Chondrostei
Chondrostei is a group of primarily cartilaginous fish showing some degree of ossification. The cartilaginous condition is thought to be derived, and the ancestors of this group were bony fish with fully ossified skeletons. Members of this group share with the Elasmobranchii certain features such as the possession of spiracles, a heterocercal tail, and the absence of scales. Nevertheless, the fossil record suggests they have more in common with the teleosts. Chondrostei is probably a paraphyletic grouping; the 52 living species are divided among two orders, the Acipenseriformes (sturgeons and paddlefishes), and the Polypteriformes (reedfishes and bichirs).
| Chondrostei | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus | |
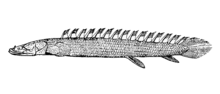 | |
| Nile bichir, Polypterus bichir | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| (unranked): | Actinopteri |
| Subclass: | Chondrostei |
| Orders | |
Characteristics
The main distinguishing feature of this group is the cartilaginous nature of the skeleton, although some older fish show a degree of calcification. The ancestors of the chondrosteans are thought to be bony fish, but that this characteristic of an ossified skeleton was lost in later evolutionary development, resulting in a lightening of the frame. Elderly chondrostean individuals show beginnings of ossification of the skeleton, which suggests this process is delayed rather than wholly lost in these fishes.[1]
Taxonomy
This group has at times been classified with the sharks because the chondrosteans, like the latter, mostly lack bone, and their structure of the jaw is more akin to that of sharks than of other bony fish; further, both groups lack scales (excluding the Polypteriforms). Additional shared features include spiracles and, in sturgeons and paddlefishes, a heterocercal tail (the vertebrae extend into the larger lobe of the caudal fin). However, the fossil record suggests these fish have more characters in common with the Teleostei than their external appearance might suggest.[1]
The Chondrostei taxon as described below is paraphyletic, meaning this subclass does not contain all the descendants of their common ancestor; reclassification of the Chondrostei is therefore not out of the question. In particular, the article Actinopteri, describing the chondrosteans' parent group, places the Polypteriformes outside the Chondrostei as a sister group to the Actinopteri.
The name comes from Greek chondros meaning cartilage and osteo meaning bone.
Classification
- Acipenseriformes
- Acipenseridae — sturgeons
- Polyodontidae — paddlefishes
- Chondrosteidae(†)
- Errolichthyidae(†)
- Cheirolepidiformes(†)
- Guildayichthyiformes(†)
- Luganoiiformes(†)
- Palaeonisciformes(†)
- Acrolepidae(†)
- Birgeriidae(†)
- Palaeoniscidae(†)
- Perleidiformes(†)
- Phanerorhynchiformes(†)
- Pholidopleuriformes(†)
- Polypteriformes
- Polypteridae - bichirs and reedfish
- Ptycholepiformes(†)
- Saurichthyiformes(†)
- Tarrasiiformes(†)
| Wikispecies has information related to Chondrostei |
References
- "Chondrosteans: Sturgeon Relatives". paleos.com. Archived from the original on 2010-12-25.