Comparison of birth control methods
There are many different methods of birth control, which vary in what is required of the user, side effects, and effectiveness. It is also important to note that not each type of birth control is ideal for each user. Outlined here are the different types of barrier methods, spermicides, or coitus interruptus that must be used at or before every act of intercourse. Immediate contraception, like physical barriers, include diaphragms, caps, the contraceptive sponge, and female condoms may be placed several hours before intercourse begins (note that when using the female condom, the penis must be guided into place when initiating intercourse). The female condom should be removed immediately after intercourse, and before arising.[1] Some other female barrier methods must be left in place for several hours after sex. Depending on the form of spermicide used, they may be applied several minutes to an hour before intercourse begins. Additionally, the male condom should be applied when the penis is erect so that it is properly applied prior to intercourse.
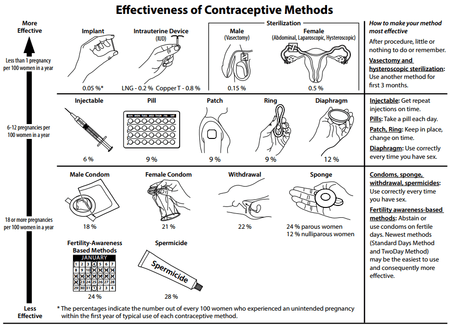
With an insertion of an IUD (intrauterine device), female or male sterilization, or hormone implant, there is very little required of the user post initial procedure; there is nothing to put in place before intercourse to prevent pregnancy.[2] Intrauterine methods require clinic visits for installation and removal or replacement (if desired) only once every several years (5-12), depending on the device. This allows the user to be able to try and become pregnant if they so desire, upon removal of the IUD. Conversely, sterilization is a one-time, permanent procedure. After the success of surgery is verified (for vasectomy), no subsequent action is usually required of users.
Implants provide effective birth control for three years without any user action between insertion and removal of the implant. Insertion and removal of the Implant involves a minor surgical procedure. Oral contraceptives require some action every day. Other hormonal methods require less frequent action - weekly for the patch, twice a month for vaginal ring, monthly for combined injectable contraceptive, and every twelve weeks for MPA shots. Fertility awareness-based methods require some action every day to monitor and record fertility signs. The lactational amenorrhea method (LAM) requires breast feeding at least every four to six hours.
User dependence
Different methods require different levels of diligence by users. Methods with little or nothing to do or remember, or that require a clinic visit less than once per year are said to be non-user dependent, forgettable or top-tier methods.[1] Intrauterine methods, implants and sterilization fall into this category.[1] For methods that are not user dependent, the actual and perfect-use failure rates are very similar.
Many hormonal methods of birth control, and LAM require a moderate level of thoughtfulness. For many hormonal methods, clinic visits must be made every three months to a year to renew the prescription. The pill must be taken every day, the patch must be reapplied weekly, or the ring must be replaced monthly. Injections are required every 12 weeks. The rules for LAM must be followed every day. Both LAM and hormonal methods provide a reduced level of protection against pregnancy if they are occasionally used incorrectly (rarely going longer than 4–6 hours between breastfeeds, a late pill or injection, or forgetting to replace a patch or ring on time). The actual failure rates for LAM and hormonal methods are somewhat higher than the perfect-use failure rates.
Higher levels of user commitment are required for other methods.[2] Barrier methods, coitus interruptus, and spermicides must be used at every act of intercourse. Fertility awareness-based methods may require daily tracking of the menstrual cycle. The actual failure rates for these methods may be much higher than the perfect-use failure rates.[3]
Side effects
Different forms of birth control have different potential side effects. Not all, or even most, users will experience side effects from a method.
The less effective the method, the greater the risk of the side-effects associated with pregnancy.
Minimal or no other side effects are possible with coitus interruptus, fertility awareness-based, and LAM. Some forms of periodic abstinence encourage examination of the cervix; insertion of the fingers into the vagina to perform this examination may cause changes in the vaginal environment. Following the rules for LAM may delay a woman's first post-partum menstruation beyond what would be expected from different breastfeeding practices.
Barrier methods have a risk of allergic reaction. Users sensitive to latex may use barriers made of less allergenic materials - polyurethane condoms, or silicone diaphragms, for example. Barrier methods are also often combined with spermicides, which have possible side effects of genital irritation, vaginal infection, and urinary tract infection.
