1953 Yenice–Gönen earthquake
The 1953 Yenice–Gönen earthquake occurred at 21:06 local time (19:06 UTC on 18 March in the province of Çanakkale and Balıkesir in the Marmara Region at western Turkey. It had a magnitude 7.5 on the surface wave magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of IX (Violent) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It caused widespread damage, killing 1,070 and causing damage that was estimated at US$3,570,000 repair value.[2]
 | |
| UTC time | 1953-03-18 19:06:17 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 891561 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 18 March 1953 |
| Local time | 21:06:17 |
| Magnitude | 7.5 Ms[1] |
| Epicenter | 40.02°N 27.53°E |
| Areas affected | Turkey Yenice, Çanakkale, Gönen |
| Total damage | $3.57 million |
| Max. intensity | IX (Violent) |
| Casualties | at least 1,070 dead |
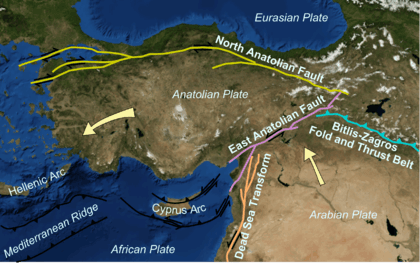
Tectonic setting
The tectonics of northern and eastern Turkey are dominated by the two strike-slip fault zones that accommodate the west to southwestward movement of the Anatolian Plate relative to the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate as it is effectively being squeezed out by convergence between them. The quake occurred along the Yenice–Gönen Fault, which is a southern extension of the North Anatolian Fault Zone.[3]
Damage and casualties
The quake had a surface wave magnitude of 7.3 and it killed at least 1070; 998 of those deaths were in Yenice, with another 50 in Gönen, 20 in Çan, and 3 in Manyas. The cost of repair was estimated at US$3,570,000. Several thousand buildings were affected in the Can-Yenice-Gonen area. Damage of intensity VI occurred at Sakarya (Adapazari), Bursa, Edirne, Istanbul and Izmir. The quake was felt throughout the Aegean Islands and in much of mainland Greece, with damage occurring as far away as Crete. Shaking was also recorded in Bulgaria.[2]
Although officials predicted the earthquake would cause only 265 deaths, it multiplied with a death toll seven times the number as expected.[4]
Characteristics
Approximately 70 km (43 mi) of surface faulting occurred, with as much as 4.3 m (14 ft) of strike-slip (horizontal) faulting was observed by geologists east of Yenice.[2]
Aftermath
The damage caused by this earthquake led to a new national reconstruction law in Turkey.[5] In Greece the damage was severe enough that new building codes were introduced.[6]
Future seismic hazard
Trenching and other fieldwork along the trace of the Yenice–Gönen Fault has identified three earthquakes before the 1953 event, about 1440 AD, between 620 and 1270 AD, and another event of uncertain age. These past events give a mean recurrence interval for large earthquakes of 660±160 years. This indicates that there is no significant current threat from ruptures along this fault zone.[3]
Notes
- NGDC. "Comments for the Significant Earthquake". Retrieved 5 February 2011.
- "Today In Earthquake History:March 18". USGS. 2008-07-16. Retrieved 2008-10-30.
- Kürçer, A.; Chatzipetros A.; Tutkun S.Z.; Pavlides S.; Ateş Ö. & Valkanniotis S. (2008). "The Yenice–Gönen active fault (NW Turkey): Active tectonics and palaeoseismology". Tectonophysics. 453 (1): 263–275. Bibcode:2008Tectp.453..263K. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2007.07.010.
- "Turkey Rocked; Deaths Set at 150". The Washington Post. 1953-03-19. Retrieved 2008-10-30.
- Ural, D.N. "Emergency Management in Turkey: Disasters Experienced, Lessons Learned, and Recommendations for the Future". Retrieved 5 February 2011.
- De Wire, E.; Reyes-Pergioudakis, D. (2010). The Lighthouses of Greece. Pineapple Press Inc. p. 16. ISBN 978-1-56164-452-0.
Further reading
- Dewey, J.E. (1976), "Seismicity of Northern Anatolia", Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 66 (3): 843–868
External links
- The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.