Wellington railway station
Wellington railway station is the main railway station serving Wellington, New Zealand, and is the southern terminus of the North Island Main Trunk, Wairarapa Line and Johnsonville Line.
Wellington | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metlink regional rail | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Wellington railway station frontage at night, 14 May 2003. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Bunny Street, Pipitea, Wellington, New Zealand | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°16′43″S 174°46′51″E | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owned by | New Zealand Railways Corporation[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line(s) | North Island Main Trunk Wairarapa Line Johnsonville Line | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platforms | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Connections | Services | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure type | At-grade terminal station | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parking | Yes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disabled access | most Metlink services (operated by Transdev Wellington) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Station code | WELL (Metlink) WLG (KiwiRail Network) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fare zone | 1[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | 19 June 1937 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrified | 1938 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Designated | 25 September 1986 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference no. | 1452 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The station opened in June 1937, replacing the two previous Wellington termini, Lambton and Thorndon.
History
Development
The capital's first Wellington railway station was a group of small buildings at Pipitea Point built in 1874 on earthquake-raised harbour floor for a temporary terminus of the railway line to the Hutt Valley. A series of reclamations allowed the line to reach well down Featherston Street and in 1880 a new Wellington railway station was, as it turned out, temporarily placed near the goods station for the new Railway Wharf. Traffic at the wharf quickly grew beyond expectations. The 1880 building was pulled north on rollers in 1885 to a less congested site on Featherston Street opposite the junction of Mulgrave Street and Sydney Street now Kate Sheppard Place.[3]
The third site named Wellington railway station was only the passenger terminus for the Hutt and Wairarapa lines. After the Government took control of the Manawatu line in December 1908, the Wellington railway station was renamed Wellington Lambton station and the Manawatu station which became the terminus for the North Island Main Trunk was named Wellington Thorndon station. The Thorndon station had been opened in September 1885 by the private Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company. The Government bought the line from its shareholders in 1908 to incorporate the Manawatu line into their system.[4]
Once both stations were in government control, public pressure began to build for a single terminal. In 1908, a joint reclamation scheme was drawn up by the Railways Department and the Wellington Harbour Board and in 1912 a new railway station was proposed, to supersede the Lambton and Thorndon stations.[5] The government decided on a co-ordinated development that included a new station building, and after agreement in 1922 between the Railways Department and the Wellington Harbour Board, the reclamation of about 68 acres (27 hectares) incorporating a new double-track line, train marshalling areas, goods yards and sheds and using fill from the Tawa Flat Deviation.[6] The Thorndon reclamation began in 1923 and was on track to be completed by 1932, which allowing the government in 1929 to confirm in 1929 that Bunny Street would be the location of a new station, so removing the inconvenience of two separate stations.
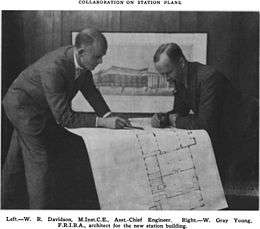
In 1929, W. Gray Young,an architect known for his neo-Georgian styles, of Wellington architectural firm of Gray Young, Morton & Young, was selected (without a design competition) to design the new station, over the Auckland firm of Gummer & Ford, which had designed Auckland railway station. Gray Young, Morton and Young was formed in 1923 and consisted of William Gray Young, Hubert Morton and Gray Young's brother Jack. The firm had recently finished large commissions for Victoria University, designing the Stout Building (1930) and Weir House (1930), and later the Kirk Building (1938).
The need to review building techniques after the Napier earthquake and the impact of the Depression on finances delayed the government formally committing to the project until June 1933.
Design
As the planned location was on reclaimed land, test piles were driven in 1928 to test the quality of soil. On the basis of the test results the decision was made to use Vibro cast-in-place piles to support the structure. The building was the first major New Zealand structure to incorporate a significant measure of earthquake resistance.
