French destroyer Janissaire
Janissaire was one of four Chasseur-class destroyers built for the French Navy in the first decade of the 20th century.
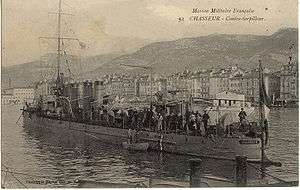 A postcard of sister ship Chasseur at anchor | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Janissaire |
| Namesake: | Janissary |
| Builder: | Ateliers et Chantiers de Penhoët, Saint-Nazaire |
| Launched: | 12 April 1910 |
| Completed: | June 1911 |
| Stricken: | October 1920 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Chasseur-class destroyer |
| Displacement: | |
| Length: | 64.5 m (211 ft 7 in) (p/p) |
| Beam: | 6.6 m (21 ft 8 in) |
| Draft: | 3.1 m (10 ft 2 in) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: | 3 shafts; 3 steam turbines |
| Speed: | 28 knots (52 km/h; 32 mph) |
| Range: | 1,400–1,500 nmi (2,600–2,800 km; 1,600–1,700 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement: | 77–79 |
| Armament: |
|
Design and description
The Chasseur class was based on the preceding Spahi-class destroyer, albeit oil-fired boilers rather than the coal-fired ones of the earlier ships.[1] Janissaire had an length between perpendiculars of 64.5 meters (211 ft 7 in), a beam of 6.6 meters (21 ft 8 in),[2] and a draft of 3.1 meters (10 ft 2 in). Designed to displaced 450 metric tons (443 long tons), the ships displaced 520 t (512 long tons) at deep load. Their crew numbered 77–79 men.[1]
Janissaire was powered by three Parsons direct-drive steam turbines, each driving one propeller shaft, using steam provided by three Foster-Wheeler boilers. The engines were designed to produce 7,200 shaft horsepower (5,400 kW) which was intended to give the ships a speed of 28 knots (52 km/h; 32 mph). Janissaire exceeded that speed during her sea trials, reaching 28.6 knots (53.0 km/h; 32.9 mph). The ships carried enough fuel oil to give them a range of 1,400–1,500 nautical miles (2,600–2,800 km; 1,600–1,700 mi) at a cruising speed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph).[3]
The primary armament of the Chasseur-class ships consisted of six 65-millimeter (2.6 in) Modèle 1902 guns in single mounts, one each fore and aft of the superstructure and the others were distributed amidships. They were also fitted with three 450-millimeter (17.7 in) torpedo tubes. One of these was in a fixed mount in the bow and the other two were on single rotating mounts amidships.[1]
Construction and career
Janissaire was ordered from Ateliers et Chantiers de Penhoët and was launched from its Saint-Nazaire shipyard on 12 April 1910. The ship was completed in June 1911. She survived the First World War to be condemned in October 1920.[4]
References
- Gardiner & Gray, p. 202
- Couhat, p. 99
- Couhat, pp. 99–100
- Couhat, p. 100
Bibliography
- Couhat, Jean Labayle (1974). French Warships of World War I. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0445-5.
- Gardiner, Robert & Gray, Randal (1985). Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.