Headland
A headland is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.[1] Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff.
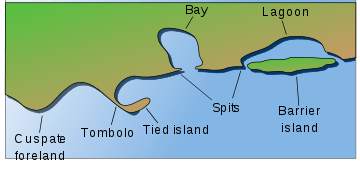
Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of the headlands, coastlines eventually straighten out then start the same process all over again.
List of notable headlands
Africa

- Cap-Vert, Senegal
- Cape Agulhas, South Africa, Africa's southernmost point
- Cape Blanc, Mauritania
- Cape Bojador, Western Sahara
- Cape Correntes, Mozambique
- Cape Delgado, Mozambique
- Cape Juby, Morocco
- Cape Malabata, Morocco
- Cape of Good Hope, South Africa
- Ras ben Sakka, Tunisia, Africa's northernmost point
Asia
- Beirut, Lebanon
- Cabo de Rama, Goa, India
- Cape Dezhnev, Russia
- Cape Engano, Philippines
- Indira Point, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India
- Kanyakumari or Cape Comorin, Tamil Nadu, India
Europe


- Beachy Head, England
- Cabo da Roca, Portugal, the western tip of mainland Europe
- Cabo de São Vicente/Sagres, Portugal, the southwestern tip of mainland Europe
- Cap Gris Nez, France
- Cape Arkona, Germany
- Cape Emine, Bulgaria
- Cape Enniberg, Faroe Islands
- Cape Finisterre, Galicia, Spain
- Cape Greco, Cyprus
- Cape Kaliakra, Bulgaria
- Cape Tainaron, Greece, the southern tip of mainland Europe
- Cape Wrath, Scotland
- Gibraltar
- Great Orme, Wales
- Land's End, Cornwall, England
- Mull of Kintyre, Scotland
- North Cape, Norway, the northern tip of mainland Europe
- Pointe du Raz, France
- St Bees Head, UK, the most westerly point of northern England
North America



Canada
- Cape Chidley, Newfoundland and Labrador/Nunavut
- Cape Columbia, Nunavut, Canada's northernmost point
- Cape Freels, Newfoundland and Labrador
- Cape Norman, Newfoundland and Labrador
- Cape Spear, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada's easternmost point
- Cape Tormentine, New Brunswick
Greenland
- Cape Farewell, Greenland's southernmost point
Mexico
- Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur, Mexico
United States
- Cape Ann, Massachusetts
- Cape Canaveral, Florida
- Cape Charles, Virginia
- Cape Cod, Massachusetts
- Cape Fear, North Carolina
- Cape Flattery, Washington
- Cape Hatteras, North Carolina
- Cape Henlopen, Delaware
- Cape Henry, Virginia
- Cape May, New Jersey
- Cape Mendocino, California
- Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska
- Cascade Head, Oregon
- Diamond Head, Hawaii
- Heceta Head, Oregon
- Hilton Head, South Carolina
- Koko Head, Hawaii
- Marin Headlands, California
- Mount Mitchill, New Jersey
- North Shore, Lake Superior, Minnesota
- Point Reyes, California

Oceania
Australia
- Cape Leeuwin, Western Australia
- Cape York, Queensland
- South East Cape, Tasmania
- South West Cape, Tasmania
- Sydney Heads, New South Wales
New Zealand

- Cape Egmont
- Cape Foulwind
- Cape Reinga
- East Cape
- North Cape
- Young Nick's Head
South America
- Cape Froward, Chile
- Cape Horn, Chile, South America's southernmost point
- Cape Virgenes, Argentina
See also
References
- Whittow, John (1984). Dictionary of Physical Geography. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. ISBN 0-14-051094-X.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Headlands. |