Argentine Senate
The Argentine Senate (Spanish: Honorable Senado de la Nación Argentina; lit. "Honourable Senate of the Argentine Nation") is the upper house of the National Congress of Argentina.
Argentine Senate Senado | |
|---|---|
| 2019–2021 period | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
President of the Senate | |
Provisional President | |
Majority Leader | |
First Minority Leader | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 72 (List) |
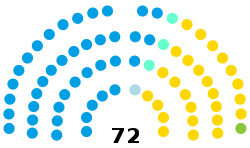 | |
Political groups | Government (41)
Opposition (31)
|
| Elections | |
| Limited voting | |
Last election | 27 October 2019 |
Next election | 2023 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Chamber of Senators, Congress Palace, Buenos Aires, Argentina | |
| Website | |
| senado.gob.ar | |

Overview
The National Senate was established by the Argentine Confederation on July 29, 1854, pursuant to Articles 46 to 54 of the 1853 Constitution.[1] There are 72 members: three for each province and three for the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires. The number of senators per province was raised from two to three following the 1994 amendment of the Argentine Constitution, and the change took effect following the May 14, 1995, general elections.
Senators are elected to six-year terms by direct election on a provincial basis, with the party with the most votes being awarded two of the province's senate seats and the second-place party receiving the third seat. Historically, Senators were indirectly elected to nine-year terms by each provincial legislature. These provisions were abrogated by a 1994 constitutional amendment, and direct elections to the Senate took effect in 2001. Currently one-third of the members are elected every two years. One-third of the provinces hold senatorial elections every two years; there are no term limits.
The Vice President of the Republic is ex officio President of the Senate, with a casting vote in the event of a tie. In practice, the Provisional President presides over the chamber most of the time.
The Senate must obtain quorum to deliberate, this being an absolute majority. It has the power to approve bills passed by the Chamber of Deputies, call for joint sessions with the Lower House or special sessions with experts and interested parties, and submit bills for the president's signature; bills introduced in the Senate must, in turn, be approved by the Lower House for their submittal to the president. The Senate must introduce any changes to federal revenue sharing policies, ratify international treaties, approve changes to constitutional or federal criminal laws, as well as confirm or impeach presidential nominees to the cabinet, the judiciary, the armed forces, and the diplomatic corps, among other federal posts.[2]
There are twenty-four standing committees made up of fifteen members each, namely:[2]
- Agreements (confirmation of federal nominees)
- Constitutional Affairs
- Foreign Affairs and Worship
- Justice and Criminal Affairs
- General Legislation
- Budget and Finance
- Administrative and Municipal Affairs
- National Defense
- Domestic Security and Drug Trafficking
- National Economy and Investment
- Industry and Trade
- Regional Economies, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Labor and Social Security
- Agriculture, Cattle Raising and Fishing
- Education, Culture, Science and Technology
- Rights and Guarantees
- Mining, Energy and Fuels
- Health and Sports
- Infrastructure, Housing and Transport
- Systems, Media and Freedom of Speech
- Environment and Human Development
- Population and Human Development
- Federal Revenue Sharing
- Tourism.
Requirements
According to Section 55 of the Argentine Constitution, candidates for the Argentine Senate must:
- be at least 30 years old
- have been a citizen of Argentina for six years
- be native to the province of his office, or have been a resident of that province for two years.
Composition
| Block | Parties | Presidents | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frente de Todos (41) | José Mayans | ||
| Juntos por el Cambio (26) (President: Luis Petcoff Naidenoff) |
Unión Cívica Radical (15) | Luis Petcoff Naidenoff | |
| Frente Pro (8) | Humberto Schiavoni | ||
| Frente Cívico y Social de Catamarca (1) | Oscar Aníbal Castillo | ||
| Avanzar San Luis (1) | Claudio Javier Poggi | ||
| Producción y Trabajo (1) | Roberto Gustavo Basualdo | ||
| Parliamentario Federal (3) (President: Juan Carlos Romero)[3] |
Santa Fe Federal (1) | Carlos Reutemann | |
| Justicialista 8 de Octubre (1) | Juan Carlos Romero | ||
| Movimiento Neuquino (1) | Carmen Lucila Crexell | ||
| Frente Renovador de la Concordia (1) | Magdalena Solari | ||
| Juntos Somos Río Negro (1) | Alberto Weretilneck | ||
The current members of the Senate were elected in 2015, 2017 and 2019.
Senate leadership
The titular President of the Senate is the Vice President of Argentina. However, day to day leadership of the Senate is exercised by the Provisional President.
Current leadership positions include:[4]
| Title | Officeholder | Caucus | Province |
|---|---|---|---|
| President of the Senate | Cristina Fernández de Kirchner | Frente de Todos | |
| Provisional President | Claudia Ledesma Abdala | Frente de Todos | |
| Vice President | Martín Lousteau | Juntos por el Cambio | |
| First Vice President | Maurice Closs | Frente de Todos | |
| Second Vice President | Laura Rodríguez Machado | Juntos por el Cambio | |
| Parliamentary Secretary | Marcelo Fuentes | N/A | |
| Administrative Secretary | María Luz Alonso | ||
| Majority Leader | José Mayans | Frente de Todos | |
| Minority Leader | Luis Petcoff Naidenoff | Juntos por el Cambio | |
See also
- List of current Argentine senators
- Argentine Chamber of Deputies
- List of former Argentine Senators
- List of legislatures by country
References
- "Sesiónes preparatorias e incorporación y juramento de los senadores electos". Argentine Senate. Archived from the original on 2009-07-18.
- "National Senate Regulations" (PDF). Argentine Senate. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-05-24.
- "Comunicación de Senadores, número de expediente 3417/19". Retrieved 21 Dec 2019.
- "Autoridades". Honorable Senado de la Nación. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
