Wedge (geometry)
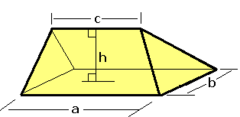
In solid geometry, a wedge is a polyhedron defined by two triangles and three trapezoid faces. A wedge has five faces, nine edges, and six vertices.
| Wedge | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Faces | 2 triangles, 3 quadrilaterals |
| Edges | 9 |
| Vertices | 6 |
| Dual polyhedron | trigonal bipyramid |
| Properties | convex |
A wedge is a subclass of the prismatoids with the base and opposite ridge in two parallel planes.
A wedge can also be classified as a digonal cupola.
Comparisons:
- A wedge is a parallelepiped where a face has collapsed into a line.
- A quadrilaterally-based pyramid is a wedge in which one of the edges between two trapezoid faces has collapsed into a point.
Volume
For a rectangle based wedge, the volume is
where the base rectangle is a by b, c is the apex edge length parallel to a, and h the height from the base rectangle to the apex edge.
Examples
Wedges can be created from decomposition of other polyhedra. For instance, the dodecahedron can be divided into a central cube with 6 wedges covering the cube faces. The orientations of the wedges are such that the triangle and trapezoid faces can connect and form a regular pentagon.
A triangular prism is a special case wedge with the two triangle faces being translationally congruent.
Two obtuse wedges can be formed by bisecting a regular tetrahedron on a plane parallel to two opposite edges.
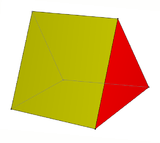 Triangular prism (Parallel triangle wedge) |
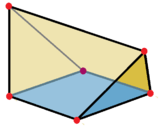 Obtuse wedge as a bisected regular tetrahedron |
 A wedge constructed from 8 triangular faces and 2 squares. It can be seen as a tetrahedron augmented by two square pyramids. |
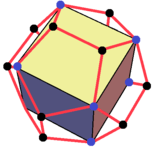 The regular dodecahedron can be decomposed into a central cube and 6 wedges over the 6 square faces. |
References
- Harris, J. W., & Stocker, H. "Wedge". §4.5.2 in Handbook of Mathematics and Computational Science. New York: Springer, p. 102, 1998. ISBN 978-0-387-94746-4