Lepton
In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer spin (spin 1⁄2) that does not undergo strong interactions.[1] Two main classes of leptons exist, charged leptons (also known as the electron-like leptons), and neutral leptons (better known as neutrinos). Charged leptons can combine with other particles to form various composite particles such as atoms and positronium, while neutrinos rarely interact with anything, and are consequently rarely observed. The best known of all leptons is the electron.
| Type | Generations of matter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | Third | |
| Quarks | |||
| up-type | up | charm | top |
| down-type | down | strange | bottom |
| Leptons | |||
| charged | electron | muon | tau |
| neutral | electron neutrino | muon neutrino | tau neutrino |
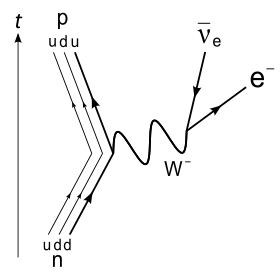 Leptons are involved in several processes such as beta decay. | |
| Composition | Elementary particle |
|---|---|
| Statistics | Fermionic |
| Generation | 1st, 2nd, 3rd |
| Interactions | Electromagnetism, Gravitation, Weak |
| Symbol | ℓ |
| Antiparticle | Antilepton ( ℓ ) |
| Types | 6 (electron, electron neutrino, muon, muon neutrino, tau, tau neutrino) |
| Electric charge | +1 e, 0 e, −1 e |
| Color charge | No |
| Spin | 1⁄2 |
There are six types of leptons, known as flavours, grouped in three generations.[2] The first-generation leptons, also called electronic leptons, comprise the electron (
e−
) and the electron neutrino (
ν
e); the second are the muonic leptons, comprising the muon (
μ−
) and the muon neutrino (
ν
μ); and the third are the tauonic leptons, comprising the tau (
τ−
) and the tau neutrino (
ν
τ). Electrons have the least mass of all the charged leptons. The heavier muons and taus will rapidly change into electrons and neutrinos through a process of particle decay: the transformation from a higher mass state to a lower mass state. Thus electrons are stable and the most common charged lepton in the universe, whereas muons and taus can only be produced in high energy collisions (such as those involving cosmic rays and those carried out in particle accelerators).
Leptons have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, spin, and mass. Unlike quarks, however, leptons are not subject to the strong interaction, but they are subject to the other three fundamental interactions: gravitation, the weak interaction, and to electromagnetism, of which the latter is proportional to charge, and is thus zero for the electrically neutral neutrinos.
For every lepton flavor, there is a corresponding type of antiparticle, known as an antilepton, that differs from the lepton only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. According to certain theories, neutrinos may be their own antiparticle. It is not currently known whether this is the case.
The first charged lepton, the electron, was theorized in the mid-19th century by several scientists[3][4][5] and was discovered in 1897 by J. J. Thomson.[6] The next lepton to be observed was the muon, discovered by Carl D. Anderson in 1936, which was classified as a meson at the time.[7] After investigation, it was realized that the muon did not have the expected properties of a meson, but rather behaved like an electron, only with higher mass. It took until 1947 for the concept of "leptons" as a family of particles to be proposed.[8] The first neutrino, the electron neutrino, was proposed by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930 to explain certain characteristics of beta decay.[8] It was first observed in the Cowan–Reines neutrino experiment conducted by Clyde Cowan and Frederick Reines in 1956.[8][9] The muon neutrino was discovered in 1962 by Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz, and Jack Steinberger,[10] and the tau discovered between 1974 and 1977 by Martin Lewis Perl and his colleagues from the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.[11] The tau neutrino remained elusive until July 2000, when the DONUT collaboration from Fermilab announced its discovery.[12][13]
Leptons are an important part of the Standard Model. Electrons are one of the components of atoms, alongside protons and neutrons. Exotic atoms with muons and taus instead of electrons can also be synthesized, as well as lepton–antilepton particles such as positronium.
Etymology
The name lepton comes from the Greek λεπτός leptós, "fine, small, thin" (neuter nominative/accusative singular form: λεπτόν leptón);[14][15] the earliest attested form of the word is the Mycenaean Greek 𐀩𐀡𐀵, re-po-to, written in Linear B syllabic script.[16] Lepton was first used by physicist Léon Rosenfeld in 1948:[17]
Following a suggestion of Prof. C. Møller, I adopt—as a pendant to "nucleon"—the denomination "lepton" (from λεπτός, small, thin, delicate) to denote a particle of small mass.
