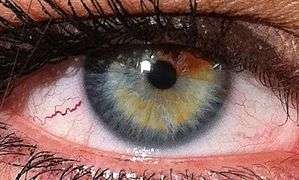
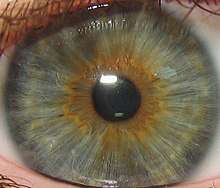
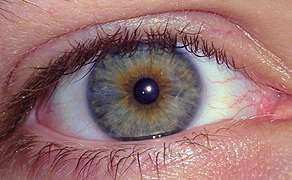
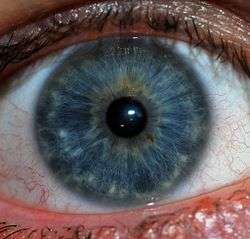
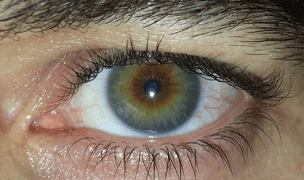
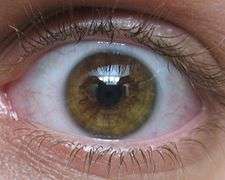
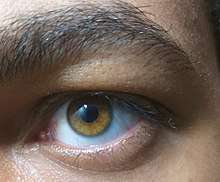
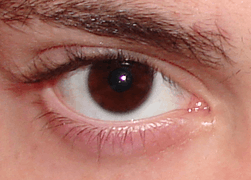
Eye color
Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris[1][2] and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.[3]:9
..jpg)
In humans, the pigmentation of the iris varies from light brown to black, depending on the concentration of melanin in the iris pigment epithelium (located on the back of the iris), the melanin content within the iris stroma (located at the front of the iris), and the cellular density of the stroma.[4] The appearance of blue and green, as well as hazel eyes, results from the Tyndall scattering of light in the stroma, a phenomenon similar to that which accounts for the blueness of the sky called Rayleigh scattering.[5] Neither blue nor green pigments are ever present in the human iris or ocular fluid.[3][6] Eye color is thus an instance of structural color and varies depending on the lighting conditions, especially for lighter-colored eyes.
The brightly colored eyes of many bird species result from the presence of other pigments, such as pteridines, purines, and carotenoids.[7] Humans and other animals have many phenotypic variations in eye color.[8]
The genetics and inheritance of eye color in humans is complicated. So far, as many as 15 genes have been associated with eye color inheritance. Some of the eye-color genes include OCA2 and HERC2.[9] The earlier belief that blue eye color is a simple recessive trait has been shown to be incorrect. The genetics of eye color are so complex that almost any parent-child combination of eye colors can occur.[10][11] However, OCA2 gene polymorphism, close to proximal 5′ regulatory region, explains most human eye-color variation.[12]
Genetic determination
Eye color is an inherited trait influenced by more than one gene.[13][14] These genes are sought using associations to small changes in the genes themselves and in neighboring genes. These changes are known as single-nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs. The actual number of genes that contribute to eye color is currently unknown, but there are a few likely candidates. A study in Rotterdam (2009) found that it was possible to predict eye color with more than 90% accuracy for brown and blue using just six SNPs.[15] There is evidence that as many as 16 different genes could be responsible for eye color in humans; however, the main two genes associated with eye color variation are OCA2 and HERC2, and both are localized in Chromosome 15.[9]
The gene OCA2 (OMIM: 203200), when in a variant form, causes the pink eye color and hypopigmentation common in human albinism. (The name of the gene is derived from the disorder it causes, oculocutaneous albinism type II.) Different SNPs within OCA2 are strongly associated with blue and green eyes as well as variations in freckling, mole counts, hair and skin tone. The polymorphisms may be in an OCA2 regulatory sequence, where they may influence the expression of the gene product, which in turn affects pigmentation.[12] A specific mutation within the HERC2 gene, a gene that regulates OCA2 expression, is partly responsible for blue eyes.[16] Other genes implicated in eye color variation are SLC24A4[17] and TYR.[17] A 2010 study on eye color variation into hue and saturation values using high-resolution digital full-eye photographs found three new loci for a total of ten genes, and now about 50% of eye colour variation can be explained.[18]
| Gene name | Effect on eye color |
|---|---|
| OCA2 | Associated with melanin producing cells. Central importance to eye color. |
| HERC2 | Affects function of OCA2, with a specific mutation strongly linked to blue eyes. |
| SLC24A4 | Associated with differences between blue and green eyes.[17] |
| TYR | Associated with differences between blue and green eyes.[17] |
Blue eyes with a brown spot, green eyes, and gray eyes are caused by an entirely different part of the genome.