Gray Young was paid a 4% fee based on the originally estimated cost of £470,000. This cost rose to £483,000 once the quantity surveying firm of Maltby & Sommerville compiled a detailed quantity schedule, for which they were paid 1% of the estimated cost. Because of the impact of the Depression on Government finances it was decided to reduce the cost by eliminating a mailroom and a section of the West wing along Featherston Street and by transferring the £28,000 cost of the platforms and verandahs to a separate budget. As a result, the official estimated cost of the station was reduced to £350,000.[7] To encourage employment of workers out of work due to the Depression the project received a subsidy of £34,000 (10% of the estimated cost) from the Employment Board.
The building is a U-shaped structure with the longest leg 105.5 metres [346 feet] long and 23.5 metres [77 feet] high. Because of delays in importing the specialized boring equipment needed to install the cast-in-place piles called for in the original design, the decision was made to use 1615 15 x 15 inch and 16 x 16 inch reinforced concrete piles. These were driven by a steam-powered hammer. On top of the piles a five- and six-storey steel-framed structure was built. The steel was encased in reinforced concrete and 1.75 million bricks. 21,000 cubic yards of aggregate from the Hutt River with cement from Whangarei were mixed on site to create the concrete. The bricks used for the outer cladding were of a special design, with slots to accommodate vertical corrosion–resistant steel rods that reinforced the brickwork and bound it to the structural members. 1500 tons of decorative Hanmer and Whangarei granite and marble were used to clad the interior and the entranceway. 2500 gallons of paint were used. The roof was clad in Marseille tiles.
The main entrance is on the south side via a colonnade of eight 13-metre- [42-foot]-high Doric columns opening into a large booking hall decorated with delicately mottled dados extending to a high vaulted ceiling.
The glazed-roof concourse contained waiting rooms and toilets, a large dining room, a barber shop, book and fruit stalls and a first aid room. There was a nursery on the top floor to allow parents to leave their children while they shopped or waited for their train.
_(cropped).jpg)
When completed the station was New Zealand’s largest building, partly covering 0.6 hectares and with a combined floor area of two hectares. It was designed to accommodate the 675 staff of the Railways Department head office and the Wellington district office, which until then had been accommodated in 11 leased buildings throughout the city.[8]
The platforms, designed to accommodate up to 12 carriages, are made of concrete covered with a sealed surface under verandahs held up by railway irons.
Platform 9 was designed to be a roadway without rails for the terminus for certain services provided by New Zealand Railways Road Services.
A park was created in the forecourt with lawns and paths of paving stones with brick edging arranged in a herringbone pattern.
Construction
The construction tender closed on 25 September 1933, extended by two weeks in an attempt to encourage local manufacturers to offer locally manufactured materials. Twelve tenders were received, with Fletcher Building the lowest at £339,000. The next lowest was £350,000 from J T Julian & Son, who had constructed a significant part of the Auckland railway station.[9]
Fletchers was awarded what was believed to be the largest single-building contract let in New Zealand up to that time, to which a performance bond of £3000 was applied.
Fletchers appointed 26-year-old Joe Craig to manage his first major project. His prior experience had been on the construction of Chateau Tongariro, Massey College and earthquake reconstruction in Hastings. His management skills, supported by a large team of experienced foremen and a close working relationship with the architect, ensured that construction progressed very smoothly on a project that was very profitable for Fletchers.[10]
Work commenced on site on January 1934 with a workforce of 12, which built up to 161 in January 1936. Fletchers reduced the cost of the construction steel to £70,000 from an estimated £85,000 by directly importing it rather than purchasing it from local steel merchants, and had it fabricated on site by Wm Cable Ltd.[11]
Progress was rapid, with 1500 of the piles driven by the time the foundation stone was laid on 17 December 1934 by the Duke of Gloucester, an occasion witnessed by an estimated 5000 people.[12]
The contract was expanded to include the construction of an electric substation (commenced 1936) at a cost of £2022 and a locomotive maintenance workshop (commenced 1936) along the Thorndon Quay side of the railway yard. This cost £37,406 and is still in use.[13]
In August 1938, to accommodate increasing staff numbers, work commenced on the construction of the section of the Featherston Street Wing removed from the original design to reduce its cost. This was undertaken as a separate project at a cost of £59,662.