The etymology incorrectly implies that all the leptons are of small mass. When Rosenfeld named them, the only known leptons were electrons and muons, whose masses are indeed small compared to nucleons—the mass of an electron (0.511 MeV/c2)[18] and the mass of a muon (with a value of 105.7 MeV/c2)[19] are fractions of the mass of the "heavy" proton (938.3 MeV/c2).[20] However, the mass of the tau (discovered in the mid-1970s) (1777 MeV/c2)[21] is nearly twice that of the proton and about 3,500 times that of the electron.
History
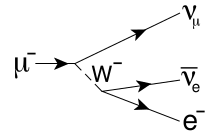
W−
boson. The
W−
boson subsequently decays into an electron and an electron antineutrino.
| Particle name | Antiparticle name |
|---|---|
| Electron | Antielectron Positron |
| Electron neutrino | Electron antineutrino |
| Muon Mu lepton Mu | Antimuon Antimu lepton Antimu |
| Muon neutrino Muonic neutrino Mu neutrino | Muon antineutrino Muonic antineutrino Mu antineutrino |
| Tauon Tau lepton Tau | Antitauon Antitau lepton Antitau |
| Tauon neutrino Tauonic neutrino Tau neutrino | Tauon antineutrino Tauonic antineutrino Tau antineutrino |
The first lepton identified was the electron, discovered by J.J. Thomson and his team of British physicists in 1897.[22][23] Then in 1930, Wolfgang Pauli postulated the electron neutrino to preserve conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, and conservation of angular momentum in beta decay.[24] Pauli theorized that an undetected particle was carrying away the difference between the energy, momentum, and angular momentum of the initial and observed final particles. The electron neutrino was simply called the neutrino, as it was not yet known that neutrinos came in different flavours (or different "generations").
Nearly 40 years after the discovery of the electron, the muon was discovered by Carl D. Anderson in 1936. Due to its mass, it was initially categorized as a meson rather than a lepton.[25] It later became clear that the muon was much more similar to the electron than to mesons, as muons do not undergo the strong interaction, and thus the muon was reclassified: electrons, muons, and the (electron) neutrino were grouped into a new group of particles—the leptons. In 1962, Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz, and Jack Steinberger showed that more than one type of neutrino exists by first detecting interactions of the muon neutrino, which earned them the 1988 Nobel Prize, although by then the different flavours of neutrino had already been theorized.[26]
The tau was first detected in a series of experiments between 1974 and 1977 by Martin Lewis Perl with his colleagues at the SLAC LBL group.[27] Like the electron and the muon, it too was expected to have an associated neutrino. The first evidence for tau neutrinos came from the observation of "missing" energy and momentum in tau decay, analogous to the "missing" energy and momentum in beta decay leading to the discovery of the electron neutrino. The first detection of tau neutrino interactions was announced in 2000 by the DONUT collaboration at Fermilab, making it the second-to-latest particle of the Standard Model to have been directly observed,[28] with Higgs boson being discovered in 2012.
Although all present data is consistent with three generations of leptons, some particle physicists are searching for a fourth generation. The current lower limit on the mass of such a fourth charged lepton is 100.8 GeV/c2,[29] while its associated neutrino would have a mass of at least 45.0 GeV/c2.[30]
Properties
Spin and chirality
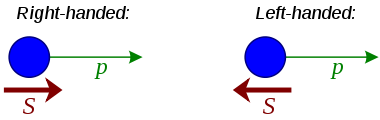
Leptons are spin 1/2 particles. The spin-statistics theorem thus implies that they are fermions and thus that they are subject to the Pauli exclusion principle: No two leptons of the same species can be in the same state at the same time. Furthermore, it means that a lepton can have only two possible spin states, namely up or down.
A closely related property is chirality, which in turn is closely related to a more easily visualized property called helicity. The helicity of a particle is the direction of its spin relative to its momentum; particles with spin in the same direction as their momentum are called right-handed and they are otherwise called left-handed. When a particle is massless, the direction of its momentum relative to its spin is the same in every reference frame, whereas for massive particles it is possible to 'overtake' the particle by choosing a faster-moving reference frame; in the faster frame, the helicity is reversed. Chirality is a technical property, defined through transformation behaviour under the Poincaré group, that does not change with reference frame. It is contrived to agrees with helicity for massless particles, and is still well defined for particles with mass.