Sterilization procedures are generally considered to have low risk of side effects, though some persons and organizations disagree.[4][5] Female sterilization is a more significant operation than vasectomy, and has greater risks; in industrialized nations, mortality is 4 per 100,000 tubal ligations, versus 0.1 per 100,000 vasectomies.[6]
After IUD insertion, users may experience irregular periods in the first 3–6 months with Mirena, and sometimes heavier periods and worse menstrual cramps with ParaGard. However, continuation rates are much higher with IUDs compared to non-long-acting methods.[7] A positive characteristic of IUDs is that fertility and the ability to become pregnant returns quickly once the IUD is removed.[8]
Because of their systemic nature, hormonal methods have the largest number of possible side effects.[9]
Sexually transmitted disease prevention
Male and female condoms provide significant protection against sexually transmitted diseases (STD) when used consistently and correctly. They also provide some protection against cervical cancer.[10][11] Condoms are often recommended as an adjunct to more effective birth control methods (such as IUD) in situations where STD protection is also desired.[12]
Other barrier methods, such as diaphragm may provide limited protection against infections in the upper genital tract. Other methods provide little or no protection against sexually transmitted diseases.
Effectiveness calculation
Failure rates may be calculated by either the Pearl Index or a life table method. A "perfect-use" rate is where any rules of the method are rigorously followed, and (if applicable) the method is used at every act of intercourse.
Actual failure rates are higher than perfect-use rates for a variety of reasons:
- mistakes on the part of those providing instructions on how to use the method
- mistakes on the part of the method's users
- conscious user non-compliance with method.
- insurance providers sometimes impede access to medications (e.g. require prescription refills on a monthly basis)[13]
For instance, someone using oral forms of hormonal birth control might be given incorrect information by a health care provider as to the frequency of intake, or for some reason not take the pill one or several days, or not go to the pharmacy on time to renew the prescription, or the pharmacy might be unwilling to provide enough pills to cover an extended absence.
Effectiveness
The table below color codes the typical-use and perfect-use failure rates, where the failure rate is measured as the expected number of pregnancies per year per woman using the method:
Blue under 1% lower risk Green up to 5% Yellow up to 10% Orange up to 20% Red over 20% higher risk Grey no data no data available
For example, a failure rate of 20% means that 20 of 100 women become pregnant during the first year of use. Note that the rate may go above 100% if all women, on average, become pregnant within less than a year. In the degenerated case of all women becoming pregnant instantly, the rate would be infinite.
In the user action required column, items that are non-user dependent (require action once per year or less) also have a blue background.
Some methods may be used simultaneously for higher effectiveness rates. For example, using condoms with spermicides the estimated perfect use failure rate would be comparable to the perfect use failure rate of the implant.[1] However, mathematically combining the rates to estimate the effectiveness of combined methods can be inaccurate, as the effectiveness of each method is not necessarily independent, except in the perfect case.[14]
If a method is known or suspected to have been ineffective, such as a condom breaking, emergency contraception (ECP) may be taken up to 72 to 120 hours after sexual intercourse. Emergency contraception should be taken shortly before or as soon after intercourse as possible, as its efficacy decreases with increasing delay. Although ECP is considered an emergency measure, levonorgestrel ECP taken shortly before sex may be used as a primary method for woman who have sex only a few times a year and want a hormonal method, but don’t want to take hormones all the time.[15] Failure rate of repeated or regular use of LNG ECP is similar to rate for those using a barrier method.[16]
This table lists the rate of pregnancy during the first year of use.
