Byzantine Empire under the Justinian dynasty
The Byzantine Empire had its first golden age under the Justinian Dynasty, which began in 518 AD with the Accession of Justin I. Under the Justinian Dynasty, particularly the reign of Justinian I, the Empire reached its largest territorial point, reincorporating North Africa, southern Illyria, southern Spain, and Italy into the Empire. The Justinian Dynasty ended in 602 with the deposition of Maurice and the ascension of his successor, Phocas.
Roman Empire Imperium Romanum | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 518–602 | |||||||||
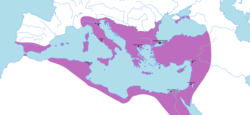 The Byzantine Empire at its greatest extent since the fall of the Western Roman Empire, under Justinian I in 555 AD. | |||||||||
| Capital | Constantinople | ||||||||
| Common languages | Latin, Greek | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||
• 518–527 | Justin I | ||||||||
• 527–565 | Justinian I | ||||||||
• 565–574 | Justin II | ||||||||
• 574–582 | Tiberius II | ||||||||
• 582–602 | Maurice | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• accession of Justin I | 10 June 518 | ||||||||
• deposition of Maurice | 27 November 602 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Justinian dynasty | |||
| Chronology | |||
| Justin I | 518–527 | ||
| Justinian I | 527–565 | ||
| Justin II | 565–578 | ||
| with Sophia and Tiberius as regents, 574–578 | |||
| Tiberius II | 578–582 | ||
| Maurice | 582–602 | ||
| with Theodosius as co-emperor, 590–602 | |||
| Succession | |||
| Preceded by Leonid dynasty |
Followed by Phocas and the Heraclian dynasty | ||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of the Byzantine Empire |
 Territorial development of the Byzantine Empire (330–1453) |
| Preceding |
|
| Early period (330–717) |
| Middle period (717–1204) |
| Late period (1204–1453) |
| Timeline |
| By topic |
|
|
Justin I
Early life and accession to the throne
The Justinian Dynasty began with the accession of its namesake Justin I to the throne. Justin I was born in a small village, Bederiana, in the 450s CE.[1] Like many country youths, he went to Constantinople and enlisted in the army, where, due to his physical abilities, he became a part of the Excubitors, the palace guards.[2] He fought in the Isaurian and Persian wars, and rose through the ranks to become the commander of the Excubitors, which was a very influential position. In this time, he also achieved the rank of senator. After the death of the Emperor Anastasius, who had left no clear heir, there was much dispute as to who would become emperor.[3] To decide who would ascend the throne, a grand meeting was called in the hippodrome. The Byzantine Senate, meanwhile, gathered in the great hall of the palace. As the senate wanted to avoid outside involvement and influence, they were pressed to quickly select a candidate; however, they could not agree. Several candidates were nominated, but were rejected for various reasons. After much arguing, the senate chose to nominate Justin; and he was crowned by the Patriarch of Constantinople John of Cappadocia on 10 July.[2]
Reign

Justin, who was from a Latin speaking province, spoke little Greek;[1] and was almost completely illiterate.[2] As such, he surrounded himself with intelligent advisers, the most notable of which was his nephew, Justinian. Justinian may have exerted great influence on his uncle and is considered by some historians, such as Procopius, to be the real power behind the throne.[3][4] After his accession, Justin removed the other candidates to the throne; two were executed and three were punished either with death or exile. Unlike most emperors before him, who were Monophysite, Justin was a devout Orthodox Christian.[5] Monophysites and the Orthodox were in conflict over the dual natures of Christ. Past emperors had supported the Monophysites' position, which was in direct conflict with the Orthodox teachings of the Papacy, and this strife led to the Acacian Schism. Justin, as an Orthodox, and the new patriarch, John of Cappadocia, immediately set about repairing relations with Rome.[6] After delicate negotiations, the Acacian Schism ended in late March, 519. After this initial ecclesiastical overhaul, the rest of Justin's reign was relatively quiet and peaceful. In 525, perhaps at the insistence of Justinian, Justin repealed a law which effectively forbade court officials from marrying people of low class. This allowed Justinian to marry Theodora, who was of low social standing. In his last years, conflict increased around the Empire. There was increased strife with the Ostrogothic Kingdom in the Italian Peninsula. Their king, Theodoric the Great, was suspicious of plots by the Byzantines; and turned on the Roman senatorial class, going so far as executing a philosopher attempting to end the persecution.[7] However, Theodoric died in 526, ending the persecution. The Sasanian Empire, likewise, resumed hostilities with the Byzantines, and the Iberian War began in the east; which would not reach its conclusion until the reign of Justinian. In 527, Justin appointed Justinian co-emperor after becoming dangerously ill. Justin recovered from the illness, however, several months later, he died of an ulcer on an old wound; and Justinian then ascended the throne.[8]
Justinian I
The strength of the dynasty was shown under Justinian I. After the Nika Riots, Justinian rebuilt the city and reformed the law with the "Code of Justinian".
