Itogon
Itogon, officially the Municipality of Itogon, (Ilocano: Ili ti Itogon; Tagalog: Bayan ng Itogon), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Benguet, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 59,820 people.[3]
Itogon | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Itogon | |
 | |
 Seal | |
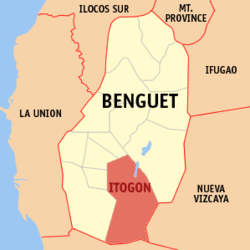 Map of Benguet with Itogon highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Itogon Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 16°22′N 120°41′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) |
| Province | Benguet |
| District | Lone District |
| Founded | May 15, 1951 |
| Barangays | 9 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Victorio T. Palangdan |
| • Vice Mayor | Adriano R. Carantes Jr. |
| • Congressman | Nestor B. Fongwan |
| • Electorate | 31,249 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 449.73 km2 (173.64 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 59,820 |
| • Density | 130/km2 (340/sq mi) |
| • Households | 14,204 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 6.32% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 247,027,611.96 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 2604 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)74 |
| Climate type | tropical rainforest climate |
| Native languages | Kankanaey language Ibaloi I-Wak Ilocano Tagalog |
| Website | www |
The largest municipality in Benguet by land area, Itogon is a mining town, being the site of the first large-scale mining operations in the country.[5][6][7]
History
Spanish period
During the Spanish Regime, a native of the historic pueblo of Itogon (or Itokhon), named Codeng, was appointed by the Spanish authorities as capitan of another nearby village, Balingway (currently Itogon Central/Proper[9]).[6][7] Balingway was later established as a town site and renamed after Codeng's native place.[6]
American period
During the American rule, Itogon was established as one of the 19 townships of the province of Benguet, upon the issuance of Act No. 48 by the Philippine Commission on November 22, 1900.[6][10][11]
Mining operations started in Itogon in 1903, after Benguet Corporation, the Philippines' first mining firm, was established in the town under the name, Benguet Consolidated Mining Company (BCMC), by Americans Nelson Peterson and Harry Clyde.[5][12]
On August 13, 1908, Benguet was established as a sub-province of the newly created Mountain Province with the enactment of Act No. 1876. As a result, six townships of Benguet were abolished, but Itogon remained a constituent town of Benguet sub-province.[11]
Post-war era
In 1948, plans by the National Power Corporation (NAPOCOR) for a second dam construction along the Agno River in the province of Benguet started, after the Ambuklao Dam construction commenced in Bokod. Bulldozers started clearing the forested area of the Guissit Mountains in 1954 for the Binga Dam. Construction of the dam took 3 years and 9 months, from August 1956 until its formal operations opening in May 1960.[7][8]
On May 15, 1951, the town was converted into a regular municipality from the former municipal district of the same name, with the enactment of Republic Act No. 616.[13]
On June 18, 1966, the sub-province of Benguet was separated from the old Mountain Province and was converted into a regular province. Itogon remained to be a component municipality of the newly established province.[11][14]
Geography
Itogon is located at 16°22′N 120°41′E, at the southeast end of the Benguet, forming a border with the provinces of Nueva Vizcaya (on the west) and Pangasinan (on the south). The town is bounded by Baguio and the municipality of Tuba on the west, La Trinidad and Tublay on the north-west, Bokod on the north-east, Kayapa and Santa Fe on the southeast, San Manuel and San Nicolas on the south, and Sison on the south-west.
According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, the municipality has a land area of 449.73 square kilometres (173.64 sq mi) [2] constituting 16.24% of the 2,769.08-square-kilometre- (1,069.15 sq mi) total area of Benguet.
The Agno River traverses the municipality and is impounded at Binga (19 kilometres or 12 miles from the Ambuklao Dam in Bokod) forming the Binga Dam.[8]
Barangays
Itogon is politically subdivided into 9 barangays.[15]
| PSGC | Barangay | Population | ±% p.a. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015[3] | 2010[16] | |||||
| 141106001 | Ampucao | 18.6% | 11,118 | 10,450 | 1.19% | |
| 141106002 | Dalupirip | 5.1% | 3,058 | 2,578 | 3.30% | |
| 141106003 | Gumatdang | 3.6% | 2,163 | 1,895 | 2.55% | |
| 141106004 | Loacan | 12.9% | 7,740 | 7,714 | 0.06% | |
| 141106005 | Poblacion (Central) | 6.1% | 3,663 | 3,267 | 2.20% | |
| 141106006 | Tinongdan | 6.0% | 3,596 | 4,216 | −2.98% | |
| 141106007 | Tuding | 13.5% | 8,082 | 7,703 | 0.92% | |
| 141106008 | Ucab | 15.7% | 9,410 | 7,870 | 3.46% | |
| 141106009 | Virac | 18.4% | 10,990 | 10,267 | 1.30% | |
| Total | 59,820 | 55,960 | 1.28% | |||
Climate
| Climate data for Itogon, Benguet | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 25 (77) |
26 (79) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
27 (81) |
26 (79) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 15 (59) |
16 (61) |
17 (63) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
19 (66) |
18 (64) |
17 (63) |
16 (61) |
18 (65) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 15 (0.6) |
16 (0.6) |
24 (0.9) |
33 (1.3) |
102 (4.0) |
121 (4.8) |
177 (7.0) |
165 (6.5) |
144 (5.7) |
170 (6.7) |
56 (2.2) |
23 (0.9) |
1,046 (41.2) |
| Average rainy days | 6.3 | 6.6 | 9.5 | 12.8 | 20.6 | 23.5 | 25.4 | 23.4 | 23.2 | 21.4 | 14.0 | 8.2 | 194.9 |
| Source: Meteoblue [17] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][16][18][19] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2015 census, Itogon had a population of 59,820.[3] The population density was 130 inhabitants per square kilometre (340/sq mi).
