Švenčionys
Švenčionys (![]()
Švenčionys | |
|---|---|
City | |
 Church | |
 Coat of arms | |
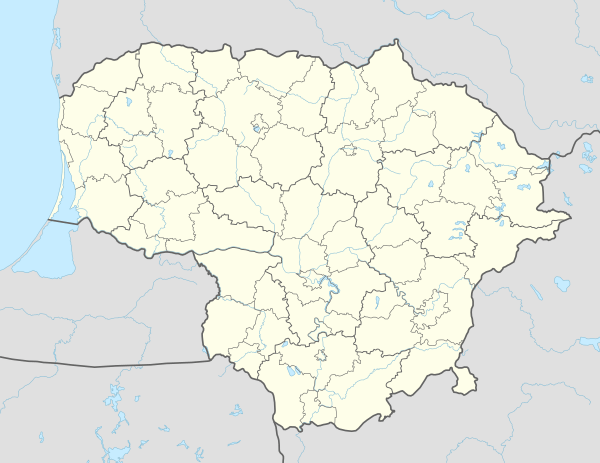 Švenčionys Location of Švenčionys | |
| Coordinates: 55°08′00″N 26°09′20″E | |
| Country | |
| County | |
| Municipality | Švenčionys district municipality |
| Eldership | Švenčionys eldership |
| Capital of | Švenčionys district municipality Švenčionys eldership |
| First mentioned | 1800 |
| Granted city rights | 1961 |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 4,963 |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
Etymology
There are two established hypotheses about the etymology of the Švenčionys name: one that it is the name of the nearby lake Šventas (literally: saint) with the addition of the Lithuanian suffix -onys; another is that it is derived from the personal name, Švenčionis. In other languages the name is rendered as Polish: Święciany, Belarusian: Свянця́ны/Svianciany, Russian: Свентя́ны/Sventiany, Yiddish: סווינציאַן /Svintsyán, and German: Swenziany.
History
| Year | Pop.[2] |
|---|---|
| 1833 | 1,128 |
| 1880 | 6,795 |
| 1897 | 6,025 |
| 1931 | 5,893 |
| 1959 | 4,006 |
| 1970 | 4,617 |
- One of the oldest towns in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the settlement was a major center of Nalšia. Grand Duke Vytautas settled Lipka Tatars in the town and built a Catholic church in 1414. The place grew from the 14th to 16th centuries, becoming the site of a local court and monastery. From 1801 the town was part of the Russian Vilna Governorate and grew significantly after completion of the Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway in 1862, but eventually lost competition to Švenčionėliai, which grew around the train station.[2] At the turn of the 20th century the town had one Greek Orthodox church and one Roman Catholic church.[3]
During the 1812 French invasion of Russia, Napoleon stayed in the town for 12 hours to write orders and receive an envoy from the King of Naples.[4] The town was one of the main centers of the November Uprising (1830–1831) in Poland and Lithuania against the Russian Empire. During World War I, it was the location of the German Sventiany Offensive.
The city was part of the Second Polish Republic for most of the interwar period. It had a significant Jewish population (according to the 1897 Russian census – 52%),[5] but during World War II, under German occupation, the Švenčionys Ghetto was established. It operated from July 1941 to April 1943. At its peak, the ghetto housed some 1,500 prisoners. The Jewish inhabitants were deported and murdered.[6] It was a powiat centre in Wilno Voivodeship as Święciany during Polish rule between 1920-1939.
On 18 September 1939, Švenčionys was occupied by the Red Army and, on 14 November 1939, incorporated into the Byelorussian SSR. The Soviets placed it firstly in part of Vileyka Oblast of the Belorussian SSR in 1939 but then incorporated into the Lithuanian SSR on 25 November 1940. Švenčionys was occupied by the German Army from 27 June 1941 until 7 July 1944 and placed under the administration of the Generalbezirk Litauen of Reichskommissariat Ostland. In 1942 the Lithuanian Security Police murdered around 1,200 Poles in the village.[7] Most of the municipal area remained part of the Lithuanian SSR except the Ashmyany region which was reincorporated into Belarus in 1944.
Notable residents
- Yitzhak Arad (born 1926), Israeli historian, director of Yad Vashem from 1972 to 1993
- Mordecai Kaplan (1881–1983), Rabbi and founder of the Reconstructionist Judaism movement
- Mark Natanson (1850–1919), Russian revolutionary
- Wiktor Thommée (1881–1962), Polish general
- Franciszek Żwirko (1895–1932), Polish aviator
- Menke Katz (1906–1991), Yiddish-language poet
References
- "Lithuania 2011 Census". Lietuvos statistikos departamentas. 2011.
- Jonas Zinkus; et al., eds. (1985–1988). "Švenčionys". Tarybų Lietuvos enciklopedija. 4. Vilnius, Lithuania: Vyriausioji enciklopedijų redakcija. p. 233. LCC 86232954.
- Meyer, Hermann Julius (1908). Meyers grosses Konvesations-Lexikon (in German). 19 (6th ed.). Leipzig and Vienna: Bibliographisches Institut. p. 227.
- Armand Augustin Louis de Caulaincourt; Jean Hanoteau (1938). Memoirs of General de Caulaincourt, Duke of Vicenza. 1. Cassell and Co. pp. 135–136.
- "The First General Census of the Russian Empire of 1897. Breakdown of population by mother tongue and districts* in 50 Governorates of the European Russia". Demoscope Weekly. Institute of Demography of the State University - Higher School of Economics.
- "Lithuania". Holocaust Encyclopedia. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Retrieved 2011-03-04.
- "PRZEGLĄD MEDIÓW - 15 marca 2005 r." (in Polish). Institute of National Remembrance. 2005-03-15. Archived from the original on 2011-06-11.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Švenčionys. |