Edgware, Highgate and London Railway
The Edgware, Highgate and London Railway was a railway in north London. The railway was a precursor of parts of London Underground's Northern line and was, in the 1930s the core of an ambitious expansion plan for that line which was thwarted by the Second World War. Parts of the line were closed in the 1950s and have since been removed.
| Edgware, Highgate & London Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Establishment
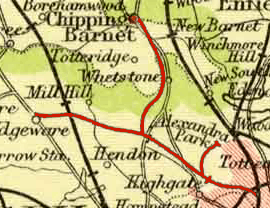
The company was established by a private act of parliament passed on 3 June 1862.[1] The route, measuring 8.75 miles (14.08 km),[2] ran through parts of rural Middlesex (now suburban north London) from Finsbury Park through Stroud Green, Crouch End, Highgate, Finchley and Mill Hill to Edgware. Additional acts in 1864 and 1866 granted powers to construct branch lines from Highgate to Muswell Hill[3] and from Finchley to High Barnet[4] respectively.
The railway was sponsored by the larger Great Northern Railway (GNR), whose main line from King's Cross ran through Finsbury Park on its way to Potters Bar and the north. Before the line to Edgware was opened, it was purchased in July 1867 by the GNR and was opened as a single track line on 22 August 1867.[2][5]
At first, services ran from Edgware to Finsbury Park, King's Cross and, via Snow Hill tunnel, to Ludgate Hill, Blackfriars and Loughborough Road on the south of the Thames. After 1869, trains terminated at Moorgate. Services could also run from Finsbury Park via the North London Railway to Broad Street after the Canonbury-Finsbury Park link opened in 1875. 21 trains a day ran to Finchley, usually in 24 minutes from Kings Cross, and 14 continued to Edgware.[6] In 1870 the track between Finsbury Park and Finchley & Hendon (now Finchley Central) was doubled in preparation for the opening of the High Barnet branch and Muswell Hill branch.
Because of the rapid rise and fall of the terrain in the area traversed by the railway, the line made extensive use of cuttings, embankments and viaducts. Particularly notable were the cutting in Highgate Hill in which Highgate station was constructed with tunnels on either side, and the viaducts over the Dollis Brook and at Muswell Hill.
Branch lines
The High Barnet branch opened on 1 April 1872[5] with two intermediate stations at Woodside Park and Totteridge & Whetstone (West Finchley did not open until 1933).[5]
The line to Barnet stopped short at Underhill, south of the main village located at the top of the hill. As Barnet was a larger village than Edgware and new residential development at Finchley grew at a faster pace than on the original line, the branch line quickly became the dominant route. Direct services from London ran to High Barnet and a shuttle service was operated between Finchley and Edgware for most passenger journeys on that section, which remained a single track.
The Muswell Hill branch from Highgate to Alexandra Palace was constructed by a separate company, the Muswell Hill Railway Company and opened on 24 May 1873 along with the Palace. However, when the Palace burned down only two weeks after opening, the service was considerably reduced and then closed for almost two years whilst the Palace was rebuilt. It reopened in May 1875.
Another separate company, the Watford and Edgware Railway (W&ER), was established in the 1860s and had various plans to build a link from the EH&LR near Edgware to Watford in Hertfordshire. The W&ER was unable to attract sufficient funds for the project and the company and the right of way that it had obtained passed through the ownership of a number of other railway companies until plans were made in the 1930s to make use of its route (see below).
Development, overcrowding and competition: 1900-1918
By the 1900s the whole line was under pressure from overcrowding. The populations of areas along the line, particularly at Hornsey, Highgate, Muswell Hill, and Finchley, had increased considerably with the rapid Victorian expansion of London, but the GNR service had not been expanded to cope. The line was also congested with goods traffic, mostly coal and building materials. By 1903 the morning trains from Barnet were full by the time they arrived at East Finchley. As the doors of the compartments in the carriages were in those days locked with aid of a simple square key, some passengers took to purchasing these keys from local ironmongers, and locking the doors from the inside. It was not unknown for harsh words and even, on odd occasions, for blows to be exchanged.
New stations were opened at Cranley Gardens (1902, between Highgate and Muswell Hill) and Mill Hill (1906, between Mill Hill East and Edgware).
