Assembly of the Representatives of the People
The Assembly of the Representatives of the People (Arabic: مجلس نواب الشعب Majlis Nuwwāb ash-Sha‘b, French: Assemblée des représentants du peuple; ARP) is Tunisia's legislative branch of government. The unicameral Assembly replaced the Constituent Assembly and was first elected on 26 October 2014.[1] The legislature consists of 217 seats.[2] Before the 2011 revolution, Tunisia's parliament was bicameral and consisted of an upper chamber called the Chamber of Advisors and a lower chamber called the Chamber of Deputies.
Assembly of the Representatives of the People مجلس نواب الشعب Majlis Nuwwāb esh-Sha‘b | |
|---|---|
| 2nd legislature | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Preceded by | Constituent Assembly of Tunisia |
New session started | 13 November 2019 |
| Leadership | |
First Deputy Speaker | |
Second Deputy Speaker | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 217 |
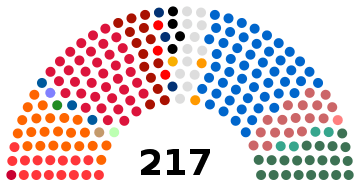 | |
Political groups | Government (106)
Confidence-and-supply (24)[lower-alpha 1]
Opposition (87)
|
| Elections | |
| Party-list proportional representation using multi-member constituencies | |
Last election | 6 October 2019 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Bardo Palace, Le Bardo (near Tunis) | |
| Website | |
| www | |
Tunisia's electoral law requires "vertical gender parity", i.e. male and female candidates must alternate within each party's regional list of candidates. Consequently, as of 2015, 68 of the chamber's members are women, the highest proportion of female legislative representatives in the Arab world.[3]
The current speaker of the Assembly is Rached Ghannouchi, who was elected on 13 November 2019.[4]
Elections
The first elections to the Assembly were held on 26 October 2014, slightly under four years since the conclusion of the Tunisian Revolution, and slightly under three years since the election to the Constituent Assembly. Nidaa Tounes gained a plurality of votes, winning 85 seats in the 217-seat parliament, beating the Ennahda Movement (69 seats) and many smaller parties.
2019 Election
The second elections to the Assembly were held on 6 October 2019.
Current affiliations
| Affiliation | Members | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 election results |
As of February 2020 | ||
| Ennahda Movement | 52 | ||
| Heart of Tunisia | 38 | ||
| Democratic Current | 22 | ||
| Dignity Coalition | 21 | 19 | |
| Free Destourian Party | 17 | ||
| People's Movement | 15 | ||
| Tahya Tounes | 14 | ||
| Machrouu Tounes | 4 | ||
| Errahma | 4 | 2 | |
| Republican People's Union | 3 | ||
| Tunisian Alternative | 3 | ||
| Nidaa Tounes | 3 | ||
| Afek Tounes | 2 | ||
| Popular Front | 1 | ||
| Aïch Tounsi | 1 | ||
| Farmers' Voice Party | 1 | ||
| Green League | 1 | ||
| Current of Love | 1 | ||
| Democratic and Social Union (VDS-PR-MDS) | 1 | ||
| Socialist Destourian Party | 1 | ||
| Independent | 12 | ||
| Dissidents | 4 | ||
| Total members | 217 | ||
See also
- Politics of Tunisia
- List of legislatures by country
- Tunisian parliamentary election, 2014
References
- "Tunisian elections intensify focus on alliances". Al Monitor. 14 September 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- "Tunisia begins landmark election race". AFP. 4 October 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- "Tunisia". freedomhouse.org. 21 January 2015.
- "Tunisia parliament elects Ennahda's Rachid Ghannouchi as speaker". Al Jazeera. 13 November 2019. Retrieved 13 November 2019.
- If a majority of the party voted in favor of Elyes Fakhfakh's investiture as Prime Minister