A two-storey brick building with a mansard roof containing a social hall and a garage was built in 1937 facing Waterloo Quay to the north of the East wing, at a cost of £15,000. The garage was on the ground floor with the social hall occupying part of the ground floor and the entire first storey. The garage also incorporated rooms for the chauffeur to the Railways Departments General Manager.
Wellington railway yard
The Wellington railway yard incorporates marshalling and storage tracks and buildings and a Multiple Unit Depot (MUD) for servicing EMUs. A rail line under the overhead stadium walkway goes to the container terminal and other freight facilities on the Port wharves, with a level crossing on Aotea Quay.[14]
The principal Wellington signal box known as the "A Box" is near the overhead stadium walkway with a commanding view of the station platforms and main lines entering the station. In 2021/2022 additional crossovers and connections to the station approaches will provide extra capacity and resilience ($4.5 million) and the signal interlocking may be replaced with a computer based system ($8 million). A second lead track is to be provided to the train storage yards to facilitate faster platform clearance (2020; $5.9 million).[15]
When a derailed goods wagon[16] near the Interisland terminal damaged both tracks through the yard out of Wellington on 3 July 2019[17] commuter service to the Hutt Valley and Kapiti lines were seriously disrupted for two days. The closed Kaiwharawhara railway station is to be developed as an emergency Wellington terminal.[18]
Use
.jpg)
The station was opened on 19 June 1937 by the Governor-General of New Zealand, Viscount Galway. Lambton closed on 19 June 1937 and Thorndon on 8 June 1937.
In 1982, the New Zealand Railways Corporation replaced the Railways Department. The application of a more commercial attitude to the running of the organization resulted in a large reduction in staff employed at the Wellington railway station. Due to the reduction of railway staff numbers in the 1980s, large parts of the building became underutilised.
In 1988, the Railways-run bookstall and cafeteria were closed with subsequently the barber's shop and men's toilets being converted into 'Trax Bar and Cafe', while the women's waiting rooms were converted into toilet blocks. The original dining hall and kitchen were converted to office space. At about this time platforms 2 to 7 were shortened at the concourse end to provide increased space for waiting passengers. Large concrete planter boxes were installed at the end of the tracks to assist in stopping runaway trains.
As part of the creation of the WestpacTrust Stadium (completed November 1999) on surplus railway land to the north of the station, an elevated walkway from Thorndon Quay to the stadium was installed with access via ramps from platforms 3/4, 5/6 and 7/8. To facilitate this work, the canopies of platforms 7/8 and 9 were shortened to the same length as platforms 3/4 and 5/6.[19]
In 1991, as a result of a major restructuring of the New Zealand Railways Corporation, ownership of the land and buildings was retained by the Railways Corporation while a new organisation known as New Zealand Rail Limited took over rail operations including freight distribution, commuter and long-distance passenger services and the Interisland ferry service. Both organisations retained offices in the building. In 1993, New Zealand Rail Limited was sold to a private business consortium, which became Tranz Rail Holdings Limited in 1995. In 2000, Tranz Rail moved to its head office to Auckland but retained space for operational management of the railway network. In 2004, Tranz Rail was sold and renamed Toll NZ Ltd, which then sold the track and infrastructure back to the Railways Corporation.[19]
Between August 2003 and October 2008, the building was refurbished at a cost of NZ$14.6 million to house part of Victoria University in the West wing and Toll NZ (now KiwiRail) in the East wing. This work included a seismic upgrade, restoration and refurbishment, and installing three new lifts and dedicated access in the south-west corner to the university wing from the concourse. The architect was Athfield Architects with construction undertaken by Fletcher Construction. As part of this reorganization of the building, the 24-hour train control centre was relocated from the western wing to the eastern side of the southern part of the building.
.jpg)
On 4 December 2006, the New World Railway Metro supermarket opened on the ground floor. This coincided with the closure of the Railway Kiosk and the American Hotdog vendor.
In 2010, the former social hall was converted into 660 square metres of boutique office space.
