Zaspopathy
Zaspopathy,[1] also called ZASP-related myofibril myopathy,[2] is a novel autosomal dominant[3] form of progressive muscular dystrophy, first described in 2005.
| Zaspopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Late-onset distal myopathy, Markesbery-Griggs type |
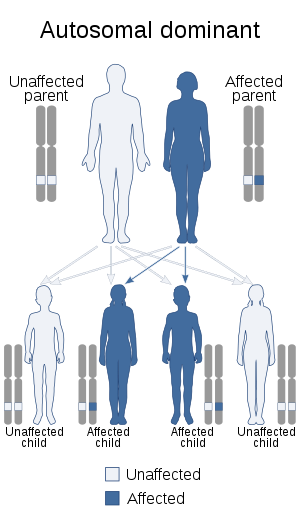 | |
| Zaspopathy has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. | |
The disease encompasses multiple forms of both distal and proximal myopathies, and is caused by mutations in the gene referred to as ZASP.[3]
Pathophysiology
The ZASP gene is located at chromosome 10, and encodes also-called Z-disk-associated protein.
Mutation in this protein causes disintegration of the Z-disk of contractile elements (myofibrils) in muscle cells.
Mutations of several other Z-disk related proteins, such as desmin, alfa-B-crystallin and myotilin can cause disorders similar to zaspopathy.
Diagnosis
Treatment
gollark: Increment the pointer by n.
gollark: See, *I* would call that `benchmark` or `cmp-time`.
gollark: Oh.
gollark: Compare 10! and also 10! for some reason?
gollark: Create... Macron?
See also
References
- Griggs R, Vihola A, Hackman P, Talvinen K, Haravuori H, Faulkner G, Eymard B, Richard I, Selcen D, Engel A, Carpen O, Udd B (Jun 2007). "Zaspopathy in a large classic late-onset distal myopathy family" (Free full text). Brain : A Journal of Neurology. 130 (Pt 6): 1477–1484. doi:10.1093/brain/awm006. PMID 17337483.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 609452
- Selcen D, Engel AG (Feb 2005). "Mutations in ZASP define a novel form of muscular dystrophy in humans". Annals of Neurology. 57 (2): 269–276. doi:10.1002/ana.20376. PMID 15668942. Archived from the original on 2012-12-17.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.