Ancient DNA and eye color in Europe
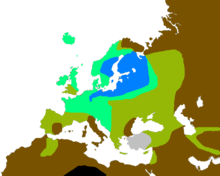
People of European descent show the greatest variety in eye color of any population worldwide. Recent advances in ancient DNA technology have revealed some of the history of eye color in Europe. All European Mesolithic hunter-gatherer remains so far investigated have shown genetic markers for light-colored eyes, in the case of western and central European hunter-gatherers combined with dark skin color. The later additions to the European gene pool, the Early Neolithic farmers from Anatolia and the Yamnaya Copper Age/Bronze Age pastoralists (possibly the Proto-Indo-European population) from the area north of the Black Sea appear to have had much higher incidences of dark eye color alleles, and alleles giving rise to lighter skin, than the original European population.[19][20]
Classification of color
Iris color can provide a large amount of information about a person, and a classification of colors may be useful in documenting pathological changes or determining how a person may respond to ocular pharmaceuticals.[21] Classification systems have ranged from a basic light or dark description to detailed gradings employing photographic standards for comparison.[21] Others have attempted to set objective standards of color comparison.[22]
Normal eye colors range from the darkest shades of brown to the lightest tints of blue.[13] To meet the need for standardized classification, at once simple yet detailed enough for research purposes, Seddon et al. developed a graded system based on the predominant iris color and the amount of brown or yellow pigment present.[23] There are three pigment colors that determine, depending on their proportion, the outward appearance of the iris, along with structural color. Green irises, for example, have blue and some yellow. Brown irises contain mostly brown. Some eyes have a dark ring around the iris, called a limbal ring.
Eye color in non-human animals is regulated differently. For example, instead of blue as in humans, autosomal recessive eye color in the skink species Corucia zebrata is black, and the autosomal dominant color is yellow-green.[24]
As the perception of color depends on viewing conditions (e.g., the amount and kind of illumination, as well as the hue of the surrounding environment), so does the perception of eye color.[25]
Changes in eye color
Most newborn babies who have European ancestry have light-colored eyes. As the child develops, melanocytes (cells found within the iris of human eyes, as well as skin and hair follicles) slowly begin to produce melanin. Because melanocyte cells continually produce pigment, in theory eye color can be changed. Adult eye color is usually established between 3 and 6 months of age, though this can be later.[27] Observing the iris of an infant from the side using only transmitted light with no reflection from the back of the iris, it is possible to detect the presence or absence of low levels of melanin. An iris that appears blue under this method of observation is more likely to remain blue as the infant ages. An iris that appears golden contains some melanin even at this early age and is likely to turn from blue to green or brown as the infant ages.
Changes (lightening or darkening) of eye colors during early childhood, puberty, pregnancy, and sometimes after serious trauma (like heterochromia) do represent cause for a plausible argument stating that some eyes can or do change, based on chemical reactions and hormonal changes within the body.
Studies on Caucasian twins, both fraternal and identical, have shown that eye color over time can be subject to change, and major demelanization of the iris may also be genetically determined. Most eye-color changes have been observed or reported in the Caucasian population with hazel and amber eyes.[28]
Eye color chart (Martin scale)
Carleton Coon created a chart by the original Martin scale. The numbering is reversed on the scale below in the (later) Martin–Schultz scale, which is (still) used in physical anthropology.
Light and light-mixed eyes (16–12 in Martin scale)
Pure light (16–15 in Martin scale)
- 16: pure light blue
- 15: gray
Light-mixed (14–12 in Martin scale)
- 14: Very light-mixed (blue with gray or green or green with gray)
- 13-12: Light-mixed (light or very light-mixed with small admixture of brown)
Mixed eyes (11–7 in Martin scale) Mixture of light eyes (blue, gray or green) with brown when light and brown appearance is at the same level.
Dark and dark-mixed eyes (6–1 in Martin scale)
- Dark-mixed: 6–5 in Martin scale. Brown with small admixture of light
- Dark: 4–1 in Martin scale. Brown (light brown and dark brown) and very dark brown (almost black)
Amber
Amber eyes are of a solid color and have a strong yellowish/golden and russet/coppery tint. This may be due to the deposition of the yellow pigment called lipochrome in the iris (which is also found in green eyes).[29][30] Amber eyes should not be confused with hazel eyes; although hazel eyes may contain specks of amber or gold, they usually tend to comprise many other colors, including green, brown and orange. Also, hazel eyes may appear to shift in color and consist of flecks and ripples, while amber eyes are of a solid gold hue. Even though amber is considered to be like gold, some people have russet or copper colored amber eyes that many people mistake for hazel, though hazel tends to be duller and contains green with red/gold flecks, as mentioned above. Amber eyes may also contain amounts of very light gold-ish gray.
The eyes of some pigeons contain yellow fluorescing pigments known as pteridines.[31] The bright yellow eyes of the great horned owl are thought to be due to the presence of the pteridine pigment xanthopterin within certain chromatophores (called xanthophores) located in the iris stroma.[32] In humans, yellowish specks or patches are thought to be due to the pigment lipofuscin, also known as lipochrome.[33] Many animals such as canines, domestic cats, owls, eagles, pigeons and fish have amber eyes as a common color, whereas in humans this color occurs less frequently.
Blue
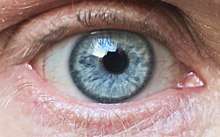
There is no blue pigmentation either in the iris or in the ocular fluid. Dissection reveals that the iris pigment epithelium is brownish black due to the presence of melanin.[34] Unlike brown eyes, blue eyes have low concentrations of melanin in the stroma of the iris, which lies in front of the dark epithelium. Longer wavelengths of light tend to be absorbed by the dark underlying epithelium, while shorter wavelengths are reflected and undergo Rayleigh scattering in the turbid medium of the stroma.[4] This is the same frequency-dependence of scattering that accounts for the blue appearance of the sky.[3]:9[6] The result is a "Tyndall blue" structural color that varies with external lighting conditions.
