Glueball
In particle physics, a glueball (also gluonium, gluon-ball) is a hypothetical composite particle.[1] It consists solely of gluon particles, without valence quarks. Such a state is possible because gluons carry color charge and experience the strong interaction between themselves. Glueballs are extremely difficult to identify in particle accelerators, because they mix with ordinary meson states.[2]
| Standard Model of particle physics |
|---|
 |
|
Scientists Rutherford · Thomson · Chadwick · Bose · Sudarshan · Koshiba · Davis Jr. · Anderson · Fermi · Dirac · Feynman · Rubbia · Gell-Mann · Kendall · Taylor · Friedman · Powell · P. W. Anderson · Glashow · Iliopoulos · Maiani · Meer · Cowan · Nambu · Chamberlain · Cabibbo · Schwartz · Perl · Majorana · Weinberg · Lee · Ward · Salam · Kobayashi · Maskawa · Yang · Yukawa · 't Hooft · Veltman · Gross · Politzer · Wilczek · Cronin · Fitch · Vleck · Higgs · Englert · Brout · Hagen · Guralnik · Kibble · Ting · Richter |
Theoretical calculations show that glueballs should exist at energy ranges accessible with current collider technology. However, due to the aforementioned difficulty (among others), they have so far not been observed and identified with certainty,[3] although phenomenological calculations have suggested that an experimentally identified glueball candidate, denoted , has properties consistent with those expected of a Standard Model glueball.[4]
The prediction that glueballs exist is one of the most important predictions of the Standard Model of particle physics that has not yet been confirmed experimentally.[5] Glueballs are the only particles predicted by the Standard Model with total angular momentum (J) (sometimes called "intrinsic spin") that could be either 2 or 3 in their ground states.
Properties
In principle, it is theoretically possible for all properties of glueballs to be calculated exactly and derived directly from the equations and fundamental physical constants of quantum chromodynamics (QCD) without further experimental input. So, the predicted properties of these hypothetical particles can be described in exquisite detail using only Standard Model physics which have wide acceptance in the theoretical physics literature. But, there is considerable uncertainty in the measurement of some of the relevant key physical constants, and the QCD calculations are so difficult that solutions to these equations are almost always numerical approximations (reached by several very different methodologies). This can lead to variation in theoretical predictions of glueball properties like mass and branching ratios in glueball decays.
Constituent particles and color charge
Theoretical studies of glueballs have focused on glueballs consisting of either two gluons or three gluons, by analogy to mesons and baryons that have two and three quarks respectively. As in the case of mesons and baryons, glueballs would be QCD color charge neutral. The baryon number of a glueball is zero.
Total angular momentum
Two gluon glueballs can have total angular momentum (J) of 0 (which are scalar or pseudo-scalar) or 2 (tensor). Three gluon glueballs can have total angular momentum (J) of 1 (vector boson) or 3. All glueballs have integer total angular momentum which implies that they are bosons rather than fermions.
Glueballs are the only particles predicted by the Standard Model with total angular momentum (J) (sometimes called "intrinsic spin") that could be either 2 or 3 in their ground states, although mesons made of two quarks with J=0 and J=1 with similar masses have been observed and excited states of other mesons can have these values of total angular momentum.
Fundamental particles with ground states having J=0 or J=2 are easily distinguished from glueballs. The hypothetical graviton, while having a total angular momentum J=2 would be massless and lack color charge, and so would be easily distinguished from glueballs. The Standard Model Higgs boson for which an experimentally measured mass of about 125–126 GeV/c2 has been determined is the only fundamental particle with J=0 in the Standard Model. It also lacks color charge and hence does not engage in strong force interactions. The Higgs boson is also about 25–80 times as heavy as the mass of the various glueball states predicted by the Standard Model.
Electric charge
All glueballs would have an electric charge of zero as gluons themselves do not have an electric charge.
Mass and parity
Glueballs are predicted by quantum chromodynamics to be massive, despite the fact that gluons themselves have zero rest mass in the Standard Model. Glueballs with all four possible combinations of quantum numbers P (parity) and C (c-parity) for every possible total angular momentum have been considered, producing at least fifteen possible glueball states including excited glueball states that share the same quantum numbers but have differing masses with the lightest states having masses as low as 1.4 GeV/c2 (for a glueball with quantum numbers J=0, P=+, C=+), and the heaviest states having masses as great as almost 5 GeV/c2 (for a glueball with quantum numbers J=0, P=+, C=-).[3]
These masses are on the same order of magnitude as the masses of many experimentally observed mesons and baryons, as well as to the masses of the tau lepton, charm quark, bottom quark, some hydrogen isotopes, and some helium isotopes.
Stability and decay channels
Just as all Standard Model mesons and baryons, except the proton, are unstable in isolation, all glueballs are predicted by the Standard Model to be unstable in isolation, with various QCD calculations predicting the total decay width (which is functionally related to half-life) for various glueball states. QCD calculations also make predictions regarding the expected decay patterns of glueballs.[6][7] For example, glueballs would not have radiative or two photon decays, but would have decays into pairs of pions, pairs of kaons, or pairs of eta mesons.[6]
Practical impact on macroscopic low energy physics
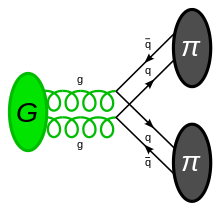
π
). Such decays help the study of and search for glueballs.[8]
Because Standard Model glueballs are so ephemeral (decaying almost immediately into more stable decay products) and are only generated in high energy physics, glueballs only arise synthetically in the natural conditions found on Earth that humans can easily observe. They are scientifically notable mostly because they are a testable prediction of the Standard Model, and not because of phenomenological impact on macroscopic processes, or their engineering applications.