In 1905 tram services were established in both Hendon and Finchley, and extended shortly after to Barnet. This combined with motor transport alleviated some of the problem. This relief was also competition, and the GNR introduced new engines, specially designed to manage the steep inclines on the routes which slowed up the services.
Further competition came from the opening of the new underground Charing Cross, Euston & Hampstead Railway (CCE&HR) to Archway (then named Highgate) and Golders Green in June 1907 a move that stimulated large scale house building to the south of the Edgware branch spreading out from Golders Green.
The GNR took over the Muswell Hill Railway (renamed to the Muswell Hill and Palace Railway) in September 1911 and merged it with the rest of the line. Further developments were halted by the First World War.
Amalgamation: 1918-1939
In 1923 as a consequence of the railway grouping instigated by the 1921 Railways Act, the GNR became part of the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER). In January 1924 the newly enlarged company announced that the line would be electrified, although little was done.
Meanwhile, the CCE&HR, now part of the London Electric Railway (Underground Group), was using plans dating back to 1901 for the Edgware and Hampstead Railway[7] to construct an extension of its line from Golders Green through Hendon to a new station at Edgware where it would be in direct competition with the LNER line. The Underground Group had also bought up the rights of the W&ER and published proposals to further extend the line to Bushey and Watford although nothing was done immediately.
Following the nationalisation of the Underground Group in 1933, the London Passenger Transport Board announced the 1935-1940 New Works Programme which included the following proposals for the Finsbury Park to Edgware, High Barnet and Muswell Hill lines:
- Upgrade the line to allow electric tube trains on all the lines and double the line from Finchley to Edgware.
- To run the LNER Edgware line into Edgware Underground station where the trains from East Finchley could terminate.
- To connect the Underground from Archway to East Finchley via a new tunnel under the LNER's Highgate station.
- To activate the dormant proposals to extend the line from Edgware to Bushey Heath with intermediate stations at Brockley Hill and Elstree South.
Much of the work was carried out, with East Finchley and Highgate stations being completely rebuilt and the electrification works were well advanced before the Second World War put a stop to progress. Passenger services on the Finchley Central to Edgware line were ended in September 1939.

End of the line: 1939 onwards
Underground trains took over from LNER steam services between East Finchley and High Barnet on the 14th April 1940. LNER Services were withdrawn between Highgate and East Finchley in March 1941 (both services having briefly operated to the latter station from the two parts of Highgate station). Underground trains began serving Mill Hill East in May 1941 but never ran to Edgware as planned.
In 1942 the Finsbury Park - Highgate - Alexandra Palace line was reduced to a peak service shuttle to Finsbury Park, ending through running to central London.
After the war, the introduction of London's Metropolitan Green Belt made the project to continue the line to Bushey unnecessary as the intended housing development proposed in the area was prevented by the new legislation. The plan was formally cancelled in October 1950. In 1953 the modernisation and electrification of the remaining sections of track between Mill Hill East to Edgware also Finsbury Park to Alexandra Park were also abandoned.
The last regular passenger service between Finsbury Park, Highgate and Alexandra Palace was run on 3 July 1954. In 1957 the goods yards at Cranley Gardens and Muswell Hill were closed and the line from Park Junction (Highgate Station) to Alexandra Palace was abandoned.
The line from Finsbury Park to Edgware continued to be used for goods traffic, primarily coal, milk and building materials, even into the period when diesel engines had replaced steam locomotion. However, the introduction of the Clean Air Act 1956 established a shift away from coal as a fuel for domestic heating and the demand for coal slumped. At the same time, the expansion of road haulage reduced the demand for rail transportation of other bulk loads and the line closed completely between Edgware and Mill Hill East in 1964 with equipment and track removed by the following year.
London Underground regularly moved stock for the Northern City Line along the old lines between Highgate Wood Depot, Finsbury Park and Drayton Park Depot until September 1970. The movements ran regularly on Tuesdays, and occasionally on Mondays and Wednesdays. The tracks were removed in 1971 following which the Northern City Line empty stock movements ran from Neasden via King's Cross (York Road) and the Widened Lines.[8] The sections of the line from Finsbury Park to the southern portals of the southern tunnels at Highgate station and between the sites of Cranley Gardens and Muswell Hill stations now form a linear urban park known as Parkland Walk. Stretches of the Mill Hill East to Edgware line are now local nature reserves: Copthall Railway Walk and Mill Hill Old Railway Nature Reserve.