In many quantum field theories, such as quantum electrodynamics and quantum chromodynamics, left- and right-handed fermions are identical. However, the Standard Model's Weak interaction treats left-handed and right-handed fermions differently: Only left-handed fermions (and right-handed anti-fermions) participate in the weak interaction. This is an example of parity violation explicitly written into the model. In the literature, left-handed fields are often denoted by a capital L subscript (e.g. the normal electron: eL−) and right-handed fields are denoted by a capital R subscript (e.g. a positron eR+).
Right-handed neutrinos and left-handed anti-neutrinos have no possible interaction with other particles (see sterile neutrinos) and so are not a functional part of the Standard Model, although their exclusion is not a strict requirement; they are sometimes listed in particle tables to emphasize that they would have no active role if included in the model. Even though electrically charged right-handed particles (electron, muon, or tau) do not engage in the weak interaction specifically, they can still interact electrically, and hence still participate in the combined electro-weak force, although with different strengths (YW).
Electromagnetic interaction
One of the most prominent properties of leptons is their electric charge, Q. The electric charge determines the strength of their electromagnetic interactions. It determines the strength of the electric field generated by the particle (see Coulomb's law) and how strongly the particle reacts to an external electric or magnetic field (see Lorentz force). Each generation contains one lepton with Q = −e (conventionally the charge of a particle is expressed in units of the elementary charge) and one lepton with zero electric charge. The lepton with electric charge is commonly simply referred to as a 'charged lepton' while the neutral lepton is called a neutrino. For example, the first generation consists of the electron
e−
with a negative electric charge and the electrically neutral electron neutrino
ν
e.
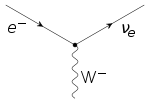
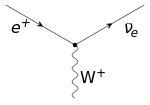
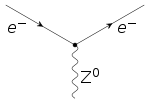
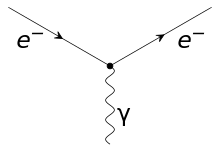
In the language of quantum field theory, the electromagnetic interaction of the charged leptons is expressed by the fact that the particles interact with the quantum of the electromagnetic field, the photon. The Feynman diagram of the electron–photon interaction is shown on the right.
Because leptons possess an intrinsic rotation in the form of their spin, charged leptons generate a magnetic field. The size of their magnetic dipole moment μ is given by
where m is the mass of the lepton and g is the so-called g-factor for the lepton. First-order approximation quantum mechanics predicts that the g-factor is 2 for all leptons. However, higher-order quantum effects caused by loops in Feynman diagrams introduce corrections to this value. These corrections, referred to as the anomalous magnetic dipole moment, are very sensitive to the details of a quantum field theory model and thus provide the opportunity for precision tests of the standard model. The theoretical and measured values for the electron anomalous magnetic dipole moment are within agreement within eight significant figures.[31]
Weak interaction
| ||||||
In the Standard Model, the left-handed charged lepton and the left-handed neutrino are arranged in doublet (
ν
eL,
e−
L) that transforms in the spinor representation (T = 1⁄2) of the weak isospin SU(2) gauge symmetry. This means that these particles are eigenstates of the isospin projection T3 with eigenvalues 1⁄2 and −1⁄2 respectively. In the meantime, the right-handed charged lepton transforms as a weak isospin scalar (T = 0) and thus does not participate in the weak interaction, while there is no evidence that a right-handed neutrino exists at all.
The Higgs mechanism recombines the gauge fields of the weak isospin SU(2) and the weak hypercharge U(1) symmetries to three massive vector bosons (
W+
,
W−
,
Z0
) mediating the weak interaction, and one massless vector boson, the photon, responsible for the electromagnetic interaction. The electric charge Q can be calculated from the isospin projection T3 and weak hypercharge YW through the Gell-Mann–Nishijima formula,
- Q = T3 + ½ YW
To recover the observed electric charges for all particles, the left-handed weak isospin doublet (
ν
eL,
e−
L) must thus have YW = −1, while the right-handed isospin scalar e−
R must have YW = −2. The interaction of the leptons with the massive weak interaction vector bosons is shown in the figure on the right.
