Gammaproteobacteria
The Gammaproteobacteria are a class of bacteria. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. Like all Proteobacteria, the Gammaproteobacteria are Gram-negative.
| Gammaproteobacteria | |
|---|---|
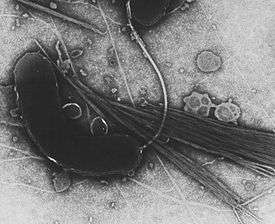 | |
| Vibrio cholerae | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Gammaproteobacteria |
| Orders | |
|
Acidiferrobacterales | |
Significance
The Gammaproteobacteria comprise several medically and scientifically important groups of bacteria, such as the Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae, and Pseudomonadaceae. A number of important pathogens belong to this class, e.g. Salmonella spp. (enteritis and typhoid fever), Yersinia pestis (plague), Vibrio cholerae (cholera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (lung infections in hospitalized or cystic fibrosis patients), and Escherichia coli (food poisoning). Important plant pathogens such as Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (citrus canker), Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae (kiwifruit Psa outbreak), and Xylella fastidiosa are also Gammaproteobacteria. Members of Chromatium are photosynthetic and oxidize hydrogen sulfide instead of water, producing sulfur as a waste product. Some Gammaproteobacteria are methane oxidizers, and many are symbiotic with geothermic ocean vent-dwelling animals.[1]
Phylogeny
| Phylogeny of Gammaproteobacteria | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylogeny of Gammaproteobacteria after[2] Not all orders are monophyletic, consequently families or genera are shown for the Pseudomonadales, Oceanospirillales, and Alteromonadales. In the case of singleton orders, the genus is shown. (In bacterial taxonomy, orders have the suffix -ales, while families have -aceae.) |
A number of bacteria have been described as members of the Gammaproteobacteria, but have not yet been assigned an order or family. These include bacteria of the genera Alkalimarinus, Alkalimonas, Arenicella, Gallaecimonas, Ignatzschineria, Litorivivens, Marinicella, Methylohalomonas, Methylonatrum, Plasticicumulans, Pseudohongiella, Sedimenticola, Thiohalobacter, Thiohalomonas, Thiohalorhabdus, Thiolapillus, and Wohlfahrtiimonas.[3]
See also
References
- Holt JR (6 February 2013). "Description of the Phylum Gammaproteobacteria". Susquehanna University - Systematic Biology Course Website. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- Williams, K. P.; Gillespie, J. J.; Sobral, B. W. S.; Nordberg, E. K.; Snyder, E. E.; Shallom, J. M.; Dickerman, A. W. (2010). "Phylogeny of Gammaproteobacteria". Journal of Bacteriology. 192 (9): 2305–2314. doi:10.1128/JB.01480-09. PMC 2863478. PMID 20207755.
- "Classification of domains and phyla - Hierarchical classification of prokaryotes (bacteria) - Gammaproteobacteria". List of Prokaryotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
External links
- Gammaproteobacteria at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)