| Birth control method | Brand/common name | Typical-use failure rate (%) | Perfect-use failure rate (%) | Type | Implementation | User action required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contraceptive implant | Implanon,[17] Jadelle,[18] the implant | 0.05 (1 of 2000) | 0.05 | Progestogen | Subdermal implant | 3-5 years |
| Vasectomy[17] | male sterilization | 0.15 (1 of 666) | 0.1 | Sterilization | Surgical procedure | Once |
| Combined injectable[19] | Lunelle, Cyclofem | 0.2 (1 of 500) | 0.2 | Estrogen + progestogen | Injection | Monthly |
| IUD with progestogen[17] | Mirena, Skyla, Liletta | 0.2 (1 of 500) | 0.2 | Intrauterine & progestogen | Intrauterine | 3-7 years |
| Essure[20] | female sterilization | 0.26 (1 of 384) | 0.26 | Sterilization | Surgical procedure | Once |
| Tubal ligation[17] | female sterilization | 0.5 (1 of 200) | 0.5 | Sterilization | Surgical procedure | Once |
| IUD with copper[17] | Paragard, Copper T, the coil | 0.8 (1 of 125) | 0.6 | Intrauterine & copper | Intrauterine | 3 to 12+ years |
| Forschungsgruppe NFP symptothermal method, teaching sessions + application[17][21] | Sensiplan by Arbeitsgruppe NFP (Malteser Germany gGmbh) | 1.8 (1 of 55) | 0.4 | Behavioral | Teaching sessions, observation, charting and evaluating a combination of fertility symptoms | Three teaching sessions + daily application |
| LAM for 6 months only; not applicable if menstruation resumes[22][note 1] | ecological breastfeeding | 2 (1 of 50) | 0.5 | Behavioral | Breastfeeding | Every few hours |
| 2002[23] cervical cap and spermicide (discontinued in 2008) used by nulliparous[24][note 2][note 3] | Lea's Shield | 5 (1 of 20) | no data | Barrier + spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| MPA shot[17] | Depo Provera, the shot | 6 (1 of 17) | 0.2 | Progestogen | Injection | 12 weeks |
| Testosterone injection for male (unapproved, experimental method)[25] | Testosterone Undecanoate | 6.1 (1 of 16) | 1.1 | Testosterone | Intramuscular Injection | Every 4 weeks |
| 1999 cervical cap and spermicide (replaced by second generation in 2003)[26] | FemCap | 7.6 (estimated) (1 of 13) | no data | Barrier & spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| Contraceptive patch[17] | Ortho Evra, the patch | 9 (1 of 12) | 0.3 | Estrogen & progestogen | Transdermal patch | Weekly |
| Combined oral contraceptive pill[17] | the Pill | 9 (1 of 11)[27] | 0.3 | Estrogen & progestogen + Placebo[28] | Oral medication | Daily |
| Ethinylestradiol/etonogestrel vaginal ring[17] | NuvaRing, the ring | 9 (1 of 11) | 0.3 | Estrogen & progestogen | Vaginal insertion | In place 3 weeks / 1 week break |
| Progestogen only pill[17] | POP, minipill | 9[27] | 0.3 | Progestogen[28] | Oral medication | Daily |
| Ormeloxifene[29] | Saheli, Centron | 9 | 2 | SERM | Oral medication | Weekly |
| Emergency contraception pill | Plan B One-Step® | no data | no data | Levonorgestrel | Oral medication | Every act of intercourse |
| Standard Days Method[17] | CycleBeads, iCycleBeads | 12 (1 of 8.3) | 5 | Behavioral | Counting days since menstruation | Daily |
| Diaphragm and spermicide[17] | 12 (1 of 6) | 6 | Barrier & spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse | |
| Plastic contraceptive sponge with spermicide used by nulliparous[17][note 3] | Today sponge, the sponge | 12 | 9 | Barrier & spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| 2002[23] cervical cap and spermicide (discontinued in 2008) used by parous[24][note 2][note 4] | Lea's Shield | 15 (1 of 6) | no data | Barrier + spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| 1988 cervical cap and spermicide (discontinued in 2005) used by nulliparous[note 3] | Prentif | 16 | 9 | Barrier + spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| Male latex condom[17][27] | Condom | 18 (1 of 5) | 2 | Barrier | Placed on erect penis | Every act of intercourse |
| Female condom[17] | 21 (1 of 4.7) | 5 | Barrier | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse | |
| Coitus interruptus[17] | withdrawal method, pulling out | 22 (1 of 5)[30] | 4 | Behavioral | Withdrawal | Every act of intercourse |
| Symptoms-based fertility awareness ex. symptothermal and calendar-based methods[17][note 5][note 6] | TwoDay method, Billings ovulation method, Creighton Model | 24 (1 of 4) | 3–4 | Behavioral | Observation and charting of basal body temperature, cervical mucus or cervical position | Throughout day or daily[note 7] |
| Calendar-based methods[17] | the rhythm method, Knaus-Ogino method, Standard Days method | no data | 5 | Behavioral | Calendar-based | Daily |
