Timeline of audio formats
An audio format is a medium for sound recording and reproduction. The term is applied to both the physical recording media and the recording formats of the audio content—in computer science it is often limited to the audio file format, but its wider use usually refers to the physical method used to store the data.
Music is recorded and distributed using a variety of audio formats, some of which store additional information.
Timeline of audio format developments
| Year | Physical media formats | Recording formats |
|---|---|---|
| 1860 | Phonautogram | 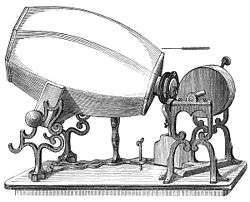 1859 model of Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville's phonautograph |
| 1877 | Tinfoil Phonograph |  In 1877, Thomas Edison invented the first recorder that could also play back |
| 1883 | Piano roll |  A piano roll used in a player piano |
| 1886 | Music Box disc |  8'' disc for playback on a music box |
| Late
1880s |
Brown Wax Cylinder |  A collection of brown wax cylinders, vertical-groove |
| Organ Cob | Mechanical digital (Vacuum operated organ) | |
| Ediphone, Dictaphone |  A Dictaphone cylinder for voice recording | |
| Phonograph disk (Emile Berliner Patent) | Mechanical analog; lateral grooves, horizontal stylus motion | |
| 1894 | Pathé cylinder |  The vertical-groove pathé cylinder |
| 1898 | Wire recording |  A Peirce 55-B dictation wire recorder from 1945 |
| 1901 | 10'' 78rpm Record | .jpg) 78rpm record - playable on modern turntables |
| 1902 | Edison Gold Moulded Record |  Edison's "gold moulded" black wax cylinder record |
| 1903 | 12'' 78rpm record | Mechanical analog; lateral grooves, horizontal stylus motion |
| Gramophone Postcard |  A gramophone post card, playable on 78rpm turntables | |
| 1905 | Centre-start phonograph Record |  A modern vinyl LP with a centre-start cut |
| Pathé Disc |  The vertical-groove pathé disc | |
| 1907 | Indestructible Record |  Indestructible Record cylinder, vertical groove. Constructed of black celluloid on a cardboard core with metal bands at each end |
| 1908 | Amberol Cylinder Record |  The Edison "Amberol" cylinder record, vertical groove |
| 1912 | Diamond Disc |  The Edison vertical-groove "diamond disc" |
| Blue Amberol cylinder record |  The Edison vertical-groove "Blue Amberol" cylinder | |
| 1925 | Electrical cut record | Mechanical analog; electrically cut from amplified microphone signal, lateral grooves, horizontal stylus motion, discs at 7", 10", 12", most at 78 rpm |
| 1930 | Filmophone flexible record |  A red Filmophone record |
| 1930s | Reel-to-reel, magnetic tape |  Studio master tape reel |
| Electrical transcriptions | Mechanical analog; electrically cut from amplified microphone signal, high fidelity sound, lateral or vertical grooves, horizontal or vertical stylus motion, most discs 16" at 33⅓ rpm | |
| 1932 | Durium Record |  A brown Durium 78rpm record |
| 1942 | SoundScriber |  Green, vertical groove Sound Scriber disks |
| 1947 | Dictabelt (Memobelt) | Analog, medium consisting of a thin, plastic belt 3.5" wide that was placed on a cylinder and rotated like a tank tread, developed by the Dictaphone company in 1947 |
| 1948 | Vinyl LP record (Columbia) | 
A Vinyl LP record
|
| 1949 | Vinyl 45 record (RCA) |  A 7'' 45rpm record |
| 1950 | Tefifon | A stand-alone Tefifon player with cartridge loaded |
| 16 2/3rpm vinyl record |  A label close-up on a 16rpm vinyl | |
| 1951 | Minifon P55 |  Minifon cassette |
| 1957 | Stereophonic vinyl record |  An early stereo record label |
| 1957 | Dictet |  Cassette for the Dictaphone Dictet dictation machine |
| 1958 | RCA tape cartridge (Sound Tape) (Magazine Loading Cartridge) |  The cassette format created by RCA |
| 1959 | NAB Cart Tape (Fidelipac) |  The cartridge known as a "Fidelipac" |
| 1962 | 4-Track (Muntz Stereo-Pak) | Analog, 1⁄4-inch-wide (6.4 mm) tape, 3¾ in/s, endless-loop cartridge |
| 1962 | Compact cassette |  Variants of the Compact Cassette |
| 1964 | Sanyo Micro Pack 35 Channel Master 6546 Westinghouse H29R1 |