The station was registered on 25 September 1986 as a Category I Historic Place.[19]
In August 2018, the proposed sale of the building by KiwiRail was stopped by Winston Peters the Minister of State-Owned Enterprises as "premature". The building requires earthquake strengthening (cost $62 million), and the anticipated sale price of $80 million had already been included in KiwiRail's budget.[20] The Port Nicholson Block Settlement Trust decided not to purchase the building in 2016.[21]
World War I Roll of Honour

In the office entrance to the station, a roll of honour lists 450 members of the New Zealand Railways Department who lost their lives in World War I. (Transcript of the names with links to their records on the Auckland War Memorial Museum's Cenotaph database.) As many as 5,000 of the department's permanent staff, out of a 1914 workforce of 14,000, enlisted during the war, and many casual workers also served.
The roll was unveiled by Prime Minister William Massey in the Railways Department's head office in Featherston St on 30 April 1922. It originally listed 446 names, including two out of alphabetical order at the end, presumably late additions. Four names were added later, including those of three men who died after the war.
When the station opened in 1937, the memorial was moved along the road to its present location.[22]
Filming location
Wellington railway station featured prominently in the 1981 film Goodbye Pork Pie, in which the protagonists drive a Mini through the station concourse in order to escape pursuing police officers.
The station was used in a 2009 TV advert in the United Kingdom for train ticketing company TheTrainLine, where a large flock of sheep use the facilities.[23]
In May 2014, the station foyer was used by celebrity chef Nigella Lawson to film a commercial for Whittaker's a local chocolate manufacturing firm.[24][25]
Airspace development
In 1972, NZR proposed developing the airspace above the station's platforms. The proposed development included four buildings built north of the current station over the platforms and part of the marshaling yards.[26] The development would include a 200-bed hotel, tavern, car-parking, shopping facilities and a revolving restaurant.[26] NZR made an application to Wellington City Council for consent to begin the project in 1977.[26]
Head Office and occupants
The Railways Head office had been combined in an ornate three-story brick building at 75 Featherston Street in 1903. The foundation stone was laid by the Duke of Cornwall (later King George V) on 21 June 1901. One of the first Wellington buildings reinforced against earthquakes, the style was Classical Baroque and Jacobean; ornamented in white Oamaru stone with carved cornicles and balustrades and roofed with Marsiette tiles. In 1937 it became the Defence Department headquarters but the decorative features, high roof and lighting turrets were removed, and it was demolished in 1982.[27]
The new station building was also designed to house the head office of the New Zealand Railways Department. The building now houses the Wellington office of its successor, the New Zealand Railways Corporation in the east wing of the building. The Victoria University of Wellington occupies the west wing.
The New World Railway Metro supermarket occupies part of the ground floor. Other occupants include cafes, a bar, a shoe repair shop, and a drycleaners.[28]
Services

The station copes with large daily passenger numbers with very little alteration having proved necessary. In its first year, 7,600 passengers made 15,200 trips on 140 trains daily. In the 1960s it was estimated that over 42,000 people used the station each day. Today, 29,000 passengers make 44,000 trips on 390 trains, excluding long-distance services.
Work from 2019 as part of the Wellington Metro upgrade improved the station approaches, and new foundations were built for 80 masts for the traction overhead as steel masts are to replace wooden masts.[29]
Rail
Two companies operate train services from Wellington.
Transdev operates the Wellington suburban rail network on behalf of the Greater Wellington Regional Council. This includes the electrified lines serving the Wellington and Kapiti urban areas, plus the Wairarapa Connection service to Masterton via the Hutt Valley and the Rimutaka Tunnel. At off-peak, 8–10 trains per hour leave Wellington, broken down they are:-
- 2 tph Johnsonville Line services to Johnsonville
- 3 tph Kapiti Line services to Waikanae (2tph on weekends)
- 3 tph Hutt Valley Line services to Upper Hutt (2tph on weekends)
- 1 tph Melling Line to Melling (weekdays only)
- Five Wairarapa Connection services per day to Masterton (2 per day at weekends)
KiwiRail Scenic Journeys operates two-long distance services from Wellington up the North Island Main Trunk. The Capital Connection service operates to Palmerston North once daily on weekdays. The Northern Explorer service operates to Auckland Strand three times per week.
