Gongylonema
Gongylonema is a genus of thread-like nematode that was described by Molin in 1857. It is the only currently valid genus in the family Gongylonematidae, though the mysterious Spiruroides – usually placed in the Subuluridae, which are not closely related to Gongylonema among the Spiruria – might actually belong here. They are parasites of birds and mammals, transmitted by insects (especially beetles).[2] Some 38 species are known, about 12 of which have been recorded in Europe.[3][4]
| Gongylonema | |
|---|---|
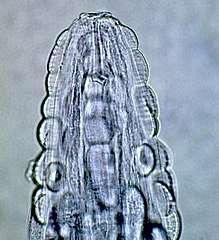 | |
| Head of male Gongylonema pulchrum, from human infection;[1] note characteristic bosses | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | Hall, 1916 |
| Genus: | Gongylonema Molin, 1857 |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Several species are significant parasites of domestic animals, causing gongylonemiasis. Human infection by these nematodes is very rare: since its discovery fewer than 100 people have been reported to be infected with these parasites,[5] always with the species G. pulchrum.[1][6]
Species
- Gongylonema aegypti Ashour & Lewis, 1986
- Gongylonema aequispicularis Kadenazii, 1957
- Gongylonema alecturae Johnston & Mawson, 1942
- Gongylonema baylisi Freitas & Lent, 1937
- Gongylonema beveridgei Mawson, 1971
- Gongylonema brevispiculum Seurat, 1914 [7]
- Gongylonema caucasica Kurashvili, 1941
- Gongylonema confusum Sonsino, 1896
- Gongylonema congolense Fain, 1955
- Gongylonema dipodomysi Kruidenier & Peebles, 1958
- Gongylonema dupuisi Quentin, 1965
- Gongylonema fotedari Gupta & Trivedi, 1986
- Gongylonema graberi Barre, 1980
- Gongylonema ingluvicola Ransom, 1904
- Gongylonema longispiculum Schulz, 1927
- Gongylonema macrogubernaculum Lubimov, 1931
- Gongylonema madeleinensis Diouf, Bâ, Marchand & Vassiliadès, 1997
- Gongylonema marsupialis Vaz & Pereira, 1934
- Gongylonema mesasiatica Sultanov, 1961
- Gongylonema metopidiusi Gupta & Kumar, 1977
- Gongylonema mexicanum Caballero & Zerecero, 1944
- Gongylonema minimum Molin, 1857
- Gongylonema monnigi
- Gongylonema mucronatum Seurat, 1916
- Gongylonema musculi Rudolphi, 1819
- Gongylonema neoplasticum Fibiger & Ditlevsen, 1914
- Gongylonema pacoi Hernandez & Gutierrez, 1992 [8]
- Gongylonema pithyusensis Mas-Coma, 1977 [9]
- Gongylonema problematicum Schulz, 1924
- Gongylonema pulchrum Molin, 1857
- Gongylonema rodhaini Fain, 1948
- Gongylonema saimirisi Artigas, 1933
- Gongylonema soricis Fain, 1955
- Gongylonema spalacis Schulz, 1927
- Gongylonema verrucosum Giles, 1892
References
- Pesson, B.; Hersant, C.; Biehler, JF.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Brunet, J.; Pfaff, AW.; Ferté, H.; Candolfi, E. (2013). "First case of human gongylonemosis in France". Parasite. 20: 5. doi:10.1051/parasite/2013007. PMC 3718519. PMID 23425508.

- Quentin, J.-C.; Seguignes, M. (1979). "Cycle biologique de Gongylonema mucronatum Seurat, 1916 parasite du Hérisson d'Afrique du Nord". Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 54 (6): 637–644. doi:10.1051/parasite/1979546637.

- David Gibson (April 19, 2007). "Gongylonema". Fauna Europaea. Retrieved November 4, 2008.
- Joel Hallan, ed. (August 7, 2007). "Family Gongylonematidae". Retrieved November 4, 2008.
- Haruki, K., Furuya, H., Saito, S., Kamiya, S. & Kagei, N. 2005: Gongylonema infection in man: A first case of gongylonemosis in Japan. Helminthologia, 42, 63-66. Free PDF
- "Gongylonema". Biology Online. October 3, 2005. Retrieved November 4, 2008.
- Quentin, J.-C.; Seureau, C. (1978). "Identification et biologie du Gongylonème parasite du Macroscélide en Tunisie". Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 53 (6): 631–640. doi:10.1051/parasite/1978536631.

- Hernandez-Rodriguez, S.; Gutiérrez-Palomino, P. N. (1992). "Gongylonema (Progongylonema) pacoi n. subgen. n. sp. (Spiruroidea : Gongylonematidae) parasite d'oiseaux Corvidae" (PDF). Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 67 (6): 188–193. doi:10.1051/parasite/1992676188. ISSN 0003-4150.

- Mas-Coma, S. (1977). "Gongylonema pithyusensis n. sp. (Nematoda : Spiruridae), parasite œsophagien du Lérot Eliomys quercinus ophiusae Thomas, 1925 (Rodentia : Gliridae) à Formentera (Baléares)". Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 52 (1): 13–18. doi:10.1051/parasite/1977521013.