 The micro pack recording system, intended for dictation |
| 1964 | Sabamobil | A cartridge format for embedding and easy handling usual 3-inch-tape-reels with ¼ inch tape, compatible to reel-to-reel audio recording in 3¾ ips. |
| 1965 | 8-Track (Stereo-8) | The inside of an 8-track cartridge |
| DC-International cassette system |  DC-International cassette | |
| 1966 | PlayTape |  Two PlayTape cartridges |
| 1969 | Microcassette |  A comparison of sizes for the Microcassette and Minicassette |
| Minicassette | Analog, ⅛ inch wide tape, used generally for note taking, 1.2 cm/s | |
| 1970 | Quadraphonic 8-Track (Quad-8) (Q8) |  A Quadraphonic 8-Track Cartridge |
| 1971 | Quadraphonic Vinyl Record (CD-4) (SQ Matrix) |  An SQ quadraphonic record Recorded two tracks on both stereo channels, requiring a decoder to hear all four tracks. Despite this, the format is playable on any LP turntable. |
| 1971 | HiPac | Analog, a successor of the 1966 PlayTape, using tape width of the 1963 Compact Cassette, Japan only |
| 1976 | Dolby Stereo cinema surround sound | Analog |
| Elcaset |  Elcaset (left) compared to a typical compact cassette (right) | |
| 1978 | LaserDisc |  Close-up of grooves on a LaserDisc |
| 1981 | Capacitance Electronic Disc (CED) | 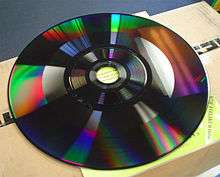 Exposed CED disc |
| 1982 | Compact Disc (CD-DA) |  The underside of a compact disc |
| 1983 | Betamax Digital Audio |  A Betamax tape |
| 1986 | High Definition Compatible Digital (HDCD) |  An HDCD album |
| 1987 | Digital Audio Tape (DAT) |  A DAT tape This audio format famously caused controversy among recording companies when released due to the potential of perfect digital copies to increase piracy[1] |
| 1988 | AIFF (File Format) | Digital. Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF) |
| 1992 | Digital Compact Cassette (DCC) |  A Digital Compact Cassette |
| WAV (File Format) | Digital. named after the waveform created by a sound wave | |
| Dolby Digital Cinema Sound | Digital. also known as Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994 | |
| MiniDisc (MD)[2] |  A red, translucent MiniDisc cartridge | |
| 1993 | DTS, SDDS, MP3 (File Formats) | .jpg) A photo of a theatrical DTS CD-ROM disc used for the original 1993 release of Jurassic Park |
| 1994 | TwinVQ | Digital. |
| 1995 | RealAudio[2] | |
| 1997 | DVD |  A stack of DVD RW disks |
| DTS-CD | Digital. DTS Audio | |
| 1999 | DVD-Audio | Digital. Including Meridian Lossless Packing (MLP), Linear PCM (LPCM), Dolby Digital (AC-3) and Digital Theatre System (DTS) |
| Super Audio CD (SACD) | Digital. Direct Stream Digital | |
| WMA (File Format) | Digital. Windows Media Audio | |
| TTA (File Format) | Digital. The True Audio Lossless Codec | |
| 2000 | FLAC (File Format) | Digital. Free Lossless Audio Codec |
| APE (File Format) | Digital. Monkey's Audio | |
| 2001 | AAC (File Format) | Digital. Advanced audio coding |
| 2003 | DualDisc |  One side DVD, one side CD - It's the DualDisc |
| 2004 | ALE or ALAC (File Formats) | Digital. Apple Lossless |
| 2005 | HD DVD |  An HD DVD |
| 2006 | Blu-ray Disc | _(by_HDTVTotalDOTcom).jpg) Blu-Ray discs and their containers |
| 2008 | slotMusic |  A SlotMusic microSD card: an early attempt to sell pre-recorded music on an SD card |
| Blu-spec CD | Digital. PCM | |
| 2012 | Opus | Digital |
gollark: I'm sure you'd like to think so.
gollark: I could not do that, yes.
gollark: Hey, maybe ABR could be extended to work as an IRC bot somehow.
gollark: Anyway, if DDGBot is truly apioforms then I guess ABRSearch™ is to occur.
gollark: Fascinating.
References
- "The challenge of introducing digital audio tape technology into consumer markets". Technology in Society. 12 (1): 91–100. 1990-01-01. doi:10.1016/0160-791X(90)90031-7. ISSN 0160-791X.
- Cornell University Library (2003). "Digital Preservation and Technology Timeline". Digital Preservation Management. USA. Retrieved February 28, 2017.
See also
- Audio data compression
- Format war
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.