In humans, the inheritance pattern followed by blue eyes is considered similar to that of a recessive trait (in general, eye color inheritance is considered a polygenic trait, meaning that it is controlled by the interactions of several genes, not just one).[14] In 2008, new research tracked down a single genetic mutation that leads to blue eyes. "Originally, we all had brown eyes," said Eiberg.[35] Eiberg and colleagues suggested in a study published in Human Genetics that a mutation in the 86th intron of the HERC2 gene, which is hypothesized to interact with the OCA2 gene promoter, reduced expression of OCA2 with subsequent reduction in melanin production.[36] The authors suggest that the mutation may have arisen in the northwestern part of the Black Sea region, and add that it is "difficult to calculate the age of the mutation."[35][36][37]
Blue eyes are common in northern and eastern Europe, particularly around the Baltic Sea. Blue eyes are also found in southern Europe, Central Asia, South Asia, North Africa and West Asia.[38][39]
 A Birman kitten with distinctive sapphire blue eyes
A Birman kitten with distinctive sapphire blue eyes

The same DNA sequence in the region of the OCA2 gene among blue-eyed people suggests they may have a single common ancestor.[42][43][44]
As of 2016, the earliest light-pigmented and blue-eyed remains of Homo sapiens were found in 7,700 years old Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from Motala, Sweden.[45]
A 2002 study found that the prevalence of blue eye color among the white population in the United States to be 33.8% for those born from 1936 through 1951, compared with 57.4% for those born from 1899 through 1905.[14] As of 2006, one out of every six people, or 16.6% of the total population, has blue eyes, including 22.3% of whites. Blue eyes are continuing to become less common among American children.[46]

Blue eyes are rare in mammals; one example is the recently discovered marsupial, the blue-eyed spotted cuscus (Spilocuscus wilsoni). The trait is hitherto known only from a single primate other than humans – Sclater's lemur (Eulemur flavifrons) of Madagascar. While some cats and dogs have blue eyes, this is usually due to another mutation that is associated with deafness. But in cats alone, there are four identified gene mutations that produce blue eyes, some of which are associated with congenital neurological disorders. The mutation found in the Siamese cats is associated with strabismus (crossed eyes). The mutation found in blue-eyed solid white cats (where the coat color is caused by the gene for "epistatic white") is linked with deafness. However, there are phenotypically identical, but genotypically different, blue-eyed white cats (where the coat color is caused by the gene for white spotting) where the coat color is not strongly associated with deafness. In the blue-eyed Ojos Azules breed, there may be other neurological defects. Blue-eyed non-white cats of unknown genotype also occur at random in the cat population.
Brown

In humans, brown eyes result from a relatively high concentration of melanin in the stroma of the iris, which causes light of both shorter and longer wavelengths to be absorbed.[47]
Dark brown eyes are dominant in humans[48] and in many parts of the world, it is nearly the only iris color present.[49] Brown eyes are common in Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, West Asia, Oceania, Africa and the Americas.[17] The majority of people in the world overall have brown eyes to dark brown eyes.
Light or medium-pigmented brown eyes can also be commonly found in South Europe, among the Americas, and parts of Central Asia (Middle East and South Asia).
Gray
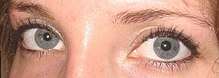
Like blue eyes, gray eyes have a dark epithelium at the back of the iris and a relatively clear stroma at the front. One possible explanation for the difference in the appearance of gray and blue eyes is that gray eyes have larger deposits of collagen in the stroma, so that the light that is reflected from the epithelium undergoes Mie scattering (which is not strongly frequency-dependent) rather than Rayleigh scattering (in which shorter wavelengths of light are scattered more). This would be analogous to the change in the color of the sky, from the blue given by the Rayleigh scattering of sunlight by small gas molecules when the sky is clear, to the gray caused by Mie scattering of large water droplets when the sky is cloudy.[50] Alternatively, it has been suggested that gray and blue eyes might differ in the concentration of melanin at the front of the stroma.[50]
Gray eyes are most common in Northern and Eastern Europe.[51] Gray eyes can also be found among the Algerian Shawia people[52] of the Aurès Mountains in Northwest Africa, in the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia. The Greek goddess Athene appears with grey eyes (γλαυκῶπις).[53] Under magnification, gray eyes exhibit small amounts of yellow and brown color in the iris.
Green
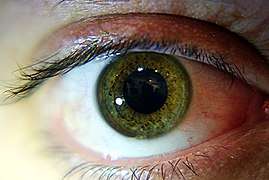


As with blue eyes, the color of green eyes does not result simply from the pigmentation of the iris. The green color is caused by the combination of: 1) an amber or light brown pigmentation in the stroma of the iris (which has a low or moderate concentration of melanin) with: 2) a blue shade created by the Rayleigh scattering of reflected light.[47] Green eyes contain the yellowish pigment lipochrome.[54]
Green eyes probably result from the interaction of multiple variants within the OCA2 and other genes. They were present in south Siberia during the Bronze Age.[55]
_Caracas_Venezuela_Vicente_Quintero.jpg)
They are most common in Northern, Western and Central Europe.[56][57] In Ireland and Scotland, 86% of people have either blue or green eyes.[58] In Iceland, 89% of women and 87% of men have either blue or green eye color.[59] A study of Icelandic and Dutch adults found green eyes to be much more prevalent in women than in men.[60] Among European Americans, green eyes are most common among those of recent Celtic and Germanic ancestry, about 16%. 37.2% of Italians from Verona and 56% of Slovenes have blue/green eyes.[61][62]
Green eyes are common in tabby cats as well as the Chinchilla Longhair and its short-haired equivalents; they are notable for their black-rimmed sea-green eyes.