Lattice QCD simulations
Lattice QCD provides a way to study the glueball spectrum theoretically and from first principles. Some of the first quantities calculated using lattice QCD methods (in 1980) were glueball mass estimates.[9] Morningstar and Peardon[10] computed in 1999 the masses of the lightest glueballs in QCD without dynamical quarks. The three lowest states are tabulated below. The presence of dynamical quarks would slightly alter these data, but also makes the computations more difficult. Since that time calculations within QCD (lattice and sum rules) find the lightest glueball to be a scalar with mass in the range of about 1000–1700 MeV.[3]
| J P'C | mass |
|---|---|
| 0++ | 1730 ±80 MeV |
| 2++ | 2400 ±120 MeV |
| 0−+ | 2590 ±130 MeV |
Experimental candidates
Particle accelerator experiments are often able to identify unstable composite particles and assign masses to those particles to a precision of approximately 10 MeV/c2, without being able to immediately assign to the particle resonance that is observed all of the properties of that particle. Scores of such particles have been detected, although particles detected in some experiments but not others can be viewed as doubtful. Some of the candidate particle resonances that could be glueballs, although the evidence is not definitive, include the following:
Vector, pseudo-vector, or tensor glueball candidates
Scalar glueball candidates
- f0(500) also known as σ – the properties of this particle are possibly consistent with a 1000 MeV or 1500 MeV mass glueball.[3]
- f0(980) – the structure of this composite particle is consistent with the existence of a light glueball.[3]
- f0(1370) – existence of this resonance is disputed but is a candidate for a glueball-meson mixing state[3]
- f0(1500) – existence of this resonance is undisputed but its status as a glueball-meson mixing state or pure glueball is not well established.[3]
- f0(1710) – existence of this resonance is undisputed but its status as a glueball-meson mixing state or pure glueball is not well established.[3]
Other candidates
- Gluon jets at the LEP experiment show a 40% excess over theoretical expectations of electromagnetically neutral clusters which suggests that electromagnetically neutral particles expected in gluon rich environments such as glueballs are likely to be present.[3]
Many of these candidates have been the subject of active investigation for at least eighteen years.[6] The GlueX experiment has been specifically designed to produce more definitive experimental evidence of glueballs.[11]
See also
References
- Frank Close and Phillip R. Page, "Glueballs", Scientific American, vol. 279 no. 5 (November 1998) pp. 80–85
- Vincent Mathieu; Nikolai Kochelev; Vicente Vento (2009). "The Physics of Glueballs". International Journal of Modern Physics E. 18 (1): 1–49. arXiv:0810.4453. Bibcode:2009IJMPE..18....1M. doi:10.1142/S0218301309012124. S2CID 119229404. Glueball on arxiv.org
- Wolfgang Ochs (2013). "The status of glueballs". Journal of Physics G. 40 (4): 043001. arXiv:1301.5183. Bibcode:2013JPhG...40d3001O. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/40/4/043001. S2CID 73696704.
- Frederic Brünner; Anton Rebhan (2015-09-21). "Nonchiral Enhancement of Scalar Glueball Decay in the Witten-Sakai-Sugimoto Model". Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 (13): 131601. arXiv:1504.05815. Bibcode:2015PhRvL.115m1601B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.131601. PMID 26451541. S2CID 14043746.
- Hsiao, Y.K.; Geng, C.Q. (2013). "Identifying glueball at 3.02 GeV in baryonic B decays". Physics Letters B. 727 (1–3): 168–171. arXiv:1302.3331. Bibcode:2013PhLB..727..168H. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2013.10.008. S2CID 119235634.
- Walter Taki, "Search for Glueballs" (1996) http://www.slac.stanford.edu/cgi-wrap/getdoc/ssi96-006.pdf
- Eshraim, Walaa I.; Janowski, Stanislaus (2013). "Branching ratios of the pseudoscalar glueball with a mass of 2.6 GeV". arXiv:1301.3345. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - T. Cohen; F. J. Llanes-Estrada; J. R. Pelaez; J. Ruiz de Elvira (2014). "Non-ordinary light meson couplings and the 1/Nc expansion". Physical Review D. 90 (3): 036003. arXiv:1405.4831. Bibcode:2014PhRvD..90c6003C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.90.036003. S2CID 53313057.
- B. Berg. Plaquette-plaquette correlations in the su(2) lattice gauge theory. Phys. Lett., B97:401, 1980.
- Colin J. Morningstar; Mike Peardon (1999). "Glueball spectrum from an anisotropic lattice study". Physical Review D. 60 (3): 034509. arXiv:hep-lat/9901004. Bibcode:1999PhRvD..60c4509M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.60.034509. S2CID 18787544.
- "The Physics of GlueX".