Justinian had inherited a war with Persia from his uncle and previous emperor, Justin I. Justinian continued the war, succeeding in sending a force all the way down the Euphrates, but the raid stalled, and he lost the beginnings of a new fortress in a crushing defeat. This impasse of sorts led to Justinian negotiating the "Eternal Peace" in which he agreed to pay eleven thousand pounds of gold in return for a cease in hostilities and the defense of several mountain passes.[9]
He then set about satisfying his dream to rebuild the Roman Empire. On his command, his favored general, Belisarius, began reconquering old Roman territory, starting with the Vandals.
The Vandals, after maintaining North African dominance since the fall of the Western Roman Empire, had become content and laid back; their army, despite being twice the size to the 15,000 men commanded by Belisarius, was poorly trained, and ill-equipped to deal with an Imperial threat. The Vandal king, Gelimer, attempted to surround the Byzantines at the battle of Ad Decimum; he defeated Belisarius, but went hysterical after finding the body of his dead brother. Belisarius rounded up his remaining men and broke the disorganized mass of Vandals, now poorly commanded. Belisarius went on to capture Carthage, and the Byzantines were victorious.[10]
Justinian then recalled the victorious Belisarius. In Italy, dynastic squabbles amongst the ruling Ostrogoths gave Justinian an opportunity to invade, and he sent Belisarius to Sicily with 7500 men. Belisarius arrived and received only token resistance.[11] He then moved on to mainland Italy. After putting down a mutiny in recently conquered North Africa, Belisarius landed in mainland Italy; finding the same token resistance. The Gothic garrison of Naples resisted however, and after several months siege,[12] Belisarius sacked the city. After more ensuing dynastic squabbles, resulting in the deaths of two kings, Belisarius was invited to Rome by the pope while the king was in Ravenna. Hearing of this, the Gothic king, Witigis, sent a huge force, some accounts put the force as large as 150,000, to besiege Rome.[13] Belisarius had been fortifying Rome, and a siege ensued. One year and nine days later, after a grueling siege, Witigis had displayed his utter inabilities as a king, and Belisarius had showed his brilliance as a commander. The Goth army then moved to besiege Ariminium, which suffered due to lack of food. Narses, another Byzantine general, was called in to help and he used his influence to help Belisarius break the siege. After a massacre at Milan, breaks in Narses' command chain were revealed; following a letter from Belisarius, Narses was recalled by Justinian. Thereafter, the campaign became a war of sieges, which came to an end after Belisarius pretended to accept an offer to become Western Roman Emperor.[14] He marched into the city unopposed, occupied it, then disposed of King Witigis.