Hazel
Hazel eyes are due to a combination of Rayleigh scattering and a moderate amount of melanin in the iris' anterior border layer.[4][33] Hazel eyes often appear to shift in color from a brown to a green. Although hazel mostly consists of brown and green, the dominant color in the eye can either be brown/gold or green. This is how many people mistake hazel eyes to be amber and vice versa.[63][64][65][66][67][68][69] This can sometimes produce a multicolored iris, i.e., an eye that is light brown/amber near the pupil and charcoal or dark green on the outer part of the iris (or vice versa) when observed in sunlight.
Definitions of the eye color hazel vary: it is sometimes considered to be synonymous with light brown or gold, as in the color of a hazelnut shell.[63][65][68][70]
Red and violet
The eyes of people with severe forms of albinism may appear red under certain lighting conditions owing to the extremely low quantities of melanin,[71] allowing the blood vessels to show through. In addition, flash photography can sometimes cause a "red-eye effect", in which the very bright light from a flash reflects off the retina, which is abundantly vascular, causing the pupil to appear red in the photograph.[72] Although the deep blue eyes of some people such as Elizabeth Taylor can appear violet at certain times, "true" violet-colored eyes occur only due to albinism.[73]
Spectrum of eye color
Medical implications
Those with lighter iris color have been found to have a higher prevalence of age-related macular degeneration (ARMD) than those with darker iris color;[67] lighter eye color is also associated with an increased risk of ARMD progression.[74] A gray iris may indicate the presence of a uveitis, and an increased risk of uveal melanoma has been found in those with blue, green or gray eyes.[59][75] However, a study in 2000 suggests that people with dark brown eyes are at increased risk of developing cataracts and therefore should protect their eyes from direct exposure to sunlight.[76]
Wilson's disease
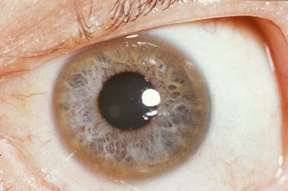
Wilson's disease involves a mutation of the gene coding for the enzyme ATPase 7B, which prevents copper within the liver from entering the Golgi apparatus in cells. Instead, the copper accumulates in the liver and in other tissues, including the iris of the eye. This results in the formation of Kayser–Fleischer rings, which are dark rings that encircle the periphery of the iris.[77]
Coloration of the sclera
Eye color outside of the iris may also be symptomatic of disease. Yellowing of the sclera (the "whites of the eyes") is associated with jaundice,[78] and may be symptomatic of liver diseases such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.[79] A blue coloration of the sclera may also be symptomatic of disease.[78] In general, any sudden changes in the color of the sclera should be addressed by a medical professional.
Aniridia
Aniridia is a congenital condition characterized by an extremely underdeveloped iris, which appears absent on superficial examination.[80]
Ocular albinism and eye color
Normally, there is a thick layer of melanin on the back of the iris. Even people with the lightest blue eyes, with no melanin on the front of the iris at all, have dark brown coloration on the back of it, to prevent light from scattering around inside the eye. In those with milder forms of albinism, the color of the iris is typically blue but can vary from blue to brown. In severe forms of albinism, there is no pigment on the back of the iris, and light from inside the eye can pass through the iris to the front. In these cases, the only color seen is the red from the hemoglobin of the blood in the capillaries of the iris. Such albinos have pink eyes, as do albino rabbits, mice, or any other animal with a total lack of melanin. Transillumination defects can almost always be observed during an eye examination due to lack of iridial pigmentation.[81] The ocular albino also lacks normal amounts of melanin in the retina as well, which allows more light than normal to reflect off the retina and out of the eye. Because of this, the pupillary reflex is much more pronounced in albino individuals, and this can emphasize the red eye effect in photographs.
Heterochromia

Heterochromia (heterochromia iridum or heterochromia iridis) is an eye condition in which one iris is a different color from the other (complete heterochromia), or where a part of one iris is a different color from the remainder (partial heterochromia or sectoral heterochromia). It is a result of the relative excess or lack of pigment within an iris or part of an iris, which may be inherited or acquired by disease or injury.[82] This uncommon condition usually results due to uneven melanin content. A number of causes are responsible, including genetic, such as chimerism, Horner's syndrome and Waardenburg syndrome.
A chimera can have two different colored eyes just like any two siblings can—because each cell has different eye color genes. A mosaic can have two different colored eyes if the DNA difference happens to be in an eye-color gene.
There are many other possible reasons for having two different-colored eyes. For example, the film actor Lee Van Cleef was born with one blue eye and one green eye, a trait that reportedly was common in his family, suggesting that it was a genetic trait. This anomaly, which film producers thought would be disturbing to film audiences, was "corrected" by having Van Cleef wear brown contact lenses.[83] David Bowie, on the other hand, had the appearance of different eye colors due to an injury that caused one pupil to be permanently dilated.