| Plastic contraceptive sponge with spermicide used by parous[17][note 4] | Today sponge, the sponge | 24 (1 of 4) | 20 | Barrier & spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| Spermicidal gel, foam, suppository, or film[17] | 28 (1 of 4) | 18 | Spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse | |
| 1988 cervical cap and spermicide (discontinued in 2005) used by parous[note 4] | Prentif | 32 | 26 | Barrier + spermicide | Vaginal insertion | Every act of intercourse |
| Abstinence pledge[note 8][31] | 50–57.5 (estimated) (1 of 2) | no data | Behavioral | Commitment | Once | |
| None (unprotected intercourse)[17] | 85 (6 of 7) | 85 | Behavioral | Discontinuing birth control | N/A | |
| Placebo[32] | 100[note 9] (all, after about half a year) | 100 | Placebo | Oral medication | Daily | |
| Birth control method | Brand/common name | Typical-use failure rate (%) | Perfect-use failure rate (%) | Type | Implementation | User action required |
Table notes
- The pregnancy rate applies until the user reaches six months postpartum, or until menstruation resumes, whichever comes first. If menstruation occurs earlier than six months postpartum, the method is no longer effective. For users for whom menstruation does not occur within the six months: after six months postpartum, the method becomes less effective.
- In the effectiveness study of Lea's Shield, 84% of participants were parous. The unadjusted pregnancy rate in the six-month study was 8.7% among spermicide users and 12.9% among non-spermicide users. No pregnancies occurred among nulliparous users of the Lea's Shield. Assuming the effectiveness ratio of nulliparous to parous users is the same for the Lea's Shield as for the Prentif cervical cap and the Today contraceptive sponge, the unadjusted six-month pregnancy rate would be 2.2% for spermicide users and 2.9% for those who used the device without spermicide.
- Nulliparous refers to those who have not given birth.
- Parous refers to those who have given birth.
- No formal studies meet the standards of Contraceptive Technology for determining typical effectiveness. The typical effectiveness listed here is from the CDC's National Survey of Family Growth, which grouped symptoms-based methods together with calendar-based methods. See Fertility awareness#Effectiveness.
- The term fertility awareness is sometimes used interchangeably with the term natural family planning (NFP), though NFP usually refers to use of periodic abstinence in accordance with Catholic beliefs.
- Users may observe one of the three primary fertility signs. Basal body temperature (BBT) and cervical position are checked once per day. Cervical mucus is checked before each urination, and vaginal sensation is observed throughout the day. The observed sign or signs are recorded once per day.
- Strictly speaking, abstinence pledges are not a method of birth control, as their purpose is preservation of the virginity of unmarried girls, with prevention of pregnancies only being a side-effect. This also means that they are restricted to the time before marriage.
- Several factors may contribute to the fact that the placebo was observed to be significantly less effective than unprotected intercourse: 1. The study was not representative, as it only considered women of low socioeconomic level who had aborted spontaneously and desired pregnancy, 2. the placebo may have caused behavioral differences compared to unprotected intercourse: the couples might assume to be protected and thus be less reluctant to have sex and/or be in a different psychological mood that increases fertility via psychosomatic action
Table references
- Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL, eds. (2011). Contraceptive Technology (20th ed.). New York: Ardent Media. ISBN 978-1-59708-004-0.
- Shears KH, Aradhya KW (July 2008). Helping women understand contraceptive effectiveness (PDF) (Report). Family Health International.
- Trussell J (2007). "Contraceptive Efficacy". In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL (eds.). Contraceptive Technology (19th ed.). New York: Ardent Media. ISBN 978-0-9664902-0-6.
- Bloomquist M (May 2000). "Getting Your Tubes Tied: Is this common procedure causing uncommon problems?". MedicineNet.com. WebMD. Retrieved 2006-09-25.
- Hauber KC. "If It Works, Don't Fix It!". Retrieved 2006-09-25.
- Awsare NS, Krishnan J, Boustead GB, Hanbury DC, McNicholas TA (November 2005). "Complications of vasectomy". Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 87 (6): 406–10. doi:10.1308/003588405X71054. PMC 1964127. PMID 16263006.
- Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology, Long-Acting Reversible Contraception Work Group (November 2017). "Practice Bulletin No. 186: Long-Acting Reversible Contraception: Implants and Intrauterine Devices". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 130 (5): e251–e269. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000002400. ISSN 1873-233X. PMID 29064972.
- "Planned Parenthood IUD Birth Control - Mirena IUD - ParaGard IUD". Retrieved 2012-02-26.
- Staff, Healthwise. "Advantages and Disadvantages of Hormonal Birth Control". Retrieved 2010-07-06.
- Winer RL, Hughes JP, Feng Q, O'Reilly S, Kiviat NB, Holmes KK, Koutsky LA (June 2006). "Condom use and the risk of genital human papillomavirus infection in young women". The New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (25): 2645–54. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa053284. PMID 16790697.
- Hogewoning CJ, Bleeker MC, van den Brule AJ, Voorhorst FJ, Snijders PJ, Berkhof J, Westenend PJ, Meijer CJ (December 2003). "Condom use promotes regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and clearance of human papillomavirus: a randomized clinical trial". International Journal of Cancer. 107 (5): 811–6. doi:10.1002/ijc.11474. PMID 14566832.
- Cates W, Steiner MJ (March 2002). "Dual protection against unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections: what is the best contraceptive approach?". Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 29 (3): 168–74. doi:10.1097/00007435-200203000-00007. PMID 11875378.
- Trussell J, Wynn LL (January 2008). "Reducing unintended pregnancy in the United States". Contraception. 77 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2007.09.001. PMID 18082659.
- Kestelman P, Trussell J (1991). "Efficacy of the simultaneous use of condoms and spermicides". Family Planning Perspectives. 23 (5): 226–7, 232. doi:10.2307/2135759. JSTOR 2135759. PMID 1743276.
- Shelton JD (July 2002). "Repeat emergency contraception: facing our fears". Contraception. 66 (1): 15–7. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(02)00313-X. PMID 12169375.
- "Efficacy and side effects of immediate postcoital levonorgestrel used repeatedly for contraception. United Nations Development Programme/ United Nations Population Fund/World Health Organization/World Bank Special Programme of Research, Development and Research Training in Human Reproduction, Task Force on Post-Ovulatory Methods of Fertility Regulation. vonhertzenh@who.ch". Contraception. 61 (5): 303–8. May 2000. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(00)00116-5. PMID 10906500.
- Trussell J (May 2011). "Contraceptive failure in the United States". Contraception. 83 (5): 397–404. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2011.01.021. PMC 3638209. PMID 21477680.
- Sivin I, Campodonico I, Kiriwat O, Holma P, Diaz S, Wan L, Biswas A, Viegas O, et al. (December 1998). "The performance of levonorgestrel rod and Norplant contraceptive implants: a 5 year randomized study". Human Reproduction. 13 (12): 3371–8. doi:10.1093/humrep/13.12.3371. PMID 9886517.
- "FDA Approves Combined Monthly Injectable Contraceptive". The Contraception Report. Contraception Online. June 2001. Archived from the original on October 18, 2007. Retrieved 2008-04-13.
- "Essure System - P020014". United States Food and Drug Administration Center for Devices and Radiological Health. Archived from the original on 2008-12-04.
- Frank-Herrmann P, Heil J, Gnoth C, Toledo E, Baur S, Pyper C, Jenetzky E, Strowitzki T, et al. (May 2007). "The effectiveness of a fertility awareness based method to avoid pregnancy in relation to a couple's sexual behaviour during the fertile time: a prospective longitudinal study". Human Reproduction. 22 (5): 1310–9. doi:10.1093/humrep/dem003. PMID 17314078.
- Trussell J (2007). "Contraceptive Efficacy". In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL (eds.). Contraceptive Technology (19th ed.). New York: Ardent Media. pp. 773–845. ISBN 978-0-9664902-0-6.
- "FDA approves Leas Shield". Contraception Report. 13 (2). 1 June 2002. Archived from the original on 11 December 2017. Retrieved 10 December 2017.
