1892 Japanese general election
The Japanese General Election of 1892 (第2回衆議院議員総選挙, Dai-nikai Shūgiin Giinsōsenkyō) was the Empire of Japan’s second general election for members of the House of Representatives of the Diet of Japan, held on February 15, 1892.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 300 seats to the House of Representatives 151 seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History and background
After the 1890 general election for the lower house of the Diet of Japan, the elected members proved much less amenable to government persuasion than had been anticipated by Itō Hirobumi and other members of the Meiji oligarchy. Rather than docilely rubber stamp legislation issued from the House of Peers and the genrō, the leaders of the lower house used the only leverage granted to them under the Meiji Constitution: withholding budgetary approval to show resistance. This stalemate led to earlier than anticipated dissolution of the government and new elections. Emperor Meiji expressed concern that if the same people were elected again, the same problem would recur, and suggested that regional offices encourage good people to run for office.[1]
Home Minister Shinagawa Yajirō interpreted this as a condemnation of political party activity, and sent memorandums to all regional government offices encouraging the dismissal of men deeply involved in political party activity. He also instructed the police to deal severely with any acts of bribery and intimidation. Ironically, the 1892 election was the most violent in Japanese history, with numerous riots, in which 25 people were killed and 388 wounded. Violence was particularly severe in areas of the country in which support for the opposition Liberal Party (Jiyutō) was strong[2] Encouraged by Prime Minister Matsukata Masayoshi, Shinagawa arrested candidates he deemed “disloyal”, and had gangs of toughs molest voters and burn opposition politicians' property. Prefectural governors and police chiefs were secretly ordered to disrupt campaigns of "disloyal" opposition politicians and to aid pro-government supporters.[3] Ballot boxes were stolen in Kōchi Prefecture, and voting was made impossible in parts of Saga Prefecture; violations were most conspicuous in these two prefectures, Ishikawa and Fukuoka.
As with the 1890 election, the electorate was based on limited suffrage, with only male citizens 25 years of age and over, who had paid 15 Japanese Yen or more in national taxes, and who had been resident in their prefecture for at least a year, qualified to vote. The number of eligible voters who met this requirement was 434,594. The number of candidates for office was 900. Voter turnout was 91.54%.[4]
Despite the violence, the so-called mintō (liberal parties)- the Jiyutō, the Rikken Kaishintō and their affiliates) maintained their majority in the House of Representatives, winning 132 seats as opposed to 124 for pro-government candidates, with 44 independents.[5]
The government faced an angry lower house when the next Diet term convened on May 6; even members of the House of Peers were outraged, issuing a resolution condemning the manner in which the election was held on May 11. Shinagawa was forced to resign the following month.[3]
Results
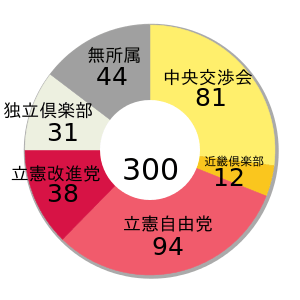
| Political Parties | Seats |
|---|---|
| Jiyutō (自由党) | 94 |
| Rikken Kaishintō (立憲改進党) | 38 |
| Chuo Club (中央交渉会) | 81 |
| Dokuritsu Club (独立倶楽部) | 31 |
| Kinki Club (近畿倶楽部) | 12 |
| Independents (無所属) | 44 |
| Total | 300 |
Notes
- Keene, Donald. (2002). Emperor of Japan: Meiji and his World, p. 460.
- W. Scott Morton, J. Kenneth Olenik. Japan: Its History and Culture, p.163. McGraw-Hill Professional, 2004, ISBN 0-07-141280-8
- Richard H. Mitchell. Political Bribery in Japan, p.16. University of Hawaii Press, 1996, ISBN 0-8248-1819-9
- Mason, R.H.P. Japan's First General Election, 1890.
- Keene, pp. 461-464.
References
- Jansen, Marius B. (1989). Cambridge History of Japan: Vol. 5: The Nineteenth Century. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-22356-3.
- Fraser, Andrew (1995). Japan's Early Parliaments, 1890-1905: Structure, Issues and Trends. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-03075-7.
- Keene, Donald (2002). Emperor Of Japan: Meiji And His World, 1852-1912. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-12341-8. ISBN 978-0-231-12340-2; OCLC 46731178
- Mason, R.H.P. (1969). Japan's First General Election, 1890. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-07147-X.
- Meyer, Milton Walter (1992). Japan: A Concise History. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0-8226-3018-4.