Generally inhabited by 60 percent Ibalois, 40 percent Kankanaey, and other ethnicities such as the Ilocano, Itogon was the most populous municipality in the province, with a population of 61,773 in the 1990 census. Its population abruptly declined five years after as illustrated in the census of 1995.[19]
Economy
Itogon’s main source of livelihood is mining.[5] Secondary to mining is agriculture. Major mining companies which operate in the town include Benguet Corporation, Philex Mining Corporation, Atok Big Wedge Mining Company (now called Atok Gold Mining Company) and Itogon Suyoc Mines.[20]
Tourism
Known tourist destination areas in Itogon include the Binga Dam in Tinongdan and Balatoc Mines Tours in Balatoc, Virac. Other tourist spots include the open pit mines in Loacan, hot spring in Dalupirip, Mount Ugo in Tinongdan, Level 1300 swimming pools in Poblacion with hot steams and bath and the mummies in Domolpos also in Tinongdan.[21][22]
Transportation
Highways through Itogon:
- Baguio-Bua-Itogon National Road
- Ambuklao Road
- Benguet-Nueva Vizcaya Road
Education
Public schools
As of 2014, Itogon has 39 public elementary schools and 7 public secondary schools.[23][24][25]
|
|
Private schools
- Sacred Heart High School of Itogon
- Saint Louis High School of Antamok
- Saint Louis High School of Balatoc
- Saint Louis High School of Philex
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved May 31, 2013.
- "Province: Benguet". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved November 12, 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved October 12, 2019.
- Cabreza, Vincent (October 20, 2012). "Country's first mine town should have been richest in PH". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on August 18, 2016. Retrieved November 3, 2014.
- "Municipality of Itogon, Benguet". Department of Interior and Local Government - Cordillera Administrative Region. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- Pungayan, Morr Tadeo. "History of Itogon: Chronology of Itogon History". Official Website of the Municipality of Itogon. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- "Binga Dam". National Power Corporation. NAPOCOR. Archived from the original on March 7, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
Binga Dam forms an impoundment on the Agno River, approximately 19 km downstream of the Ambuklao dam, in Benguet province, northern Luzon.
- Gimenez, Lulu A. (1996). On the Basis of Custom and History: Land Resource Ownership and Access Rights Among the Igorot of the Itogon Mining Area. Mining Communities Development Center. p. 49. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- "Facts & Figures: Benguet Province". Philippine Statistics Authority - National Statistical Coordination Board - Cordillera Administrative Region. Archived from the original on May 17, 2007. Retrieved October 9, 2014.
- "History: Benguet Province". Province of Benguet (official website). Archived from the original on October 19, 2014. Retrieved October 9, 2014.
- "Weighing the cost of gold rush in Benguet". ABS-CBN News. ABS-CBN Corporation. October 16, 2008. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- "R.A. No. 616: An Act to Convert the Municipal District of Itogon, Sub-province of Benguet, Mountain Province, into a Regular Municipality to be Known as the Municipality of Itogon". LawPH.com. Archived from the original on November 4, 2014. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- "Republic Act No. 4695: An Act Creating the Provinces of Benguet, Mountain Province, Ifugao and Kalinga-Apayao". Chan Robles Virtual Law Library. June 18, 1966. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 12, 2016.
- "Municipal: Itogon". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- "Itogon: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved March 21, 2020.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Benguet". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- "Brief Profile of the Municipality of Itogon". Official Website of the Municipality of Itogon. Archived from the original on March 6, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- "Tourism". Municipality of Itogon, Official Website. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- "Local Attractions: Itogon". Province of Benguet website. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- "Masterlist of Public Elementary Schools for the School year 2012- 2013". Department of Education (Philippines), July 15, 2013. Archived from the original (XLSX) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 28, 2014.
- "Masterlist of Secondary Schools (School Year 2013- 2014)". Department of Education (Philippines), 4 July 2013. Archived from the original (XLSX) on July 1, 2014. Retrieved November 20, 2014.
- "Masterlist of Public Schools SY 2013-2014". Department of Education (Philippines), 22 October 2014. Archived from the original (XLSX) on April 21, 2016. Retrieved December 28, 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Itogon, Benguet. |