Mădăraș, Harghita
Mădăraș (Hungarian: Csíkmadaras or colloquially Madaras, Hungarian pronunciation:[ˈtʃiːkmɒdɒrɒʃ]) is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania. It is composed of a single village, Mădăraș.
Mădăraș Csíkmadaras | |
|---|---|
Landscape of the neighbouring Harghita Mountains | |
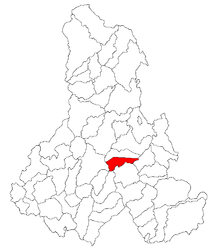 Location in Harghita County | |
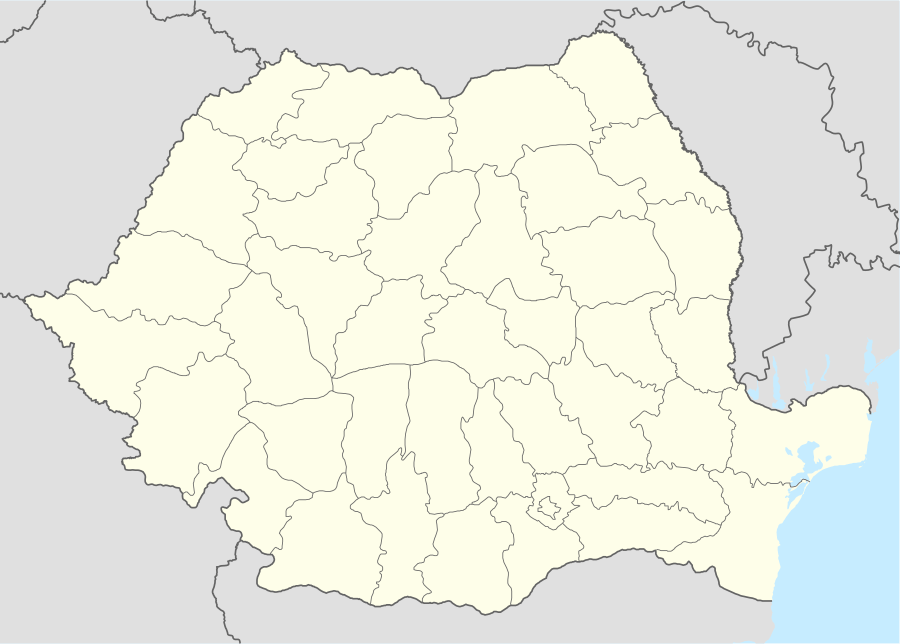 Mădăraș Location in Romania | |
| Coordinates: 46°30′N 25°45′E | |
| Country | |
| County | Harghita |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Géza Miklós (UDMR) |
| Area | 66 km2 (25 sq mi) |
| Population (2011)[1] | 2,199 |
| • Density | 33/km2 (86/sq mi) |
| Time zone | EET/EEST (UTC+2/+3) |
| Postal code | 537071 |
| Area code | +40 266 |
| Vehicle reg. | HR |
| Website | www.csikmadaras.ro |
History
The village was first mentioned in 1567 as Madaras, meaning "birdy". Its name may have referred to the abundancy of birds in the area.[2] Its Romanian name derives from the Hungarian form. According to tradition, the village was in the beginning located in the Hámorkert (Iron Hammer Garden) part also known as Fejedelem Kertje (Dukes’s Garden). Its residents used to be engaged in the mining of iron ore and mercury which was a royal monopoly. By the 18th century, the iron ore mine became exhausted, so the villagers started to deal with pottery and the village soon was famous for its potters which lasted until the end of the 19th century. More recently, thermal water sources has been discovered in the area and there are still unexploited iron ore and andezit occurrences, too.
The village historically belonged to the Székely seat of Csíkszék until the administrative reform of Transylvania in 1876, when it fell within Csík County in the Kingdom of Hungary. After the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, it became part of Romania and fell within Ciuc County during the interwar period. In 1940, the second Vienna Award granted the Northern Transylvania to Hungary and the village was held by Hungary until 1944. After Soviet occupation, the Romanian administration returned and the commune became officially part of Romania in 1947. Between 1952 and 1960, the commune fell within the Magyar Autonomous Region, between 1960 and 1968 the Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region. In 1968, the province was abolished, and since then, it has been part of Harghita County.
Demographics
The commune has an absolute Székely (Hungarian) majority. According to the 2011 census it has a population of 2,190; of which 99.27% or 2,174 are Hungarian.
Formerly part of Dănești commune, the village broke off in 2004 with a population of 2,210.
Landmarks
- The Roman Catholic church was built between 1790 and 1796, but was consecrated only in 1828. Its tower dates back to 1769.
- The St. Anthony Chapel stand in the Prince”s Garden. It was built in 1992 on the ruins of an old chapel.
- The highest peak of the Harghita Mountains (1801m) stands in its vicinity,
Twin cities
The village is twinned with:
References
- "Populaţia stabilă pe judeţe, municipii, oraşe şi localităti componenete la RPL_2011" (in Romanian). National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- János András Vistai. "Tekintő – Erdélyi Helynévkönyv". Missing or empty
|url=(help)Transylvanian Toponym Book Archived 2011-07-10 at the Wayback Machine
External links
- Official website (in Hungarian)