Belisarius was recalled from Italy and then immediately sent to the Persian front, which had flared into warfare again. During this period, the Ostrogoths retook most of Italy. After the Persian front died down, with the Persians swearing they would never fight the Byzantines again until after his death, Belisarius retook Italy and captured southern Spain in a war that lasted 18 years.[15]
Justinian's wars of reconquest had expanded the empire to include the former Roman provinces of Italia, Baetica, and Africa Proconsularis. These additions expanded the Byzantine Empire to the largest point in its history.
Justin II
After Justinian's reconquest and extensive rebuilding programs, the empire's treasury was left empty.[16] The financial mess weakened the Empire; and forced his successor, Justin II, to suspend payments to the Avars. While the Byzantines were distracted with the Persians, Lombard hordes under king Alboin invaded Italy, and soon conquered most of the peninsula. Later wars with the Persians did not go well in Syria, resulting in mental illness that drove Justin II to his grave.
Tiberius II
Tiberius II succeeded Justin II. His four-year reign was marked by Imperial weakness due to the Empire being over-stretched. He reinforced Ravenna, his generals found success against the Persians in battles in Armenia and against the Berbers in North Africa. At the same time, the Slavs began migrating all the way down into Greece. The overstretched Emperor ran out of money, couldn't pay the Army of the East which was fighting the Persians, and they threatened to mutiny. As his forces were deployed elsewhere, they took advantage of him and took the key city of Sirmium. After this defeat, Tiberius ate some bad food, which may have been intentionally poisoned, fell ill, and died.
Maurice
Maurice, the fifth and final emperor of the Justinian Dynasty, reportedly came from Armenia, and began his career in Constantinople as a Notarius. He eventually rose to the rank of secretary of the Imperial bodyguard, and, in 577 AD was appointed commander in chief of the army. He, after hard campaigning in the East in the Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591, was promoted to the rank of patricius. In 582 he married the Emperor's daughter, and succeeded him on the throne at the age of forty three.[17]
Maurice's reign was marked by constant money troubles. Maurice ascended the throne and received a completely bankrupt empire, and this Financial state continued until beyond the end of his reign. He also inherited military troubles: the Slavs were continuing to migrate into the empire, oftentimes violently; imperial hold over Italy was utterly collapsing; he also still had to continue the war with Persia that he had fought in for his entire military career. This Persian war also struggled with money difficulties, leading up to a major mutiny in 588; however, the money dispute was resolved the following spring. During the mutiny, a civil war began between rival factions in Persia, and Maurice saw an opportunity. He gave his support to Khosrau II[18] in Persia, and he succeeded in gaining the throne. This ended the Byzantine-Sassanid War of 572–591.
Maurice then turned his attention to the Balkans, which, after a decade of inattention from the army, had become completely ravaged by the Slavs. With the full attention of the army, the Byzantines drove back the Slavs, expelled them from the empire, and then ravaged their lands beyond the Danube. The Byzantines, after this decisive victory, were now easily able to hold the frontier on the Danube as it had been since the Roman Empire, as well as gain control over some minor territories in southern Dacia.
Despite these extensive military victories, Maurice was extremely unpopular within the borders of the empire, due to the fact that he always had an empty treasury, and often had to reduce payments to his soldiers. As a result of this unpopularity, he was deposed by the Greens in 602 and replaced with their choice, Phocas.
Table
| Name | Picture | Beginning of Reign | End of Reign |
|---|---|---|---|
| Justin I | .jpg) | 518 | 527 |
| Justinianus I | _(1).jpg) | 527 | 565 |
| Justin II |  | 565 | 574 |
| Tiberius II |  | 574 | 582 |
| Maurice | .jpg) | 582 | 602 |
Justinian dynasty family tree
- Justin I - (518–527)

- No issue from the marriage with Euphemia
- Vigilantia, sister of Justin
- From the marriage with Sabbatius
- Petrus Sabbatius, later adopted by Justin and raised to the rank of emperor as Justinian I - (527–565)
- No issue from the marriage with Theodora
- Vigilantia, sister of Justinian I
- From the marriage with Dulcissimus
- Justin II - (565–578)
- From his marriage to Sophia
- Arabia. Married Baduarius
- adoption of Tiberius II Constantine - (574–582)
- From his marriage to Ino Anastasia.