Another hypothesis about heterochromia is that it can result from a viral infection in utero affecting the development of one eye, possibly through some sort of genetic mutation. Occasionally, heterochromia can be a sign of a serious medical condition.
A common cause in females with heterochromia is X-inactivation, which can result in a number of heterochromatic traits, such as calico cats. Trauma and certain medications, such as some prostaglandin analogues, can also cause increased pigmentation in one eye.[84] On occasion, a difference in eye color is caused by blood staining the iris after injury.
Mate selection and traits that have been linked to iris color
Selection for rare iris colors
A study compared the frequency of eye color in commercial advertising models in Brazil and the UK; these countries were chosen because they have inverted frequencies of eye-coloration, with Brazil having an excess of brown and the UK an excess of light-colored eyes. Models are chosen for their attractiveness, and it was found that, in Brazil, models with light eyes are in a significant excess compared to the levels found in the general population, while, in the UK, models with brown or intermediate eyes were in significant excess over their frequency in the general population. This suggests that eye color rarity plays a role in sexual attraction, people with rare eye colors being perceived as being more attractive. Some research indicates that eye color variation is greater in women than in men, which may reflect sexual selection of mates with rare eye colors.[85]
Selection though imprinting of parental eye color
In contrast to the phenomenon of selection for rarity, scholarship has implied the existence another form of eye color involvement in mate selection. A study found a significant incidence of the partners of heterosexual people possessing similar eye and hair color to that of their opposite-sex parent. This is suggestive of a form of parental imprinting on eventual mate selection.[86]
See also
- Hair color
- Iridology
- Human skin color
- Xanthophore
- List of Mendelian traits in humans
References
- Wielgus AR, Sarna T (2005). "Melanin in human irides of different color and age of donors". Pigment Cell Res. 18 (6): 454–64. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0749.2005.00268.x. PMID 16280011.
- Prota G, Hu DN, Vincensi MR, McCormick SA, Napolitano A (1998). "Characterization of melanins in human irides and cultured uveal melanocytes from eyes of different colors". Exp. Eye Res. 67 (3): 293–9. doi:10.1006/exer.1998.0518. PMID 9778410.
- Fox, Denis Llewellyn (1979). Biochromy: Natural Coloration of Living Things. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-03699-4.
- Huiqiong Wang; Lin, S.; Xiaopei Liu; Sing Bing Kang (2005). "Separating reflections in human iris images for illumination estimation". Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV'05) Volume 1. pp. 1691–1698 Vol. 2. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.87.418. doi:10.1109/ICCV.2005.215. ISBN 978-0-7695-2334-7.
- Sturm R.A. & Larsson M., Genetics of human iris colour and patterns, Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 22:544-562, 2009.
- Mason, Clyde W. (1924). "Blue Eyes". Journal of Physical Chemistry. 28 (5): 498–501. doi:10.1021/j150239a007.
- Oliphant LW (1987). "Pteridines and purines as major pigments of the avian iris". Pigment Cell Res. 1 (2): 129–31. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0749.1987.tb00401.x. PMID 3507666.
- Morris, PJ. "Phenotypes and Genotypes for human eye colors." Athro Limited website. Retrieved 10 May 2006.
- White, Désirée; Rabago-Smith, Montserrat (14 October 2010). "Genotype–phenotype associations and human eye color". Journal of Human Genetics. 56 (1): 5–7. doi:10.1038/jhg.2010.126. PMID 20944644.
- No Single Gene For Eye Color, Researchers Prove. Sciencedaily.com (22 February 2007). Retrieved on 2011-12-23.
- "Eye color definition – Medical Dictionary definitions of popular medical terms easily defined on MedTerms". Medterms.com. 29 October 2003. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- Duffy, David L.; Montgomery, Grant W.; Chen, Wei; Zhao, Zhen Zhen; Le, Lien; James, Michael R.; Hayward, Nicholas K.; Martin, Nicholas G.; Sturm, Richard A. (2007). "A three-single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotype in intron 1 of OCA2 explains most human eye-color variation". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80 (2): 241–52. doi:10.1086/510885. PMC 1785344. PMID 17236130.
- Sturm RA, Frudakis TN (2004). "Eye colour: portals into pigmentation genes and ancestry" (PDF). Trends Genet. 20 (8): 327–32. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2004.06.010. PMID 15262401. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 September 2006.
- Grant MD, Lauderdale DS (2002). "Cohort effects in a genetically determined trait: eye colour among US whites". Ann. Hum. Biol. 29 (6): 657–66. doi:10.1080/03014460210157394. PMID 12573082.
- "DNA test for eye colour could help fight crime", New Scientist 14 March 2009. Liu, Fan; Van Duijn, Kate; Vingerling, Johannes R.; Hofman, Albert; Uitterlinden, André G.; Janssens, A. Cecile J.W.; Kayser, Manfred (2009). "Eye color and the prediction of complex phenotypes from genotypes". Current Biology. 19 (5): R192–R193. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.01.027. PMID 19278628.
- Kayser, Manfred; Liu, Fan; Janssens, A. Cecile J.W.; Rivadeneira, Fernando; Lao, Oscar; Van Duijn, Kate; Vermeulen, Mark; Arp, Pascal; et al. (2008). "Three genome-wide association studies and a linkage analysis identify HERC2 as a human iris color gene". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82 (2): 411–23. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.10.003. PMC 2427174. PMID 18252221.
