Guanosine monophosphate
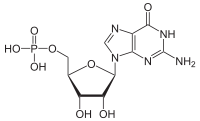
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5'-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid (conjugate base guanylate), is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine; hence it is a ribonucleoside monophosphate. Guanosine monophosphate is commercially produced by microbial fermentation.[1] It is known as E number reference E626.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-Amino-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydro-2-furanyl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | GMP |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.453 |
| E number | E626 (flavour enhancer) |
| MeSH | Guanosine+monophosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N5O8P | |
| Molar mass | 363.223 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.7, 2.4, 6.1, 9.4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Guanosine monophosphate in the form of its salts, such as disodium guanylate (E627), dipotassium guanylate (E628) and calcium guanylate (E629), are food additives used as flavor enhancers to provide the umami taste. It is often used in synergy with disodium inosinate; the combination is known as disodium 5'-ribonucleotides. Disodium guanylate is often found in instant noodles, potato chips and snacks, savoury rice, tinned vegetables, cured meats, and packet soup.
As it is a fairly expensive additive, it is usually not used independently of glutamic acid or monosodium glutamate (MSG), which also contribute umami. If inosinate and guanylate salts are present in a list of ingredients but MSG does not appear to be, the glutamic acid is likely provided as part of another ingredient, such as a processed soy protein complex (hydrolyzed soy protein), autolyzed yeast, or soy sauce.
As inhibitor of guanosine monophosphate synthesis in experimental models, the glutamine analogue DON can be used.[2]
As an acyl substituent, it takes the form of the prefix guanylyl-.
De novo synthesis
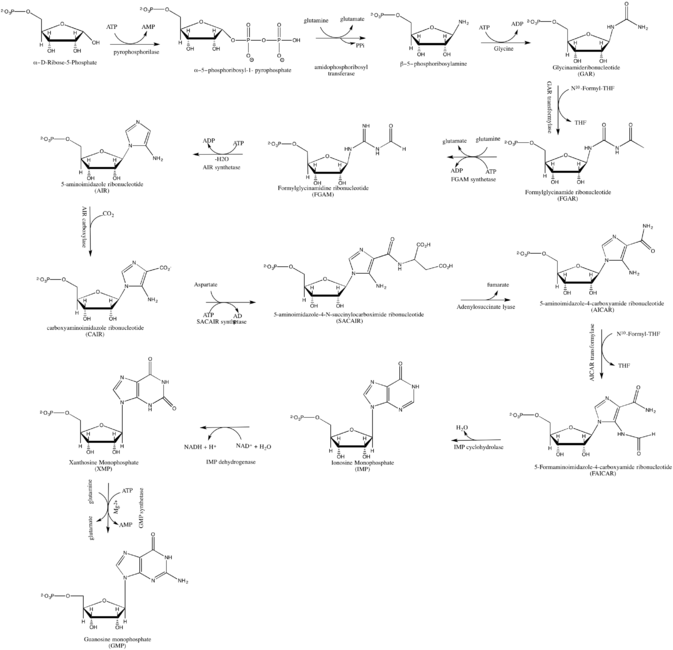
GMP synthesis starts with D-ribose 5'-phosphate, a product of the pentose phosphate pathway. The synthesis proceeds by the gradual formation of the purine ring on carbon-1 of ribose, with CO2, glutamine, glycine, aspartate and one-carbon derivatives of tetrahydrofolate donating various elements towards the building of the ring[3]
cGMP
GMP can also exist as a cyclic structure known as cyclic GMP. Within certain cells the enzyme guanylyl cyclase makes cGMP from GTP.
cGMP plays an important role in mediating hormonal signaling.[3]
See also
References
- "The Vegetarian Resource Group Blog". www.vrg.org. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- Ahluwalia GS et al. Metabolism and action of amino acid analog anti-cancer agents ”, in Pharmac. Ther. (1990) 46: 243-271
- Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G. (2012). Biochemistry. USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc. pp. 1107–1109. ISBN 978-0-470-57095-1.