Mass
In the Standard Model, each lepton starts out with no intrinsic mass. The charged leptons (i.e. the electron, muon, and tau) obtain an effective mass through interaction with the Higgs field, but the neutrinos remain massless. For technical reasons, the masslessness of the neutrinos implies that there is no mixing of the different generations of charged leptons as there is for quarks. This is in close agreement with current experimental observations.[32]
However, it is known from experiments—most prominently from observed neutrino oscillations[33]—that neutrinos do in fact have some very small mass, probably less than 2 eV/c2.[34] This implies the existence of physics beyond the Standard Model. The currently most favoured extension is the so-called seesaw mechanism, which would explain both why the left-handed neutrinos are so light compared to the corresponding charged leptons, and why we have not yet seen any right-handed neutrinos.
Leptonic numbers
The members of each generation's weak isospin doublet are assigned leptonic numbers that are conserved under the Standard Model.[35] Electrons and electron neutrinos have an electronic number of Le = 1, while muons and muon neutrinos have a muonic number of Lμ = 1, while tau particles and tau neutrinos have a tauonic number of Lτ = 1. The antileptons have their respective generation's leptonic numbers of −1.
Conservation of the leptonic numbers means that the number of leptons of the same type remains the same, when particles interact. This implies that leptons and antileptons must be created in pairs of a single generation. For example, the following processes are allowed under conservation of leptonic numbers:

but not these:
However, neutrino oscillations are known to violate the conservation of the individual leptonic numbers. Such a violation is considered to be smoking gun evidence for physics beyond the Standard Model. A much stronger conservation law is the conservation of the total number of leptons (L), conserved even in the case of neutrino oscillations, but even it is still violated by a tiny amount by the chiral anomaly.
Universality
The coupling of leptons to all types of gauge boson are flavour-independent: The interaction between leptons and a gauge boson measures the same for each lepton.[35] This property is called lepton universality and has been tested in measurements of the tau and muon lifetimes and of Z boson partial decay widths, particularly at the Stanford Linear Collider (SLC) and Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) experiments.[36](pp241–243)[37](p138)
The decay rate () of muons through the process
μ−
→
e−
+
ν
e +
ν
μ is approximately given by an expression of the form (see muon decay for more details)[35]
where K1 is some constant, and GF is the Fermi coupling constant. The decay rate of tau particles through the process
τ−
→
e−
+
ν
e +
ν
τ is given by an expression of the same form[35]
where K2 is some constant. Muon–tauon universality implies that K1 ≈ K2. On the other hand, electron–muon universality implies[35]
This explains why the branching ratios for the electronic mode (17.82%) and muonic (17.39%) mode of tau decay are equal (within error).[21]
Universality also accounts for the ratio of muon and tau lifetimes. The lifetime of a lepton (with = "τ" or "μ") is related to the decay rate by[35]
- ,
where B(x → y) and Γ(x → y) denotes the branching ratios and the resonance width of the process x → y .
The ratio of tau and muon lifetime is thus given by[35]
- .
Using the values of the 2008 Review of Particle Physics for the branching ratios of muons[19] and tau[21] yields a lifetime ratio of ~1.29×10−7, comparable to the measured lifetime ratio of ~1.32×10−7. The difference is due to K1 and K2 not actually being constants: They depend on the mass of leptons.
