Estates of Sint Maarten
The Estates of Sint Maarten (Dutch: Staten van Sint Maarten) is a unicameral legislature that consists of 15 members, each elected for a four-year term in a general election. The first Estates were installed on 10 October 2010, the date of the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, and consisted of the members of the island council elected on 17 September 2010.[1] The current President of Parliament is Rolando Brison.
Estates of Sint Maarten Staten van Sint Maarten | |
|---|---|
| 5th Sint Maarten Estates | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 10 October 2010 |
| Leadership | |
Monarch | |
| Structure | |
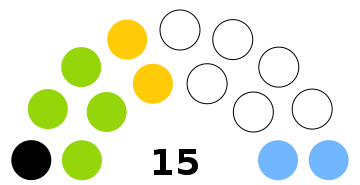
| Seats | 15 |
 | |
Estates political groups | Government
Opposition |
| Elections | |
Estates voting system | Proportional representation |
Estates last election | 9 January 2020 |
Estates next election | 2024 |
| Motto | |
| Latin: coram populo | |
| Website | |
| www | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Sint Maarten |
|
Role and function
The two most important tasks of parliament is the realization of legislation for Sint Maarten, and secondly, to exercise control over Government’s policy. Under the first task, Parliament exercises this task together with Government, so Parliament is called the co-legislator. In order to carry out the aforementioned, the Parliament has a number of powers that allows it to fulfill its two tasks: The right to approve and amend the budget; The right of interpellation where each Member of Parliament (MP) has the right to question ministers of government in the General Assembly of Parliament; The right of initiative allows MPs to submit draft laws on their own initiative; The right to amendment, allows MPs to amend legislation that has been submitted to Parliament; The right to ask questions, every MP can question a Minister orally or in writing; The right to instigate inquiries allows parliament to institute an inquiry into the state of affairs in an event in which Government is involved.
2020 general election
 | |||||||||
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Alliance | 4,715 | 35.36 | 6 | +1 | |||||
| United People's Party | 3,231 | 24.23 | 4 | +4 | |||||
| United St. Maarten Party | 1,762 | 13.21 | 2 | 0 | |||||
| Party for Progress | 1,407 | 10.55 | 2 | New | |||||
| United Democrats | 1,161 | 8.71 | 1 | –6 | |||||
| St. Maarten Christian Party | 759 | 5.69 | 0 | –1 | |||||
| People’s Progressive Alliance | 326 | 2.45 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 402 | – | – | – | |||||
| Total | 13,735 | 100 | 15 | 0 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 23,106 | 59.44 | – | – | |||||
| Source: Government of Sint Maarten | |||||||||
Current Parliament
The Government of Sint Maarten is based on a political party having a majority of the 15 seats in parliament. A political party would need to have eight seats (8) in order to govern outright. However, more than one party can form a Government if parties can reach an agreement to do so. An independent member of parliament can also be part of the ranks of the opposition or be part of the governing party(s).
The current parliament took office on 10 February 2020 following a snap election, and will serve for a four-year period, until 2024 when new elections are due. The current parliament comprises the following:
Government structure
The Government As an island territory, St. Maarten was governed by the Island Regulation of the Netherlands Antilles, and in accordance herewith the administration units of the Island Territory were: the Island Council, Executive Council and Lt. Governor. As of 10 October 2010, St. Maarten is now governed by its own Constitution and the following institutions of government: Governor as Head of State, Parliament, and the Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
The Parliament The parliament is the highest legislative body of country St. Maarten and represents the entire population of the Dutch side of the island. The parliament consists of 15 members who are elected for a four-year period. The session year of parliament commences on the second Tuesday of September. During this session, the Governor provides an explanation of the policy to be pursued by the government. The parliament elects a President and Deputy President from its own numbers. The President of Parliament shall open and close the session year of the Parliament.
The Council of Ministers The council of ministers comprises seven ministers. The ministers are answerable to the parliament. The prime minister chairs the council of ministers. The council of ministers shall debate and determine government policy in order to promote the cohesion of that policy. If the governor general attends a meeting of the council of ministers, he/she shall do so in an advisory capacity. The prime minister and other ministers shall be appointed and dismissed by national ordinance. If a minister no longer enjoys the confidence of the parliament, he/she shall surrender his/her office. The Minister of Plenipotentiary must have the Dutch nationality. This person represents the island in the Kingdom Council of Ministers meetings in The Hague, The Netherlands. The minister also has his/her office in the Netherlands under the banner of the "St. Maarten House." Each minister heads one of seven ministries which are established by national ordinance.
System of Government St. Maarten is a part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, with full autonomy in internal affairs. The Kingdom Government is responsible for defense and foreign affairs. The King of the Netherlands is Head of State and is represented by the Governor. Other institutions of government are the Council of Advice, the General Audit Chamber and Ombudsman.
The Judiciary The courts forming part of the judiciary are: the Court at First Instance; the Common Court of Justice of Aruba, Curaçao, St. Maarten and Bonaire, St. Eustatius, and Saba. The jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of the Netherlands in relation to legal cases in St. Maarten shall be regulated by Kingdom law. The responsibilities of the judiciary are: the adjudication of disputes on civil matters; the trial of criminal offences; and the adjudication of disputes on administrative law matters.
Constitutional Court The duty of the court is to assess the compatibility of any applicable statutory regulations. The constitutional court consists of three members, including a president and a vice president, and three substitute members.
.svg.png)