- Sulem, Patrick; Gudbjartsson, Daniel F; Stacey, Simon N; Helgason, Agnar; Rafnar, Thorunn; Magnusson, Kristinn P; Manolescu, Andrei; Karason, Ari; et al. (2007). "Genetic determinants of hair, eye and skin pigmentation in Europeans". Nat. Genet. 39 (12): 1443–52. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.13. PMID 17952075.
- Liu, Fan; Wollstein, Andreas; Hysi, Pirro G.; Ankra-Badu, Georgina A.; Spector, Timothy D.; Park, Daniel; Zhu, Gu; Larsson, Mats; Duffy, David L.; Montgomery, Grant W.; MacKey, David A.; Walsh, Susan; Lao, Oscar; Hofman, Albert; Rivadeneira, Fernando; Vingerling, Johannes R.; Uitterlinden, André G.; Martin, Nicholas G.; Hammond, Christopher J.; Kayser, Manfred (2010). "Digital Quantification of Human Eye Color Highlights Genetic Association of Three New Loci". PLOS Genetics. 6 (5): e1000934. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000934. PMC 2865509. PMID 20463881.
- Haak, W.; Lazaridis, I.; Patterson, N.; Rohland, N.; Mallick, S.; Llamas, B.; Brandt, G.; Nordenfelt, S.; Harney, E.; Stewardson, K.; Fu, Q.; Mittnik, A.; Bánffy, E.; Economou, C.; Francken, M.; Friederich, S.; Pena, R. G.; Hallgren, F.; Khartanovich, V.; Khokhlov, A.; Kunst, M.; Kuznetsov, P.; Meller, H.; Mochalov, O.; Moiseyev, V.; Nicklisch, N.; Pichler, S. L.; Risch, R.; Rojo Guerra, M. A.; et al. (2015). "Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe". Nature. 522 (7555): 207–211. arXiv:1502.02783. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..207H. bioRxiv 10.1101/013433. doi:10.1038/nature14317 (inactive 22 May 2020). PMC 5048219. PMID 25731166.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mathieson, Iain (2015). "Eight thousand years of natural selection in Europe". bioRxiv 10.1101/016477.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- German EJ, Hurst MA, Wood D, Gilchrist J (1998). "A novel system for the objective classification of iris colour and its correlation with response to 1% tropicamide". Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 18 (2): 103–10. doi:10.1016/S0275-5408(97)00070-7. PMID 9692029.
- Fan S, Dyer CR, Hubbard L. Quantification and Correction of Iris Color." Technical report 1495, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Dec 2003.
- Seddon, JM; CR Sahagian; RJ Glynn; RD Sperduto; ES Gragoudas (1 August 1990). "Evaluation of an iris color classification system". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 31 (8): 1592–8. PMID 2201662. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- Jones, S.L.; Schnirel, B.L. (2006). "Subspecies comparison of the Genus: Corucia". Polyphemos. 4 (1): 1–25. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009.
- Color Perception Archived 20 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Edromanguitars.com. Retrieved on 23 December 2011.
- "Frost: Why Do Europeans Have So Many Hair and Eye Colors?". cogweb.ucla.edu. Retrieved 27 February 2018.
- Burroughs, A. and Leifer, G. (2001) Maternity Nursing: An Introductory Text, W.B. Saunders Medical, p. 172
- Bito, LZ; Matheny, A; Cruickshanks, KJ; Nondahl, DM; Carino, OB (1997). "Eye Color Changes Past Early Childhood". Archives of Ophthalmology. 115 (5): 659–63. doi:10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150661017. PMID 9152135.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute: Ask A Scientist Archived 1 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Hhmi.org. Retrieved on 23 December 2011.
- Larry Bickford Eye Color Archived 23 October 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Eyecarecontacts.com. Retrieved on 23 December 2011.
- Oliphant LW (1987). "Observations on the pigmentation of the pigeon iris". Pigment Cell Res. 1 (3): 202–8. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0749.1987.tb00414.x. PMID 3508278.
- Oliphant LW (1981). "Crystalline pteridines in the stromal pigment cells of the iris of the great horned owl". Cell Tissue Res. 217 (2): 387–95. doi:10.1007/BF00233588. PMID 7237534.
- Lefohn A, Budge B, Shirley P, Caruso R, Reinhard E (2003). "An Ocularist's Approach to Human Iris Synthesis". IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 23 (6): 70–5. doi:10.1109/MCG.2003.1242384.
- Menon IA, Basu PK, Persad S, Avaria M, Felix CC, Kalyanaraman B (1987). "Is there any difference in the photobiological properties of melanins isolated from human blue and brown eyes?". Br J Ophthalmol. 71 (7): 549–52. doi:10.1136/bjo.71.7.549. PMC 1041224. PMID 2820463.
- Bryner, Jeanna (31 January 2008). "Genetic mutation makes those brown eyes blue". NBC News. Retrieved 19 October 2009.