Recent tests of lepton universality in B meson decays, performed by the LHCb, BaBar and Belle experiments, have shown consistent deviations from the Standard Model predictions. However the combined statistical and systematic significance is not yet high enough to claim an observation of new physics.[38]
Table of leptons
| Particle / Antiparticle name |
Symbol | Charge Q (e) |
Spin J |
Le | Lμ | Lτ | Mass (MeV/c2) |
Lifetime (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electron[18] | e− |
−1 | 1⁄2 | +1 | 0 | 0 | 0.510 998 910 (±13) |
Stable |
| Positron[18] | e+ |
+1 | −1 | |||||
| Muon[19] | μ− |
−1 | 1⁄2 | 0 | +1 | 0 | 105.658 366 8 (±3 8) |
2.197 019×10−6 (±21) |
| Antimuon[19] | μ+ |
+1 | −1 | |||||
| Tau[21] | τ− |
−1 | 1⁄2 | 0 | 0 | +1 | 1 776.84 (±.17) |
2.906×10−13 (±.010) |
| Antitau[21] | τ+ |
+1 | −1 | |||||
| Electron neutrino[34] | ν e |
0 | 1⁄2 | +1 | 0 | 0 | < 0.000 002 2[39] | Unknown |
| Electron antineutrino | ν e |
−1 | ||||||
| Muon neutrino[34] | ν μ |
0 | 1⁄2 | 0 | +1 | 0 | < 0.17[39] | Unknown |
| Muon antineutrino[34] | ν μ |
−1 | ||||||
| Tau neutrino[34] | ν τ |
0 | 1⁄2 | 0 | 0 | +1 | < 15.5[39] | Unknown |
| Tau antineutrino[34] | ν τ |
−1 | ||||||
See also
- Koide formula
- List of particles
- Preons—hypothetical particles which were once postulated to be subcomponents of quarks and leptons
References
{{reflist|25em |refs=
<ref name=PeltoniemiSarkamo2005>{{cite web
|first1=J. |last1=Peltoniemi |first2=J. |last2=Sarkamo |year=2005 |url=http://cupp.oulu.fi/neutrino/nd-mass.html |title=Laboratory measurements and limits for neutrino properties |work=The Ultimate Neutrino Page |accessdate=2008-11-07 |df=dmy-all
Further reading
- Amsler, C.; et al. (Particle Data Group) (2008). "Review of Particle Physics" (PDF). Physics Letters B. 667 (1): 1. Bibcode:2008PhLB..667....1A. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2008.07.018.
- Anicin, I. V. (2005). "The Neutrino: Its Past, Present and Future". arXiv:physics/0503172.
- Fukuda, Y.; et al. (1998). "Evidence for Oscillation of Atmospheric Neutrinos". Physical Review Letters. 81 (8): 1562–1567. arXiv:hep-ex/9807003. Bibcode:1998PhRvL..81.1562F. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.1562.
- Kodama, K.; et al. (2001). "Observation of tau neutrino interactions". Physics Letters B. 504 (3): 218–224. arXiv:hep-ex/0012035. Bibcode:2001PhLB..504..218D. doi:10.1016/S0370-2693(01)00307-0.
- B. R. Martin; G. Shaw (1992). "Chapter 2: Leptons, quarks and hadrons". Particle Physics. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 23–47. ISBN 978-0-471-92358-9.
- Neddermeyer, S. H.; Anderson, C. D. (1937). "Note on the Nature of Cosmic-Ray Particles" (PDF). Physical Review. 51 (10): 884–886. Bibcode:1937PhRv...51..884N. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.51.884.
- Perl, M. L.; et al. (1975). "Evidence for Anomalous Lepton Production in e+–e− Annihilation". Physical Review Letters. 35 (22): 1489–1492. Bibcode:1975PhRvL..35.1489P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.35.1489.
- Peskin, M. E.; Schroeder, D. V. (1995). Introduction to Quantum Field Theory. Westview Press. ISBN 978-0-201-50397-5.
- Riesselmann, K. (2007). "Logbook: Neutrino Invention". Symmetry Magazine. 4 (2). Archived from the original on 31 May 2009.
- Rosenfeld, L. (1948). Nuclear Forces. Interscience Publishers. p. xvii.
- Shankar, R. (1994). "Chapter 2: Rotational Invariance and Angular Momentum". Principles of Quantum Mechanics (2nd ed.). Springer. pp. 305–352. ISBN 978-0-306-44790-7.
- Weinberg, S. (2003). The Discovery of Subatomic Particles. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-82351-7.
- Wilson, R. (1997). Astronomy Through the Ages: The Story of the Human Attempt to Understand the Universe. CRC Press. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-7484-0748-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Leptons. |
| Look up lepton in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- "Particle Data Group homepage". – The PDG compiles authoritative information on particle properties.
- "Leptons". Physics & Astronomy. Georgia State University. Hyperphysics. – a summary of leptons.
- "Lepton (physics)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2010-09-29.
- Nave, R. "Leptons". HyperPhysics. Georgia State University, Department of Physics and Astronomy. Retrieved 2010-09-29.