The stations of the line

All listings are with original names.
Stations on the Finsbury Park to Edgware line, from south to north:
- Finsbury Park station
- Stroud Green - Opened in 1881.
- Crouch End
- Highgate - Rebuilt prior to the take-over by Underground services.
- East End, Finchley - Renamed to "East Finchley" in 1886. The station was completely rebuilt prior to the take-over by Underground services.
- Finchley & Hendon - Renamed twice: to "Finchley (Church End)" in 1894 and "Finchley Central" in 1940. It was the main goods yard for the Finchley area, with two separate yards in operation.
- Mill Hill - Now Mill Hill East. The station was important for two reasons: North Middlesex Gas Company established a works in 1862, with coal being carried on the line to feed the works in increasing quantity up until 1961. The Mill Hill Barracks were established in 1905.
- Hale - Opened in 1906 as a halt for milk from Mill Hill farms. But as suburban dwellings, in what is now called Mill Hill Broadway, began to appear after 1910 the platform was extended and a ticket office was established with a station master. It was renamed "The Hale for Mill Hill" no later than 1919, supplying mostly coal and commuters. In preparation for the proposed electrification during the late 1930s the station platform was extended with concrete and was closed in 1939 to allow work to be accelerated but it was never reopened and subsequent work was aborted.
- Edgware - There was a small engine shed, but after damage from "the great blizzard of January 1881" it was demolished and never replaced. Not to be confused with Edgware Underground station 200 yards to the north. All has been demolished.
On the Highgate to Alexandra Palace branch:
- Cranley Gardens - Opened in 1902.
- Muswell Hill
- Alexandra Palace
On the Finchley Central to High Barnet branch:
- West Finchley - Opened in 1933 by the LNER to serve new developments that had taken place between Church End, Finchley and the Dollis Brook. The station was built from material of older stations the company had further north in Yorkshire. The result is that the station is in keeping with the style of other stations on the same route. The footbridge, for example, comes from Wintersett and Ryhill, Barnsley.
- Torrington Park - Renamed "Woodside Park" in 1889 when the station was rebuilt. Coal sidings were built by 1906.
- Whetstone and Totteridge - Now "Totteridge and Whetstone". Pickfords had a horse hospital and stables here, and the nursery gardeners Sweets also used the station.
- High Barnet - Opened on the site of the old Barnet Fair. The name is not, as is popularly thought, a railway name, and has been in use since at least the 16th century. There was a cattle pound in the station yard.
Other notable structures were:
- Dollis Viaduct - 13 arches each with a span of 32 feet (9.8 m), and 60 feet (18 m) high (the highest point above ground on the present underground). It was designed by Sir John Fowler and Walter Marr Brydone to span Dollis Brook and was built between 1863 and 1867.
- Muswell Hill viaduct - Carried trains high on brick pylon on the way to Muswell Hill station. Affords excellent views of central London.
- United Dairies sidings - Came into use in the early 1920s and was originally owned by Manor Dairies. It had sidings of its own, and was used as a distribution depot. It was closed in 1960.
In fiction
The Alexandra Palace branch features in the novel The Horn of Mortal Danger (1980). The book begins with two children exploring Cranley Gardens station and the tunnel to Highgate; they discover a "secret railway" which can be accessed by a gate in the wall of the tunnel.
A version of the railway also features in scenes eventually cut from Shaun of the Dead[9]
References
- "No. 22632". The London Gazette. 6 June 1862. p. 2902.
- McCarthy, Colin; McCarthy, David (2009). Railways of Britain – London North of the Thames. Hersham, Surrey: Ian Allan Publishing. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-7110-3346-7.
- "No. 22855". The London Gazette. 13 May 1864. p. 2633.
- "No. 23139". The London Gazette. 17 July 1866. p. 4037.
- Clive's Underground Line Guides, Northern Line, Dates
- "London local train services of thirty five years ago". Railway Magazine. December 1907. p. 488. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
- "No. 27380". The London Gazette. 26 November 1901. p. 8200.
- Connor, Piers (1989). The 1938 Tube Stock. Harrow Weald: Capital Transport. pp. 85–86. ISBN 1-85414-115-5.
- Shaun of the Dead [2004 feature film]