- Eiberg, Hans; Troelsen, Jesper; Nielsen, Mette; Mikkelsen, Annemette; Mengel-From, Jonas; Kjaer, Klaus W.; Hansen, Lars (2008). "Blue eye color in humans may be caused by a perfectly associated founder mutation in a regulatory element located within the HERC2 gene inhibiting OCA2 expression". Hum. Genet. 123 (2): 177–87. doi:10.1007/s00439-007-0460-x. PMID 18172690.
- Highfield, Roger (30 January 2008). "Blue eyes result of ancient genetic 'mutation'". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- Cavalli-Sforza, Luigi Luca; Cavalli-Sforza, Luca; Menozzi, Paolo; Piazza, Alberto (1994). The History and Geography of Human Genes. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-08750-4.
- "Distribution of Bodily Characters. Pigmentation, the Pilous System, and Morphology of the Soft Parts". Archived from the original on 26 July 2011.
- Blue eyed Koala. Adelaidenow.com.au (11 January 2008). Retrieved on 2011-12-23.
- "Blue eyes are peeping across Britain". The Times. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- "A Single DNA Difference in the HERC2 Gene Explains Blue Eyes | Understanding Genetics". genetics.thetech.org. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- "How one ancestor helped turn our brown eyes blue". The Independent. 31 January 2008. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- "All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common". IFLScience. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- "How Europeans evolved white skin". Science | AAAS. 2 April 2015.
- Belkin, Douglas (17 October 2006). "Don't it make my blue eyes brown Americans are seeing a dramatic color change". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on 22 October 2014.
- Fox, Denis Llewellyn (1979). Biochromy: Natural Coloration of Living Things. University of California Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-520-03699-4.
- Eiberg H, Mohr J (1996). "Assignment of genes coding for brown eye colour (BEY2) and brown hair colour (HCL3) on chromosome 15q". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 4 (4): 237–41. doi:10.1159/000472205. PMID 8875191.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): SKIN/HAIR/EYE PIGMENTATION, VARIATION IN, 1; SHEP1 - 227220
- Lucy Southworth. "Are gray eyes the same as blue in terms of genetics?". Understanding Genetics: Human Health and the Genome. Stanford School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- Herbert Risley, William Crooke, The People of India, (1999)
- (in French) Provincia: bulletin trimestriel de la Société de Statistique ..., Volumes 16–17 By Société de statistique, d'histoire et d'archéologie de Marseille et de Provence p. 273 l'iris gris est celui des chaouias...
- Iliad 1:206 http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0133%3Abook%3D1%3Acard%3D206
- OCA2: The Gene for Color. allaboutgenes.weebly.com. Retrieved on 8 September 2016.
- Keyser, Christine; Bouakaze, Caroline; Crubézy, Eric; Nikolaev, Valery G.; Montagnon, Daniel; Reis, Tatiana; Ludes, Bertrand (2009). "Ancient DNA provides new insights into the history of south Siberian Kurgan people". Human Genetics. 126 (3): 395–410. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0683-0. PMID 19449030.
Indeed, among the SNPs tested was rs12913832, a single DNA variation within a regulatory element of HERC2 gene which is associated to blue eye color in humans. This polymorphism, together with the diplotypes obtained from variations of the OCA2 locus (major contributor to the human eye color variation) showed that at least 60% of the ancient Siberian specimens under study had blue (or green) eyes.
- Blue Eyes Versus Brown Eyes: A Primer on Eye Color Archived 8 December 2012 at Archive.today. Eyedoctorguide.com. Retrieved on 23 December 2011.
- Why Do Europeans Have So Many Hair and Eye Colors?. Cogweb.ucla.edu. Retrieved on 23 December 2011.
- "Why Edinburgh residents are likely to be blue-eyed". Edinburghnews.Scotsman. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- Rafnsson V, Hrafnkelsson J, Tulinius H, Sigurgeirsson B, Olafsson JH (2004). "Risk factors for malignant melanoma in an Icelandic population sample". Prev Med. 39 (2): 247–52. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.03.027. PMID 15226032.
- Genetic determinants of hair, eye and skin pigmentation in Europeans. Retrieved on 7 August 2012.
- Kastelic, V; Pośpiech, E; Draus-Barini, J; Branicki, W; Drobnič, K (2013). "Prediction of eye color in the Slovenian population using the IrisPlex SNPs". Croat. Med. J. 54 (4): 381–6. doi:10.3325/cmj.2013.54.381. PMC 3760663. PMID 23986280.
- Walsh, Susan; Wollstein, Andreas; Liu, Fan; Chakravarthy, Usha; Rahu, Mati; Seland, Johan H.; Soubrane, Gisele; Tomazzoli, Laura; Topouzis, Fotis; Vingerling, Johannes R.; Vioque, Jesus; Fletcher, Astrid E.; Ballantyne, Kaye N.; Kayser, Manfred (2012). "DNA-based eye colour prediction across Europe with the Iris Plex system". Forensic Science International: Genetics. 6 (3): 330–340. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2011.07.009. PMID 21813346.
- Zhu, Gu; Evans, David M.; Duffy, David L.; Montgomery, Grant W.; Medland, Sarah E.; Gillespie, Nathan A.; Ewen, Kelly R.; Jewell, Mary; Liew, Yew Wah; Hayward, Nicholas K.; Sturma, Richard A.; Trenta, Jeffrey M.; Martina, Nicholas G. (2004). "A genome scan for eye color in 502 twin families: most variation is due to a QTL on chromosome 15q". Twin Res. 7 (2): 197–210. doi:10.1375/136905204323016186. PMID 15169604.
