1956 Democratic Party presidential primaries
The 1956 Democratic presidential primaries were the selection process by which voters of the Democratic Party chose its nominee for President of the United States in the 1956 U.S. presidential election. Former Illinois Governor Adlai Stevenson was selected as the nominee through a series of primary elections and caucuses culminating in the 1956 Democratic National Convention held from August 13 to August 17, 1956, in Chicago, Illinois. This was the party's second consecutive nomination of Stevenson.
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Primary race
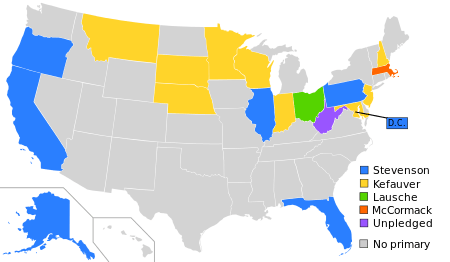
Estes Kefauver sought the Democratic presidential nomination, as he had in 1952. Initially, he again won some Democratic Party presidential primaries. In the March 13, 1956 New Hampshire presidential primary, Kefauver defeated Stevenson, his only formidable opponent for the nomination, by a margin of 21,701 to 3,806. A week later, Kefauver defeated Stevenson in the March 20, 1956 Minnesota presidential primary, winning 245,885 votes compared to Stevenson's 186,723 votes. Kefauver was also victorious in the Wisconsin presidential primary.
By April 1956, "it appeared that Kefauver was on his way to a primary sweep matching the spectacular performance in 1952."[1] Stevenson, however, was able to defeat Kefauver in the 1956 Oregon, Florida and California primaries and, overall, and ultimately won more primary votes than Kefauver before being re-nominated as the Democratic presidential nominee at the 1956 Democratic national convention.
Candidates

.jpg)

 Governor Frank Lausche of Ohio
Governor Frank Lausche of Ohio House Majority Leader John William McCormack of Massachusetts
House Majority Leader John William McCormack of Massachusetts
Polling
National polling
| Poll source | Publication | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallup[2] | Aug. 1953 | – | – | 17% | – | 53% | 1% | 11% |
| Gallup[2] | Aug. 1954 | – | – | 22% | – | 57% | – | – |
| Gallup[2] | Nov. 1954 | 4% | – | 16% | 2% | 58% | – | – |
| Gallup[2] | Mar. 1955 | 14% | – | 48% | 2% | – | 5% | 1% |
| Gallup[2] | Apr. 1955 | 17% | – | 37% | 4% | – | 3% | 1% |
| Gallup[2] | Aug. 1955 | 6% | 1% | 16% | – | 55% | – | 1% |
| Gallup[2] | Oct. 1955 | 8% | – | 16% | 2% | 51% | 2% | – |
| Gallup[2] | Nov. 1955 | 10% | 1% | 11% | 1% | 48% | 1% | 1% |
| Gallup[2] | Nov. 1955 | 8% | – | 12% | – | 38% | – | – |
| Gallup[2] | Dec. 1955 | 8% | – | 17% | 3% | 51% | – | – |
| Gallup[2] | Jan. 1956 | 8% | 3% | 17% | 3% | 49% | – | – |
| Gallup[2] | Feb. 1956 | 8% | 2% | 18% | 2% | 51% | 1% | – |
| Gallup[2] | Apr. 1956 | 6% | 3% | 33% | 2% | 39% | 2% | – |
| Gallup[2] | Apr. 1956 | 6% | 4% | 29% | 3% | 41% | 2% | – |
| Gallup[2] | June 1956 | 8% | 4% | 26% | 3% | 42% | 3% | – |
| Gallup[2] | June 1956 | 12% | 4% | 16% | 3% | 45% | 4% | – |
References
- Gorman, Joseph Bruce. Kefauver: A Political Biography. NY: Oxford University Press, 1971.
- "US President - D Primaries Polling". OurCampaigns.com. 11 Dec 2010. Retrieved 26 April 2020.