- Mauck C, Glover LH, Miller E, Allen S, Archer DF, Blumenthal P, Rosenzweig A, Dominik R, et al. (June 1996). "Lea's Shield: a study of the safety and efficacy of a new vaginal barrier contraceptive used with and without spermicide". Contraception. 53 (6): 329–35. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(96)00081-9. PMID 8773419.
- Gu Y, Liang X, Wu W, Liu M, Song S, Cheng L, Bo L, Xiong C, Wang X, Liu X, Peng L, Yao K (June 2009). "Multicenter contraceptive efficacy trial of injectable testosterone undecanoate in Chinese men". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 94 (6): 1910–5. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1846. PMID 19293262.
- "Clinician Protocol". FemCap manufacturer. Archived from the original on 2009-01-22.
- Trussell J (2011). "Contraceptive Efficacy." (PDF). In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL, Cates W, Kowal D, Policar M (eds.). Contraceptive Technology (Twentieth Revised ed.). New York NY: Ardent Media.
- see Combined oral contraceptive pill § Role of Placebo Pills
- Puri V (1988). "Results of multicentric trial of Centchroman". In Dhwan B. N., et al. (eds.). Pharmacology for Health in Asia : Proceedings of Asian Congress of Pharmacology, 15–19 January 1985, New Delhi, India. Ahmedabad: Allied Publishers.
Nityanand S (1990). "Clinical evaluation of Centchroman: a new oral contraceptive". In Puri CP, Van Look PF (eds.). Hormone Antagonists for Fertility Regulation. Bombay: Indian Society for the Study of Reproduction and Fertility. - Jones RK, Fennell J, Higgins JA, Blanchard K (2009). "Better than nothing or savvy risk-reduction practice? The importance of withdrawal" (PDF). Contraception. 79 (6): 407–10. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2008.12.008. PMID 19442773.
- Corinna H. "What's the Typical Use Effectiveness Rate of Abstinence?". Scarleteen.
- Aznar-Ramos R, Ginger-Velázquez J, Lara-Ricalde R, Martinez-Manautou J (December 1969). "Incidence of side effects with contraceptive placebo". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 105 (7): 1144–9. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(69)90142-2. PMID 5352596.
Cost and cost-effectiveness
Family planning is among the most cost-effective of all health interventions.[1] Costs of contraceptives include method costs (including supplies, office visits, training), cost of method failure (ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, induced abortion, birth, child care expenses) and cost of side effects.[2] Contraception saves money by reducing unintended pregnancies and reducing transmission of sexually transmitted infections. By comparison, in the US, method related costs vary from nothing to about $1,000 for a year or more of reversible contraception.
During the initial five years, vasectomy is comparable in cost to the IUD. Vasectomy is much less expensive and safer than tubal ligation.
Since ecological breastfeeding and fertility awareness are behavioral they cost nothing or a small amount upfront for a thermometer and / or training. Fertility awareness based methods can be used throughout a woman's reproductive lifetime.
Not using contraceptives is the most expensive option. While in that case there are no method related costs, it has the highest failure rate, and thus the highest failure related costs. Even if one only considers medical costs relating to preconception care and birth, any method of contraception saves money compared to using no method.
The most effective and the most cost-effective methods are long-acting methods. Unfortunately these methods often have significant up-front costs, requiring the user to pay a portion of these costs prevents some from using more effective methods.[3] Contraception saves money for the public health system and insurers.[4]
References
- Tsui AO, McDonald-Mosley R, Burke AE (2010). "Family planning and the burden of unintended pregnancies". Epidemiologic Reviews. 32 (1): 152–74. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxq012. PMC 3115338. PMID 20570955.
- Trussell J, Lalla AM, Doan QV, Reyes E, Pinto L, Gricar J (January 2009). "Cost effectiveness of contraceptives in the United States". Contraception. 79 (1): 5–14. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2008.08.003. PMC 3638200. PMID 19041435.
- Cleland K, Peipert JF, Westhoff C, Spear S, Trussell J (May 2011). "Family planning as a cost-saving preventive health service". The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (18): e37. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1104373. PMID 21506736.
- Jennifer J. Frost; Lawrence B. Finer; Athena Tapales (2008). "The Impact of Publicly Funded Family Planning Clinic Services on Unintended Pregnancies and Government Cost Savings". Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved. 19 (3): 778–796. doi:10.1353/hpu.0.0060. ISSN 1548-6869.