- Constantina, a daughter who married Maurice (582–602)
- Theodosius. Eldest son and co-emperor of Maurice. Married a daughter of patrikios Germanus.
- Tiberius. Second son. Supposed to inherit Italy.
- Miriam/Maria. Supposed daughter of Maurice. Married Khosrau II.
- Charito, a daughter who married Germanus
- Constantina, a daughter who married Maurice (582–602)
- From his marriage to Ino Anastasia.
- From his marriage to Sophia
- Marcellus, married Juliana, great-great-niece of Anastasius I
- Praejecta
- Justin II - (565–578)
- From the marriage with Dulcissimus
- Petrus Sabbatius, later adopted by Justin and raised to the rank of emperor as Justinian I - (527–565)
- From the marriage with Sabbatius
- Unknown brother or sister of Justin
Genealogy
| Leo I the Thracian emperor of the Romans 457-474 LEONID DYNASTY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ariadne | Anastasius I Dicorus emperor of the Romans 491-518 | (sibling) | Euphemia | Justin I emperor of the Romans 518-527 | Vigilantia | Petrus Sabbatius | (sibling) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (daughter) | Comito | Theodora | Justinian I emperor of the Romans | Vigilantia ∞ Dulcidius | Germanus | Boraides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anastasius consul 517 | Sophia ∞ Justin II | (illeg.) Theodora | Justin II emperor of the Romans 565-574 | Marcellus general ∞ Juliana (daughter of Moschinus) | Praejecta ∞ 1.Areobindus magister militum 2.Johannes (grandson of Hypatius) | Justin consul 540 | Justinian general | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Areobindus | Tiberius II emperor of the Romans ∞ Ino Anastasia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anastasia Areobinda | Peter curopalates | Maurice emperor of the Romans | Constantina | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maria | Khosrow II king of Persia | (sister) | Shahrbaraz king of Persia | Heraclius emperor of the Romans 610-641 HERACLIAN DYNASTY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nike | Theodosios | Constantine III emperor of the Romans 641 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Family trees of the Byzantine imperial dynasties
- History of the Byzantine Empire
References
- Treadgold 1997, p. 174.
- Cameron 2000, p. 63.
- Bury 1923, p. 19.
- Procopius "Secret History" cited in: Bury 1923, p. 19.
- Sarris 2011, p. 137.
- Treadgold 1997, p. 175.
- Cameron 2000, p. 64/65.
- Bury 1923, p. 23.
- Bury 1923, p. 88.
- Bury 1923, p. 135.
- Bury 1923, p. 171.
- Bury 1923, p. 176.
- Bury 1923, p. 183.
- Bury 1923, p. 213.
- Bury 1923, p. 283.
- Corrick 2006, p. 59.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 17 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 909.
- Meyer, Eduard (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 6 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 271–272.
- Cawley, Charles (29 May 2014). "Byzantium 395-1057". Medieval Lands. Archived from the original on 2009-02-03. Retrieved 2017-12-05.
Sources
- Cameron, Averil. "The Cambridge Ancient History (Chapter 3)". Cambridge University Press, 2000.
- Cameron, Averil; Ward-Perkins, Bryan; Whitby, Michael (2000). The Cambridge Ancient History. 14. Late Antiquity: Empire and Successors, A.D. 425 - 600. Cambridge University Press.
- Treadgold, Warren T. "A History of the Byzantine State and Society". Stanford University Press, 1997.
- Bury, John Bagnall History of the Later Roman Empire Macmillan & Co. Ltd. Posted at: "John Bagnall Bury: History of the Later Roman Empire". Retrieved 31 March 2013.
- Corrick, James. The Byzantine Empire Farmington Mills MI: Thompson & Gale.
.jpg)