Bus
The following bus services use the roadway beside platform 9;
- Interislander shuttles to the ferry terminal
- InterCity and Newmans long-distance coaches
Bus Terminal
The bus terminal, formerly Lambton Interchange, is served by most Wellington bus routes and is connected to the station by a subway under Featherston St.
The following bus routes serve the bus terminal: 1, 3, 7, 12e, 14, 17e, 19e, 22, 23e, 24, 25, 26, 29e, 30x, 31x, 32x, 36, 52, 56, 57, 58, 60e, 81, 83, 84 and 85x.
References
- "New Zealand Railways Corporation – Results for announcement to the market" (PDF). 30 August 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 October 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2013.
- Metlink. "Text description of fare zone boundaries". Greater Wellington Regional Council. Archived from the original on 18 December 2007. Retrieved 27 November 2007.
- Parsons 2010, p. 49.
- Parsons 2010, pp. 45, 48.
- Parsons 2010, p. 71.
- Parsons 2010, p. 7.
- Smith 2009, p. 194.
- IPENZ, Engineering Publications Co Ltd. "Wellington Railway Station" (PDF). Engineering to 1990: 36. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 February 2012.
- Smith 2009, p. 195.
- Smith 2009, p. 198.
- Smith 2009, p. 196.
- Smith 2009, p. 197.
- Smith 2009, pp. 198 and 330.
- Parsons 2010, pp. 123-126.
- Taylor, Bruce (June–July 2018). "Wellington Timetable Changes and Infrastructure Upgrades". The New Zealand Railway Observer. Vol. 75 no. 2. pp. 62, 63.
- Hunt, Tom (3 July 2019). "The 55-year old wagon that sent Wellington rail into turmoil". Stuff (Fairfax).
- "Derailed freight train in Wellington cancels services for 20,000 commuters". Stuff (Fairfax). 3 July 2019.
- George, Damian (4 July 2019). "Wellington rail meltdown would have been averted if planned contingency was in place". Stuff (Fairfax).
- "Wellington railway station". Register of Historic Places. Heritage New Zealand. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- Vance, Andrea (31 August 2018). "Kiwirail's $80m Wellington railway station headache". Stuff (Fairfax).
- Devlin, Collette (21 September 2016). "Trust will not buy Wellington railway station but looking at other sites". Stuff (Fairfax).
- "Railways Department roll of honour board, Wellington | NZHistory, New Zealand history online". nzhistory.govt.nz. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- "TV Advertising Campaign". thetrainline.com. Archived from the original on 5 April 2009.
- "Lawson filming at Wellington station". Stuff/Fairfax. 6 May 2014.
- APNZ (6 May 2014). "Nigella Lawson causes a stir in Wellington". New Zealand Herald.
- "Airspace scheme "not dead"". Rails. Southern Press Ltd. 6 (10): 14. May 1977. ISSN 0110-6155.
- Parsons 2010, pp. 56, 57.
- "Wellington Railway Station". Metlink Wellington. Archived from the original on 15 April 2017. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- "Wellington Metro Upgrade". KiwiRail. 2020.
Bibliography
- Parsons, David (2010). Wellington’s Railway: Colonial Steam to Matangi. Wellington: New Zealand Railway & Locomotive Society. ISBN 978-0-908573-88-2.
- Smith, Jack (2009). No Job Too Big – A History of Fletcher Construction Volume I: 1909–1940 (hardback). Wellington: Steele Roberts. p. 342. ISBN 978-1-877448-69-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
- Goldsmith, Paul (2009). Fletchers – A Centennial History of Fletcher Building (hardback). Auckland: Davia Ling Publishing. p. 352. ISBN 978-1-877378-35-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Train and bus timetables from Metlink
- View Beek Interactive Guide
- "Wellington Railway Station plans etc (1937)". Archives New Zealand (online).