French destroyer Fantassin
Fantassin was one of four Chasseur-class destroyers built for the French Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. During World War I, she had to be scuttled by another French ship after being badly damaged during a collision in 1915.
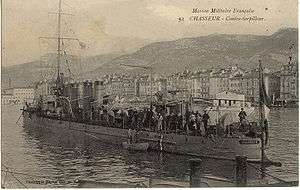 A postcard of sister ship Chasseur at anchor | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Fantassin |
| Namesake: | Infantryman |
| Builder: | Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, La Seyne-sur-Mer |
| Launched: | 17 June 1909 |
| Completed: | June 1911 |
| Fate: | Wrecked in a collision and then scuttled, 5 June 1915 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Chasseur-class destroyer |
| Displacement: | |
| Length: | 65.4 m (214 ft 7 in) (p/p) |
| Beam: | 6.7 m (22 ft 0 in) |
| Draft: | 3.1 m (10 ft 2 in) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: | 3 shafts; 3 Steam turbines |
| Speed: | 28 knots (52 km/h; 32 mph) |
| Range: | 1,400–1,500 nmi (2,600–2,800 km; 1,600–1,700 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement: | 77–79 |
| Armament: |
|
Design and description
The Chasseur class was based on the preceding Spahi-class destroyer, albeit oil-fired boilers rather than the coal-fired ones of the earlier ships.[1] Fantassin had an length between perpendiculars of 65.4 meters (214 ft 7 in), a beam of 6.65 meters (21 ft 10 in),[2] and a draft of 3.1 meters (10 ft 2 in). Designed to displaced 450 metric tons (443 long tons), the ships displaced 520 t (512 long tons) at deep load. Their crew numbered 77–79 men.[1]
The Chasseur class was powered by three Parsons direct-drive steam turbines, each driving one propeller shaft, using steam provided by four Normand boilers. The engines were designed to produce 7,200 shaft horsepower (5,400 kW) which was intended to give the ships a speed of 28 knots (52 km/h; 32 mph). Fantassin handily exceeded that speed during her sea trials, reaching 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph). The ships carried enough fuel oil to give them a range of 1,400–1,500 nautical miles (2,600–2,800 km; 1,600–1,700 mi) at a cruising speed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph).[3]
The primary armament of the Chasseur-class ships consisted of six 65-millimeter (2.6 in) Modèle 1902 guns in single mounts, one each fore and aft of the superstructure and the others were distributed amidships. They were also fitted with three 450-millimeter (17.7 in) torpedo tubes. One of these was in a fixed mount in the bow and the other two were on single rotating mounts amidships.[1]
Construction and career
Fantassin was ordered from Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée and was launched from its La Seyne-sur-Mer shipyard on 17 June 1909. The ship was completed in June 1911. During the First World War, Fantassin was badly damaged when the French destroyer Mameluck accidentally rammed her in the Ionian Sea on 5 June 1915. The French destroyer Fauconneau consequently scuttled Fantassin.[4]
References
- Gardiner & Gray, p. 202
- Couhat, p. 99
- Couhat, pp. 99–100
- Couhat, p. 100
Bibliography
- Couhat, Jean Labayle (1974). French Warships of World War I. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0445-5.
- Gardiner, Robert & Gray, Randal (1985). Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.