- Farrar, W. V. (1969). "Richard Laming and the Coal-Gas Industry, with His Views on the Structure of Matter". Annals of Science. 25 (3): 243–254. doi:10.1080/00033796900200141.
- Arabatzis, T. (2006). Representing Electrons: A Biographical Approach to Theoretical Entities. University of Chicago Press. pp. 70–74. ISBN 978-0-226-02421-9.
- Buchwald, J. Z.; Warwick, A. (2001). Histories of the Electron: The Birth of Microphysics. MIT Press. pp. 195–203. ISBN 978-0-262-52424-7.
- Thomson, J. J. (1897). "Cathode Rays". Philosophical Magazine. 44 (269): 293. doi:10.1080/14786449708621070.
- Neddermeyer, S. H.; Anderson, C. D. (1937). "Note on the Nature of Cosmic-Ray Particles" (PDF). Physical Review. 51 (10): 884–886. Bibcode:1937PhRv...51..884N. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.51.884.
- "The Reines-Cowan Experiments: Detecting the Poltergeist" (PDF). Los Alamos Science. 25: 3. 1997. Retrieved 2010-02-10.
- Reines, F.; Cowan, C.L., Jr. (1956). "The Neutrino". Nature. 178 (4531): 446. Bibcode:1956Natur.178..446R. doi:10.1038/178446a0.
- Danby, G.; et al. (1962). "Observation of high-energy neutrino reactions and the existence of two kinds of neutrinos". Physical Review Letters. 9 (1): 36. Bibcode:1962PhRvL...9...36D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.9.36.
-
Perl, M. L.; et al. (1975). "Evidence for Anomalous Lepton Production in
e+
e−
Annihilation". Physical Review Letters. 35 (22): 1489. Bibcode:1975PhRvL..35.1489P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.35.1489. - "Physicists find first direct evidence for tau neutrino at Fermilab" (Press release). Fermilab. 20 July 2000.
- "Observation of tau neutrino interactions". Physics Letters B. 504 (3): 218–224. 2001. arXiv:hep-ex/0012035. Bibcode:2001PhLB..504..218D. doi:10.1016/S0370-2693(01)00307-0.
- "lepton". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- λεπτός. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- Found on the KN L 693 and PY Un 1322 tablets. "The Linear B word re-po-to". Palaeolexicon. Word study tool of ancient languages. Raymoure, K.A. "re-po-to". Minoan Linear A & Mycenaean Linear B. Deaditerranean. "KN 693 L (103)". "PY 1322 Un + fr. (Cii)". DĀMOS: Database of Mycenaean at Oslo. University of Oslo.
- L. Rosenfeld (1948)
- C. Amsler et al. (2008): Particle listings—
e− - C. Amsler et al. (2008): Particle listings—
μ− - C. Amsler et al. (2008): Particle listings—
p+ - C. Amsler et al. (2008): Particle listings—
τ− - S. Weinberg (2003)
- R. Wilson (1997)
- K. Riesselmann (2007)
- S. H. Neddermeyer, C. D. Anderson (1937)
- I. V. Anicin (2005)
- M. L. Perl et al. (1975)
- K. Kodama (2001)
- C. Amsler et al. (2008) Heavy Charged Leptons Searches
- C. Amsler et al. (2008) Searches for Heavy Neutral Leptons
- M. E. Peskin, D. V. Schroeder (1995), p. 197
- M. E. Peskin, D. V. Schroeder (1995), p. 27
- Y. Fukuda et al. (1998)
- Amsler, C.; et al. (2008). "Particle listings — Neutrino properties" (PDF).
- B. R. Martin, G. Shaw (1992)
- Cumalat, J. P. (1993). Physics in Collision 12. Atlantica Séguier Frontières. ISBN 978-2-86332-129-4.
- Fraser, G. (1 January 1998). The Particle Century. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-5033-2.
- Ciezarek G, Franco Sevilla M, Hamilton B, Kowalewski R, Kuhr T, Lüth V, Sato Y (2017). "A challenge to lepton universality in B-meson decays". Nature. 546 (7657): 227–233. arXiv:1703.01766. Bibcode:2017Natur.546..227C. doi:10.1038/nature22346. PMID 28593973.