in modern Romania. Other cities in Transylvania also have Sapientia University faculties. Since the university opened, it has been attracting growing numbers of young people and intellectuals.
The Early Music Festival takes place every year in July, from 1980 onwards, mainly in the court of the castle. From 2008 it joins a Summer Music University for early music. Its concerts, held by the most important ensembles for early music in Romania and by the most famous ensembles of Europe, are with free admission.[7]
Sports
Miercurea Ciuc is one of the coldest cities in Romania, with winter temperatures often going under −30 °C (−22 °F), making the city ideal for winter sports. The Vákár Lajos Ice Hall annually hosts the national ice hockey championships, often won by the best-supported local team, HSC Csíkszereda. In 2006 the ice rink hosted the world junior championship in short track speed skating. The only long track speed skating oval in Romania is situated just outside the ice hockey rink.[8]
Main sights
Petőfi Street is the main pedestrian street in the city. It houses numerous restaurants and cafés. Their Székely specialties conjure up images of a small city in Western Europe. During the summer, the street is a popular destination for afternoon and evening recreational activities.
Miercurea-Ciuc is home to the Baroque church at Șumuleu Ciuc and, in the city center, the Mikó Castle, built in a late Renaissance style. The original more decorative castle was raised in the 17th century on the orders of Ferenc Mikó Hídvégi, the personal advisor of Gabriel Bethlen, then prince of Transylvania. Much of the castle was destroyed in 1661 during the Tatar raids, but it was rebuilt at the beginning of the 18th century and was mainly used as a barracks; today it houses the Csík Székely Museum. Behind the castle is a small Skanzen (museum village), consisting of a few traditional Csíki houses and wooden gates. Across the road from the castle is the city hall built in 1886, originally the county hall of the old Hungarian Csík County. Beside the castle is the 1904 Courthouse. The latest significant addition to the architectural landscape is the controversial 2001 Millennium Church, designed by Hungarian architect Imre Makovecz and located next to the Baroque Church of the Holy Cross. There is a large Romanian Orthodox church (1929-1939) in the city center. The Orthodox Church has Neo-Byzantine characteristics. It was built in the former administrative center of Miercurea Ciuc, the Castle Square.
- Theater
- Consulate of Hungary
- Roman Catholic church (designed by Imre Makovecz)
 Orthodox cathedral
Orthodox cathedral- Court House
- Library
- County Hall
 Petőfi Street
Petőfi Street
Șumuleu/Csíksomlyó Pentecost Pilgrimage

A few kilometres to the east of the city centre is the Franciscan monastery of Șumuleu Ciuc, known in Hungarian as Csíksomlyó. A wooden-sculpture figure of the Virgin Mary, known as the Weeping Mary, can be found in the monastery church, which is the destination of a traditional pilgrimage of Roman Catholic Székely held since 1567, called the "Csíksomlyó Pilgrimage" (Romanian: Pelerinajul de la Sumuleu; Hungarian: Csíksomlyói Búcsú). The event, held on the Saturday before Pentecost, attracts several hundred thousand people every year. The mass for the pilgrims is held on a meadow near the church. This traditional gathering is not only attended by Székely and Csángó Hungarians living in the region, but also by a great number of mostly Hungarian Catholics from other parts of Transylvania region, Hungary and all over the world. Beside its religious importance, the pilgrimage has also become a demonstration of the awareness and solidarity of Catholic Hungarian people living in and outside the historical region of Transylvania.[9]
Politics
The City Council has 19 members:
| Party | Seats | Current Council | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic Alliance of Hungarians in Romania | 13 | ||||||||||||||
| Hungarian Civic Party | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Hungarian People's Party of Transylvania | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Social Liberal Union | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Consulates

Twin towns — sister cities
Miercurea Ciuc is twinned with:
|
References
- "Results of the 2016 local elections". Central Electoral Bureau. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- "Populaţia stabilă pe judeţe, municipii, oraşe şi localităti componenete la RPL_2011" (in Romanian). National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- Romanian census 2011
- Romanian census 2002
- "Miercurea Ciuc climate data". Meteo Romania. Retrieved 14 December 2016.
- "Climate: Miercurea Ciuc". Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- "Early Music Festival Miercurea-Ciuc". regizene.ro. Retrieved 2016-08-14.
- Rink card of: Patinoarul Artificial Vákár Lajos Miercurea Ciuc (Csikszereda)
- Csíksomlyó Pilgrimage
- Bozsoki, Agnes. "Partnervárosok Névsora Partner és Testvérvárosok Névsora" [Partner and Twin Cities List]. City of Székesfehérvár (in Hungarian). Archived from the original on 2012-12-08. Retrieved 2013-08-05.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Miercurea Ciuc. |
- Official website (in Romanian and Hungarian)
- https://web.archive.org/web/20160814203034/http://regizene.ro/html/2016/en/
