Dacryocystocele
Dacryocystocele or timo cyst is a benign, bluish-gray mass in the inferomedial canthus that forms as a result of a narrowing or obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, usually during prenatal development. The prevalence of dacryocystocele is 1 in 3884 live births.[1]
| Dacryocystocele | |
|---|---|
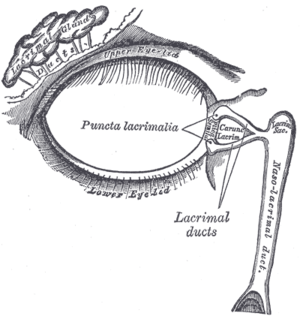 | |
| Nasolacrimal duct | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Complications like swelling, watery eyes and infection might occur. While usually filled with sterile mucus, dacryocystoceles occasionally become infected.
Pathophysiology
The nasolacrimal ducts drain the excess tears from our eyes into the nasal cavity. In dacryocystocele there this tube gets blocked on either end and as a result when mucoid fluid collects in the intermediate patent section it forms a cystic structure.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis can be made prenatally; routine obstetric ultrasound can identify the characteristic hypoechoic lesion inferior and medial to the globe. It is important to distinguish a dacrocystocele from the more serious encephalocele, which is a neural tube defect.
A dacryocystocele can be diagnosed postpartum with a non-invasive ultrasound (US).[2]
Management
Timo cysts may spontaneously resolve or with pressure directed toward the nose; however, nasolacrimal duct probing may be required to open the obstruction.
See also
References
- Julia Shekunov; Gregory J. Griepentrog; Nancy N. Diehl & Brian G. Mohney (October 2010). "Prevalence and clinical characteristics of congenital dacryocystocele". Journal of AAPOS. 14 (5): 417–420. doi:10.1016/j.jaapos.2010.07.006. PMC 3115742. PMID 21035068.
- Cavazza, S; Laffi, GL; Lodi, L; Tassinari, G; Dall'Olio, D (December 2008). "Congenital dacryocystocele: diagnosis and treatment". Acta Otorhinolaryngol Italy. 28 (6): 298–301. PMC 2689544. PMID 19205594.