- Albert, Daniel M; Green, W Richard; Zimbric, Michele L; Lo, Cecilia; Gangnon, Ronald E; Hope, Kirsten L; Gleiser, Joel (2003). "Iris melanocyte numbers in Asian, African American, and Caucasian irides". Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society. 101: 217–222. PMC 1358991. PMID 14971580.
- Mitchell R, Rochtchina E, Lee A, Wang JJ, Mitchell P (2003). "Iris color and intraocular pressure: the Blue Mountains Eye Study". Am. J. Ophthalmol. 135 (3): 384–6. doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(02)01967-0. PMID 12614760.
- Lindsey JD, Jones HL, Hewitt EG, Angert M, Weinreb RN (2001). "Induction of tyrosinase gene transcription in human iris organ cultures exposed to latanoprost". Arch. Ophthalmol. 119 (6): 853–60. doi:10.1001/archopht.119.6.853. PMID 11405836.
- Frank RN, Puklin JE, Stock C, Canter LA (2000). "Race, iris color, and age-related macular degeneration". Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 98: 109–15, discussion 115–7. PMC 1298217. PMID 11190014.
- Regan S, Judge HE, Gragoudas ES, Egan KM (1999). "Iris color as a prognostic factor in ocular melanoma". Arch. Ophthalmol. 117 (6): 811–4. doi:10.1001/archopht.117.6.811. PMID 10369595.
- Hawkins TA, Stewart WC, McMillan TA, Gwynn DR (1994). "Analysis of diode, argon, and Nd: YAG peripheral iridectomy in cadaver eyes". Doc Ophthalmol. 87 (4): 367–76. doi:10.1007/BF01203345. PMID 7851220.
- Hammond BR, Fuld K, Snodderly DM (1996). "Iris color and macular pigment optical density". Exp. Eye Res. 62 (3): 293–7. doi:10.1006/exer.1996.0035. PMID 8690039.
- NOAH — What is Albinism? Archived 14 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Albinism.org. Retrieved on 23 December 2011.
- Dave Johnson (16 January 2009). "HOW TO: Avoid the red eye effect". New Zealand PC World. Archived from the original on 24 February 2010. Retrieved 9 January 2010.
- Palmer, Roxanne (25 March 2005). "Elizabeth Taylor: Beautiful Mutant". Slate. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- Nicolas, Caroline M; Robman, Luba D; Tikellis, Gabriella; Dimitrov, Peter N; Dowrick, Adam; Guymer, Robyn H; McCarty, Catherine A (2003). "Iris colour, ethnic origin and progression of age-related macular degeneration". Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 31 (6): 465–9. doi:10.1046/j.1442-9071.2003.00711.x. PMID 14641151.
- Stang A, Ahrens W, Anastassiou G, Jöckel KH (2003). "Phenotypical characteristics, lifestyle, social class and uveal melanoma". Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 10 (5): 293–302. doi:10.1076/opep.10.5.293.17319. PMID 14566630.
- Cumming RG, Mitchell P, Lim R (2000). "Iris color and cataract: The Blue Mountains Eye Study". American Journal of Ophthalmology. 130 (2): 237–238. doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(00)00479-7. PMID 11004303.
- McDonnell G, Esmonde T (1999). "A homesick student". Postgrad Med J. 75 (884): 375–8. doi:10.1136/pgmj.75.884.375. PMC 1741256. PMID 10435182.
- de la Maza, Maite Sainz; Tauber, Joseph; Foster, C. Stephen (2012). "Noninflammatory Diseases of the Sclera". The Sclera. pp. 277–297. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-6502-8_8. ISBN 978-1-4419-6501-1.
- Wheatley, TJ (2006). "Upper gastrointestinal surgery". In Kingsnorth, Andrew N; Majid, Aljafri A (eds.). Fundamentals of Surgical Practice. pp. 230–248. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511545740.013. ISBN 978-0-511-54574-0.
- Aniridia at eMedicine
- Ocular Manifestations of Albinism at eMedicine
- Imesch PD, Wallow IH, Albert DM (1997). "The color of the human eye: a review of morphologic correlates and of some conditions that affect iridial pigmentation". Surv Ophthalmol. 41 (Suppl 2): S117–23. doi:10.1016/S0039-6257(97)80018-5. PMID 9154287.
- Biography for Lee Van Cleef on IMDb
- Hejkal TW, Camras CB (1999). "Prostaglandin analogs in the treatment of glaucoma". Seminars in Ophthalmology. 14 (3): 114–23. doi:10.3109/08820539909061464. PMID 10790575.
- Forti, Isabela Rodrigues Nogueira; Young, Robert John (2016). "Human Commercial Models' Eye Colour Shows Negative Frequency-Dependent Selection". PLOS ONE. 11 (12): e0168458. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1168458F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0168458. PMC 5179042. PMID 28005995.
- Little, A.C; Penton-Voak, I.S; Burt, D.M; Perrett, D.I (January 2003). "Investigating an imprinting-like phenomenon in humans". Evolution and Human Behavior. 24 (1): 43–51. doi:10.1016/S1090-5138(02)00119-8.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eyes by color. |